Explain about the geometrical isomerism of octahedral complexes with suitable example.
Text Solution
(i) Octahedral complexes of the type [MA2B4]n±, [M(xx)2B2]n± shows cis-trans isomerism. Hence A and B are monodentate ligands and xx is bidentate ligand with two same kind of donor atoms. In the octahedral complex, the position of ligands is indicated by the following numbering scheme.
(ii) The positions (1,2)(1,3)(1,4)(1,5),(2,3)(2,5)(2,6),(3,4)(3,6),(4,5)(4,6) and (5,6) are identical and if two similar groups are present in any one of these positions, the isomer is referred as a cis-isomer.
(iii) Similarly positions (1,6),(2,4) and (3,5) are identical and if similar groups (or) ligands are present in these positions it is referred as a trans-isomer.
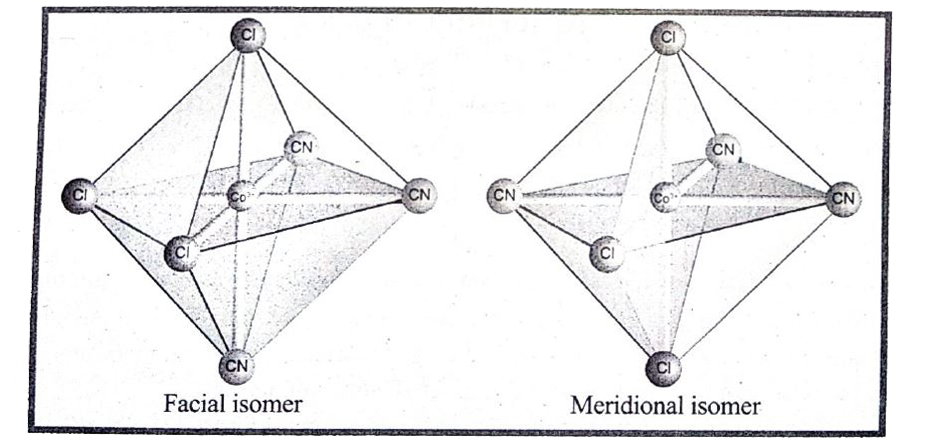
(iv) Octahedral complex of the type [MA3B3]n± also shows geometrical isomerism. If the three similar ligands (A) are present in the corners of one triangular face of the octahedron and the other 3 ligands (B) are present in the opposite triangular face, then the isomer is referred as a facial isomer (fac isomer).
(v) If the three similar ligands are present around the meridian which is an imaginary semicircle from one apex of the octahedral to the opposite apex, the isomer is called a meridional isomer (mer is omer). This is called a meridional because each set of ligands can be regarded as lying on a meridian of an octahedran.
|
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Optical isomerism is shown by octahedral complexes
Ahaving all monodentate ligandsBhaving all the three bidentate ligandsChaving two trans bidentate ligandsDhaving two trans monodentate ligandsOptical isomerism is shown by octahedral complexes
Ahaving all monodentate ligandsBhaving all the three bidentate ligandsChaving two trans bidentate ligandsDhaving two trans momodentate ligandsExample of geometrical isomerism is
A2-butanolB2-buteneCbutanolD2-butyne

