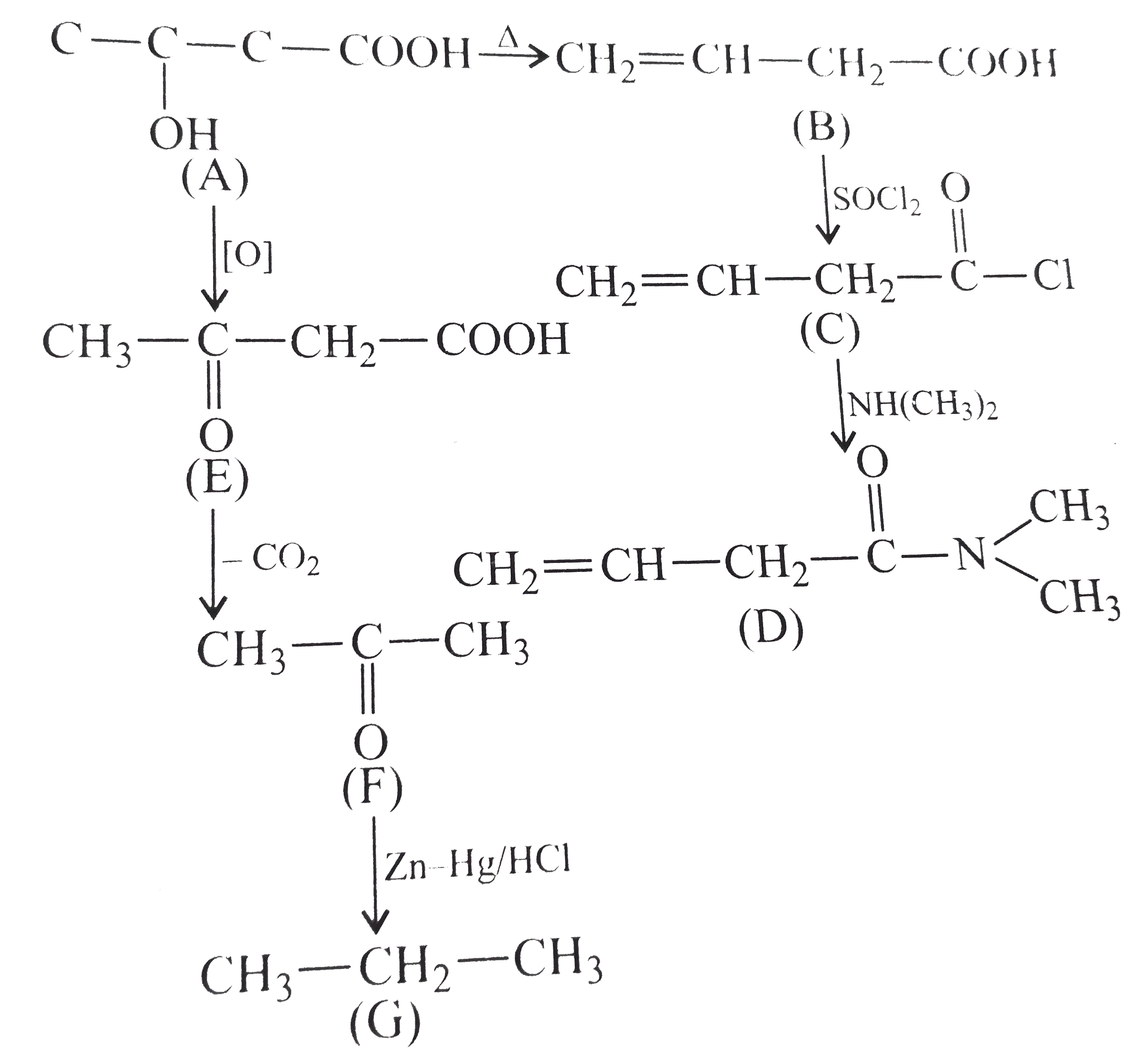
An acidic compound (A)(C4H8O3) loses its optical activity on strong heating yielding (B)(C4H6O2) which reacts readly with KMnO4. (B) forms a dervative (C) with SOCl2 which on reaction with (CH3)2NH gives (D). The compound (A) on oxidation with dilute chromic acid gives an unstable compound (E) which decarboxylates readily to give (F)(C3H6O). The compound (F) gives a hydrocarbon (G) on treatment with amalgamated Zn and HCl. Give the structures of (A) to (G) with proper reasoning.
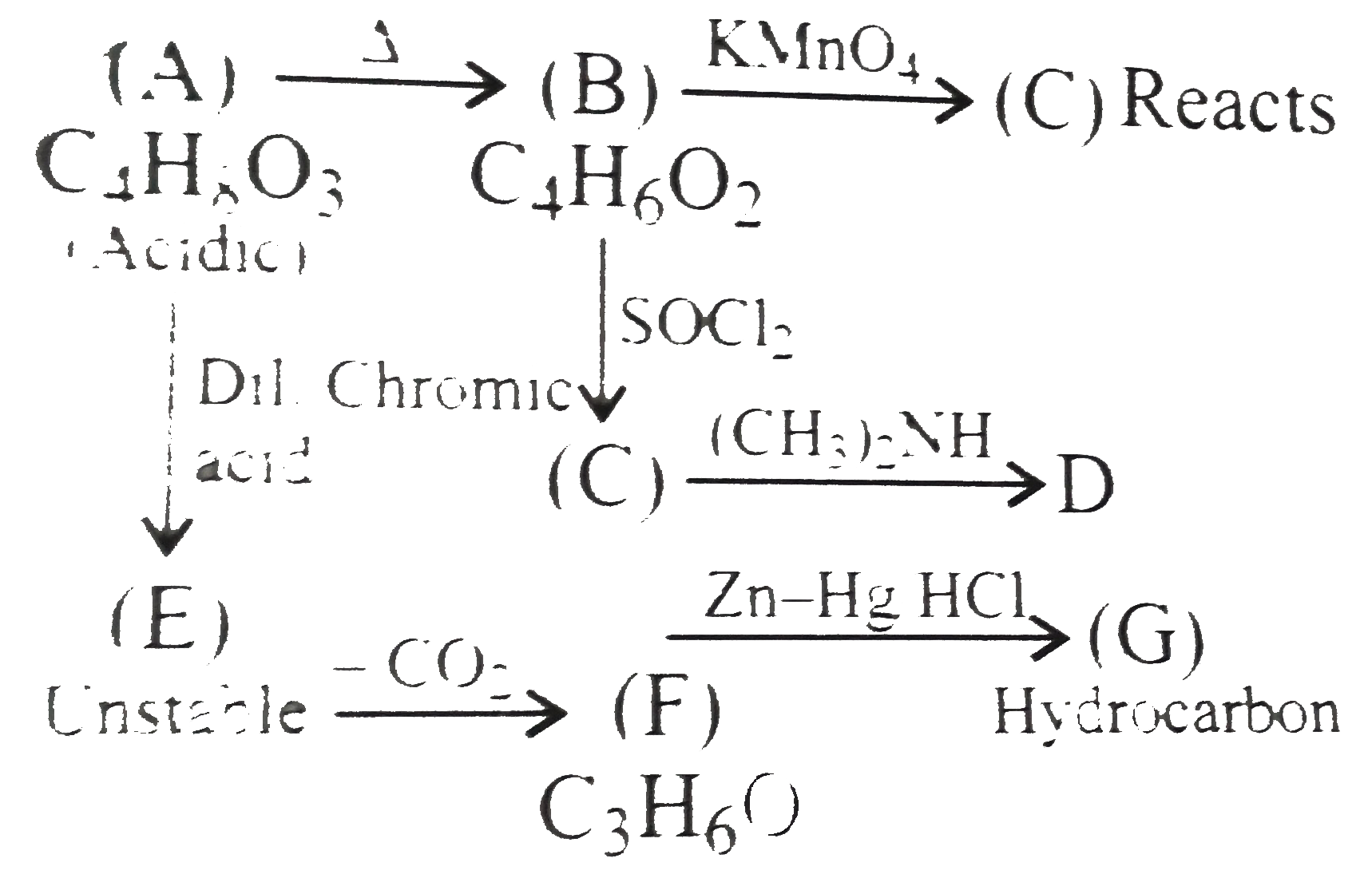
(i) [A]⇒1∘ unsaturation, on heating loses (−H2O) (Hydroxy acid) due to ⎛⎜
⎜⎝−O∣∣C−OH⎞⎟
⎟⎠group.
(ii) rArr Third oxygen atom due to (−OHgroup).
(iii) A rArr Optically active. So,
C−C∣OH−Cβ−Hydroxy−COOH[or]C−C−C∣OH−COOHα−Hydroxy
(iv) Since (A) on heating loses H2O, thus (A) is β−hydroxy not α−hydroxy. because only β−hydroxy loses H2O on heating.
Reactions :
 .
.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVESBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRYChapter:CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVESExercise:Exercises (Linked Comprehension)
Explore 34 Videos
- CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVESBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRYChapter:CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVESExercise:Exercises (Multiple Correct)
Explore 35 Videos
- CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVESBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRYChapter:CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVESExercise:Solved Examples
Explore 17 Videos
- BIOMOLECULES, POLYMERS AND CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFEBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRYChapter:BIOMOLECULES, POLYMERS AND CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFEExercise:QUESTION BANK
Explore 8 Videos
- CHEMICAL KINETICSBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRYChapter:CHEMICAL KINETICSExercise:Archives Subjective
Explore 23 Videos
Similar Questions
An acidic compound (A) C4H8O3 loses its optically activity on strong heating yielding (B), C4H6O2 which reacts readily with KMnO4. (B) forms a derivative (C ) with SOCl2, which on reaction with (CH3)2NH gives (D). The compound (A) on oxidation with dilute chromic acid gives an unstable compound (E) hich decarboxylates readily to give (F), C3H6O. The compound (F) gives a hydrocarbon (G) on treatment with amalgamated Zn and HCl. Give the structures of (A) to (G) with proper reasoning.
View SolutionAn acidic compound (A) , C4H8O3 , loses its optical activity on strong heating yielding (B), C4H6O2 , which reacts readily with KMnO4 . (B) forms a derivative (C) with SOCI2, which on reaction with (CH3)2NH gives (D). The compound (A) on oxidation with dilute chromic acid gives an unstable compound (E) which decarboxylates readily to give (F), C3H6O. The compound (F) gives a hydrocarbon (G) on treatment with amalgamated Zn and HCI. Give structures of (A) to (G) with proper reasoning.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
The compound which gives H2O2 on treatment with dilute acid is
APbO2BMnO2CTiO2DKO2The compound X(C3H6O) on oxidation gives a compound Y(C3H6O2) . The compound Y is
Apropanoic acidBbutyric acidCacetic acidDpropenoic acid
The compound F(C6H12O) on oxidative ozonolysis yirlds acetic acid and a compound (G) (C4H8O3). The new compound (G) on heating gives:A BMe−CH=C=CH−EtC
BMe−CH=C=CH−EtC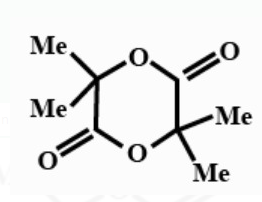 D
D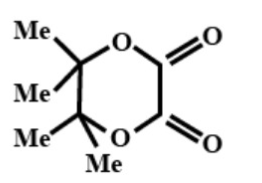
An organic compound (A)(C5H8O3) on heating with soda lime gives (B) which reacts with HCN to give (C). The compound (C) reacts with thionyl chloride to produce (D) which on reaction with KCN gives a compound (E). Alkaline hydrolysis of (E) gives a salt (F) which on heating with soda lime produces n−butane. Careful oxidation of (A) with dichromate give acetic acid and malonic acid. Give the structures to (A) to (F) with proper reasoning.
View SolutionAn organic compound (A) reacts with ethanol to give (B) and (C). On acid hydrolysis (C ) yields (B) and (D). oxidation of (D) gives (B). (B) is an acid and forms a salt with Ca(OH)2 which on dry distillation gives (E ), C3H6O. Give the structures of (A) to (E ) with proper reasoning.
View SolutionAn organic compound (A), C18H20O on ozonolysis gives (B), C10H12O and (C) C8H8O2 . Compound (B) gives iodoform reaction and products an oxime (D), C10H13ON on treatment with NH2OH. Compound (D) reacts with PCI5 in dry ether to give (E) which on hydrolysis (F), C8H11N and acetic gives acid. (F) on treatment with HNO2 followed by oxidation gives phthalic acid. Compound (C) on mild oxidation gives (G) which gives effervescence with NaHCO3 . (G) on treatment with HI produces p-hydroxy benzoic acid and CH3I. Give structures of (A) to (G) with proper reasoning.
View SolutionAn organic compound (A) gives opsitive Liebermann reaction and on treatment with CHCI3/KOH followed by hydrolysis gives (B) and (C). Compound (B) gives colour with Schiff's reagent but not (C), which is steam volatile. (C ) on treatment with LiAIH4 gives (D), C7H8O2, which on oxidation gives (E). Compound (E) reacts with (CH3CO)2)∅CH3COOH to give a pain reliever (F). Give the structures of (A) to (F) with proper reasoning.
View SolutionAn organic acid (A) (C5H10O2) reacts with Br2 in presence of phosphorus to give (B). Compound (B) contains an asymmetric carbon atom and yields (C). On dehydrohalogention, compound (C) does not show geometric isomersim and on decarboxylation gives an alkene (D) which on ozonlysis isomerism and on decarboxylation gives an alkene (D) which on ozonolysis give (E) and (F). Compound (E) gives a positive Schiff's test but (F) doesn 't. Give structures of (A) to (F) with reasons.
View Solution
