For which one of the following equations is ΔrH∘ equal to ΔfH∘ for the products (s)?
2CO(g)+O2(g)→2CO2(g)
N2(g)+O3(g)→N2O3(g)
CH4(g)+2Cl2(g)→CH2Cl2(1)+2HCl(g)
Xe(g)+2F2(g)→XeF4(g)
The correct Answer is:D
ΔrH∘ is equal to ΔfH∘ if during the reaction, one mole of the compound (XeF4) is synthersized from its elements (Xe and F2) in their standard states.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
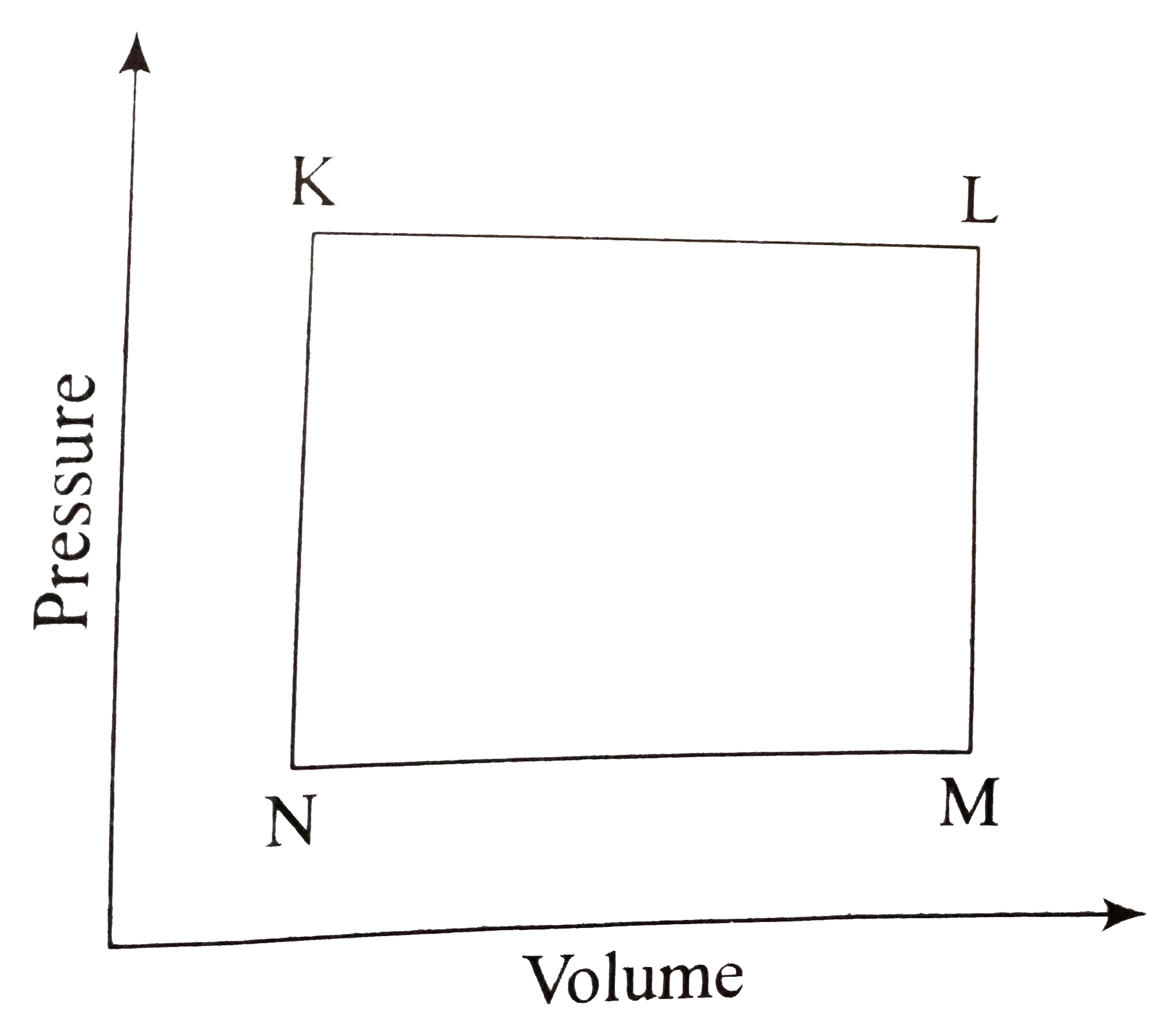
A fixed mass m of a gas is subjected to transformation of state: K to L to M and black to K as shown in the figure.
The succeeding operations that enabel this transformation of state are
View SolutionThe correct order of increasing thermal stability of K2CO3,MgCO3,CaCO3, and BeCO3 is
View SolutionThe expression Δsub1HΘ=ΔfusHΘ+ΔvapHΘ is true at al
View SolutionWhich of the reaction defines Delta_(f)H^(@) ?
View SolutionAll combustion reactions are exothermic. Enthalpies of products are greater than enthalpies of reactants (Sigmav_(p)Delta_(f)H(P)gtSigmav_(R)Delta_(f)H(R))
View SolutionWhich of the following reactions is defines ΔfHΘ?
View SolutionStandard molar enthalpy of formation, Delta_(f)H^(c-) is just a special case of enthalpy of reaction, Delta_(r)H^(c-) . Is the Delta_(r)H^(c-) for the following reaction same as Delta_(f)H^(c-) ? Give reaction for your answer. CaO(s) +CO_(2)(g) rarr CaCO_(3)(s), Delta_(f)H^(c-)= - 178. 3 kJ mol^(-1)
View SolutionIf enthalpy of overall reaction X→Y along one route is ΔrHandΔrH1,ΔrH2,ΔrH3…. Representing enthalpies of reactions leading to same product Y then ΔrH is
View SolutionFor a reaction,
CaCO3(s)→CaO(s)+CO2(g)
ΔfH∘(CaO)=−631.1 kJ mol−1
ΔfH∘(CO2)=−393.5 kJ mol−1and
ΔfH∘(CaCO3)=−1206.9 kJ mol−1
Which of the following is a correct statement?
View SolutionIf enthalpy of an overall reaction X>Y along one route is ΔrHandΔrH1,ΔrH2,ΔrH3…….representing enthalpies of reaction leading to same product Y then ΔrH is
View SolutionThe mathematical expression for the standard enthalpy of sublimation is given by _________ . (Here, Delta_("sub")H^@=Delta_("sublimation")H^@, Delta_("fus")H^@=Delta_(fusion)H^@,Delta_(vap)H^@=Delta_("vaporization")H^@,=Delta_(comb)H^@=Delta_(combustion)H^@,Delta_(diss)H^@=Delta_(dissociation)H^@)
View SolutionΔrH of which of the following reactions is zero ?
View SolutionStandard molar enthalpy of formation, ΔfH∘ is just a special case of enthalpy of reaction, ΔrH∘. Is the ΔrH∘ for the following reaction same as ΔfH∘? Give reason for your answer.
CaO(s)+CO2(g)→CaCO3(s),
ΔfH∘=−178.3kJmol−1.
View SolutionWhat is the basic difference between the two notations Delta_(r)H and Delta_(f)H ?
View SolutionFor which one of the following equations is Delta_(r) H^(theta) equal to Delta_(f) H^(theta) for the product ?
View Solution

