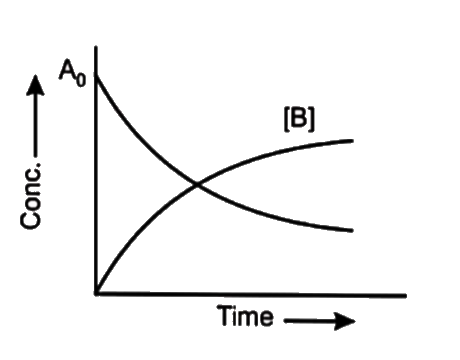
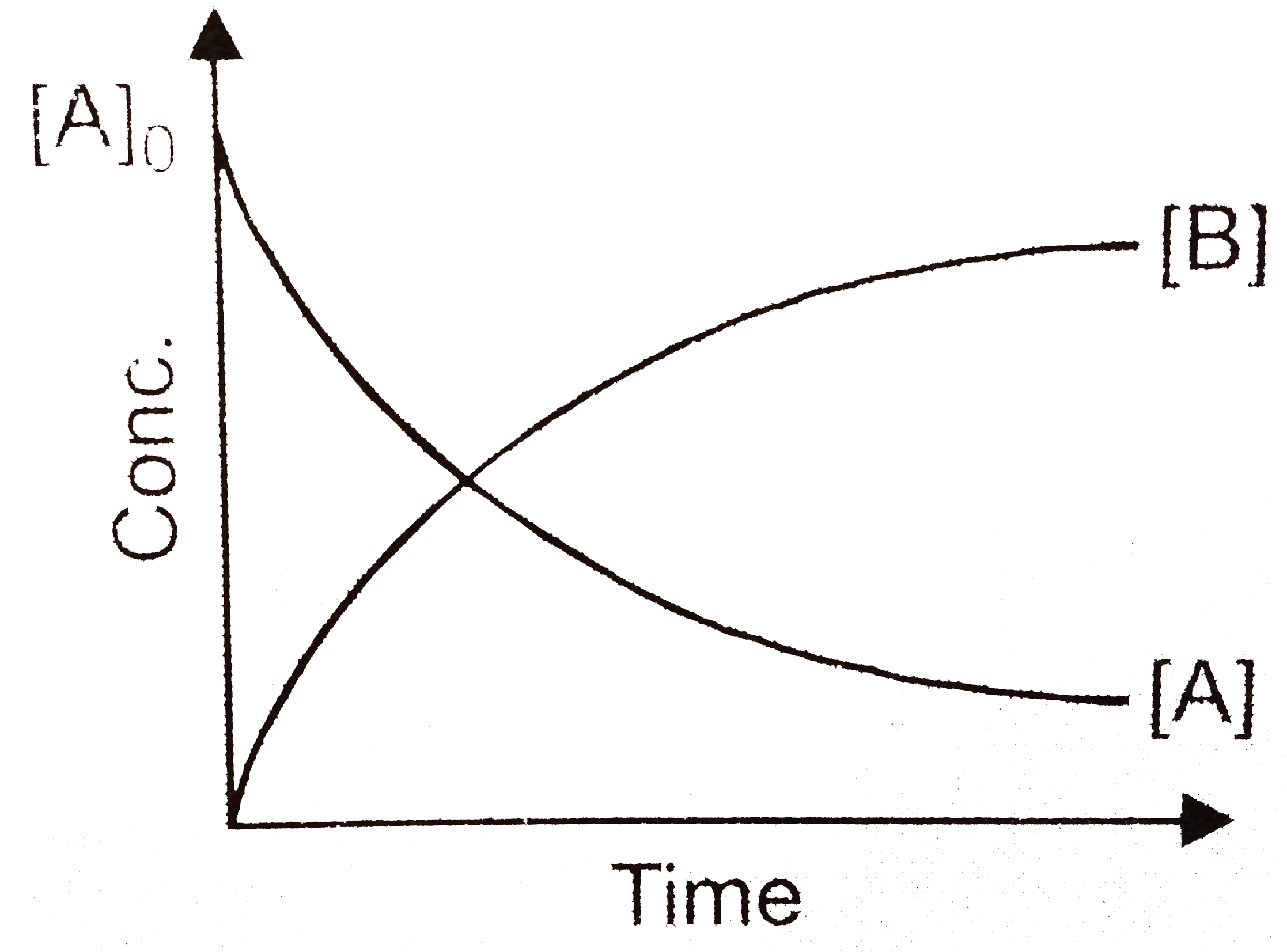
For the reaction A→nB, at the point of intersection fo two curves show, the [B] is can be given by
![For the reaction A tonB, at the point of intersection fo two curves show, the [B] is can be given by](https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.cloudfront.net/physics_images/NIK_OBJ_CHE_XII_C05_E01_314_Q01.png)
nA02
A0n−1
nA0n+1
[n−1n+1]A0
[A]left=[B]formed=n×[A]decayed
A0e−kt=n×A0[1−e−kt]
∴e−kt=nn+1
∴[B]formed=n×A0×[1−nn+1]=nA0n+1
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Choose the correct relationship for glucose and fructose
View SolutionFor an endothermic reaction where ΔH represent the enthalpy of reaction in kj/mol, the minimum value for the energy of activation will be:
View SolutionAt the point of intersection of the two curves shown, the conc. of B is given by ……… for, A rarr nB :
View Solutionक्या दो समतापी वक्र एक-दूसरे को काट सकते हैं?
View Solutionक्या दो रुद्धोष्म वक्र एक-दूसरे को काट सकते हैं?
View SolutionAt the point of intersection of the two curves shown the concentration of B is given by _______for the first reaction A→nB.
View SolutionAt the point of intersection of the two curves shown for the reaction
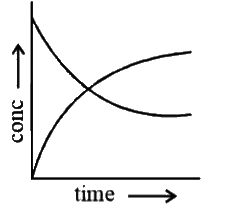
A→nB time →
then concentration of B is given by :
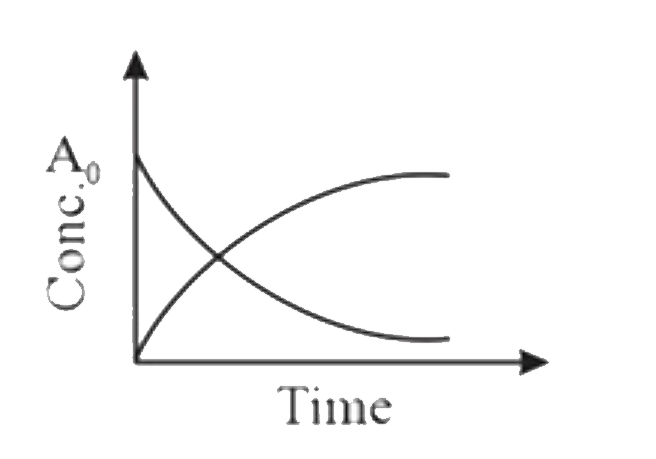
View SolutionAt the point of intersection of the two curves shown, the conc.of B is given by….. ….. ……….for, A→nB
View Solutiony=be−(xa) বক্র যে বিন্দুতে y অক্ষকে ছেদ করে, দেখাও যে সেই বিন্দুতে (xa)+(xb)=1 সরলরেখা প্রদত্ত বক্রটিকে স্পর্শ করে।
View SolutionAt the given point of intersection of the two curves shown concentration of B is given by ………for, A=3B
View SolutionCan two isothermal curves intersect each other?
View SolutionAt the point of intersection of the two curves shown the conc. Of B is given by ………for A→nB

View SolutionCan two isothermal curves intersect?
View Solutioncan two isothermal curves intersect each other ?
View Solutionप्रथम कोटि की अभिक्रिया A→nB के लिए दिखाए गए दो वक्रों के प्रतिच्छेद बिंदु पर, B की सांद्रता ------ द्वारा दी जाती है :
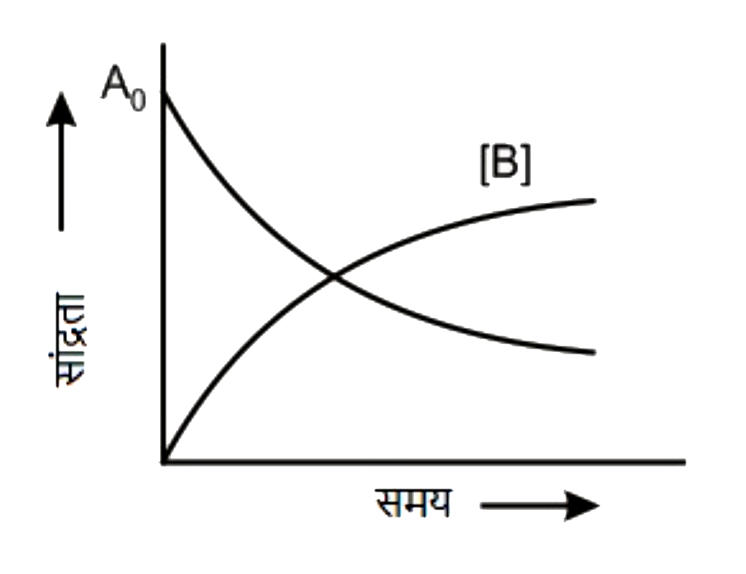
View SolutionAt the point of intersection of the two curves shown, the conc. of B is given by ……… for, A→nB:
View Solution

