The optically active species among the following is:
[Cr(NH3)6]3+
[Co(CN)6]3−
[Co(gly)3]
[Ru(NH3)6]3+
The correct Answer is:C
To determine the optically active species among the given coordination compounds, we need to analyze the symmetry of each complex. A compound is optically active if it lacks a plane of symmetry (POS) or a center of symmetry (COS). Let's evaluate each option step by step.
Step 1: Analyze the first complex (Cr(NH3)6)³⁺
- This complex has six identical NH3 ligands arranged in an octahedral geometry.
- Since all ligands are the same, the complex exhibits symmetry.
- It has multiple planes of symmetry, meaning it can be divided into two identical halves.
- Conclusion: This complex is optically inactive.
Hint: Look for identical ligands in an octahedral complex; they often lead to symmetry.
Step 2: Analyze the second complex (Co(CN)6)³⁻
- This complex also has six identical CN⁻ ligands in an octahedral arrangement.
- Similar to the first complex, it has symmetry due to identical ligands.
- It possesses a plane of symmetry, thus it is also optically inactive.
- Conclusion: This complex is optically inactive.
Hint: Identical ligands in octahedral complexes usually indicate optical inactivity.
Step 3: Analyze the third complex (Co(Gly)3)²⁺
- Glycine (Gly) is a bidentate ligand, coordinating through both the amine (NH2) and carboxylate (COO⁻) groups.
- In this complex, there are three Gly ligands, each contributing two different donor atoms.
- The arrangement of these ligands leads to a structure that lacks symmetry.
- Since the donor atoms are different, the complex does not have a plane of symmetry.
- Conclusion: This complex is optically active.
Hint: Look for bidentate ligands with different donor atoms; they can create asymmetry.
Step 4: Analyze the fourth complex (Cr(NH3)6)³⁺ (similar to the first)
- This complex is identical to the first complex, with six NH3 ligands in an octahedral geometry.
- It exhibits symmetry with multiple planes of symmetry.
- Conclusion: This complex is optically inactive.
Hint: Repeating the analysis for identical complexes will yield the same result regarding optical activity.
Final Conclusion:
Among the given complexes, the optically active species is (Co(Gly)3)²⁺.
- This complex has six identical NH3 ligands arranged in an octahedral geometry.
- Since all ligands are the same, the complex exhibits symmetry.
- It has multiple planes of symmetry, meaning it can be divided into two identical halves.
- Conclusion: This complex is optically inactive.
- This complex also has six identical CN⁻ ligands in an octahedral arrangement.
- Similar to the first complex, it has symmetry due to identical ligands.
- It possesses a plane of symmetry, thus it is also optically inactive.
- Conclusion: This complex is optically inactive.
- Glycine (Gly) is a bidentate ligand, coordinating through both the amine (NH2) and carboxylate (COO⁻) groups.
- In this complex, there are three Gly ligands, each contributing two different donor atoms.
- The arrangement of these ligands leads to a structure that lacks symmetry.
- Since the donor atoms are different, the complex does not have a plane of symmetry.
- Conclusion: This complex is optically active.
- This complex is identical to the first complex, with six NH3 ligands in an octahedral geometry.
- It exhibits symmetry with multiple planes of symmetry.
- Conclusion: This complex is optically inactive.
Among the given complexes, the optically active species is (Co(Gly)3)²⁺.
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Optically active molecules among the following are
A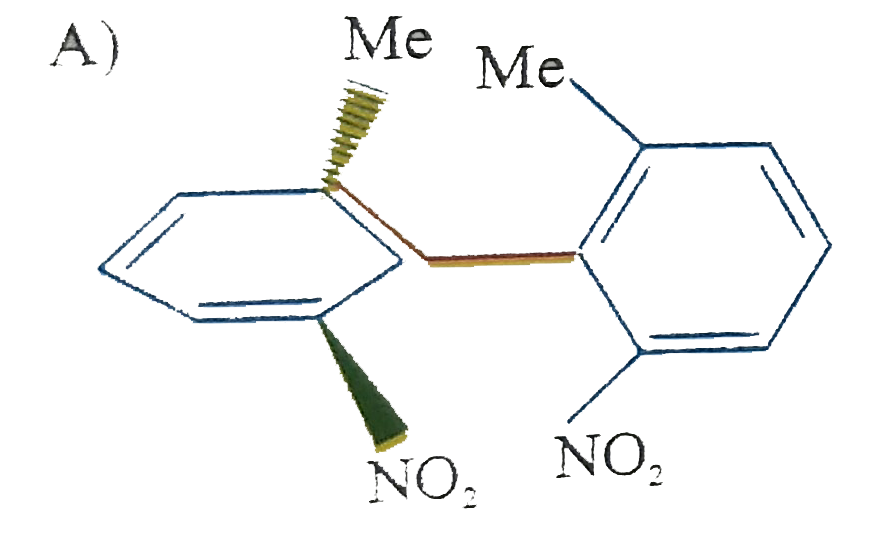 B
B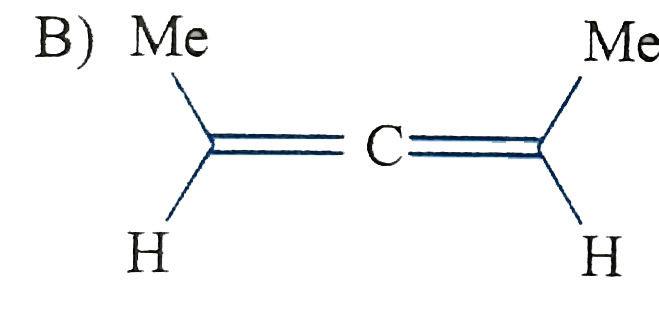 C
C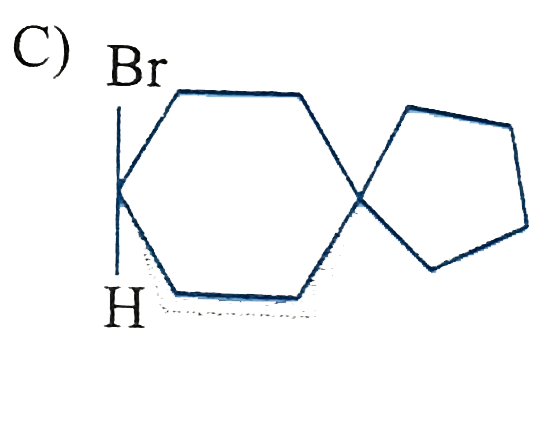 D
D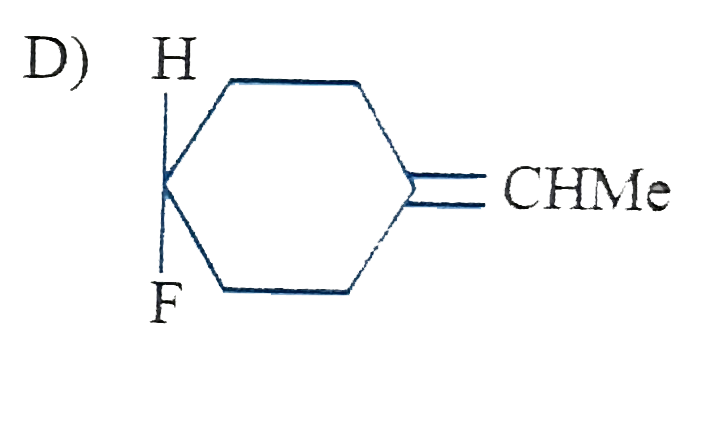
Select the optically active compound among the following :
A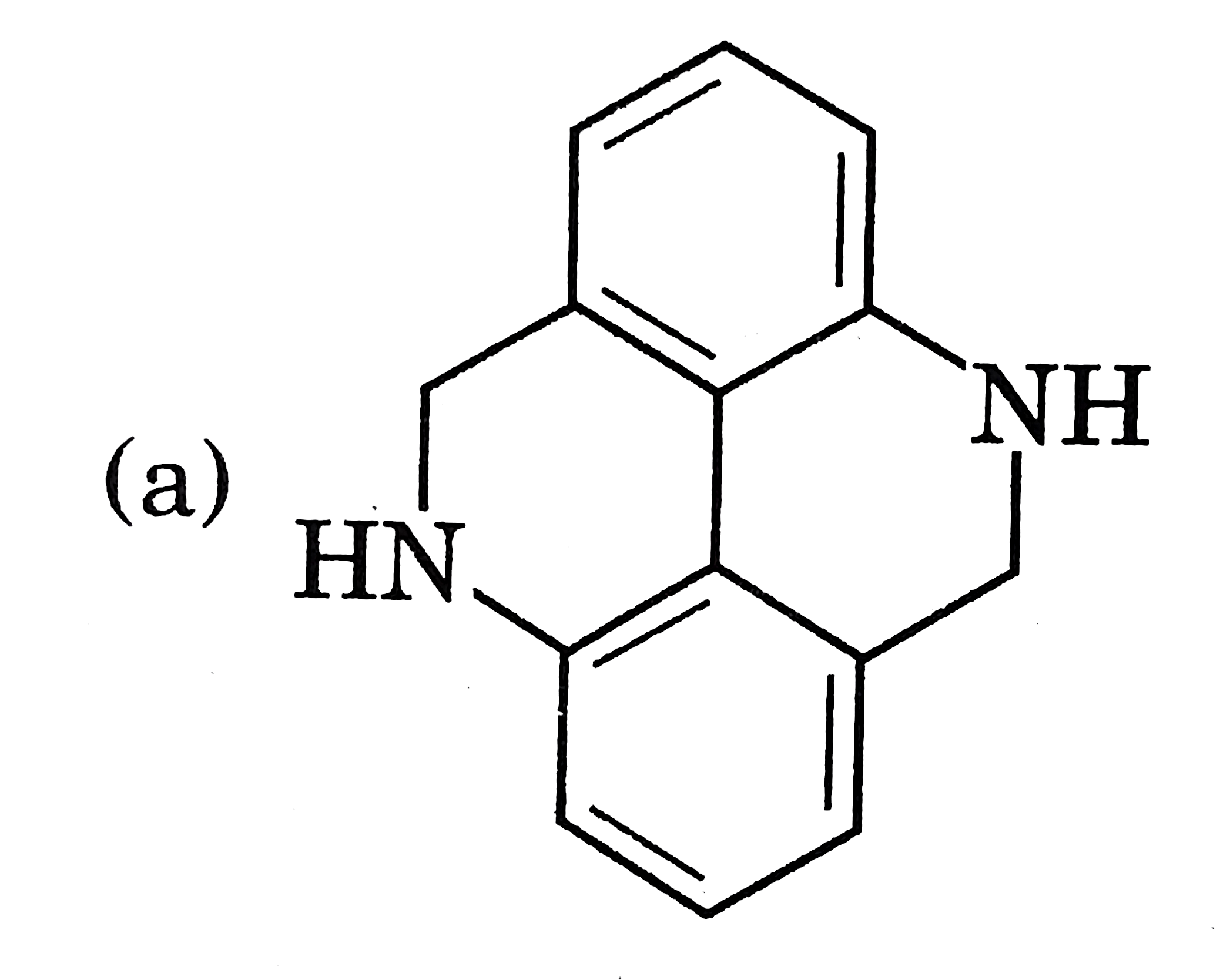 B
B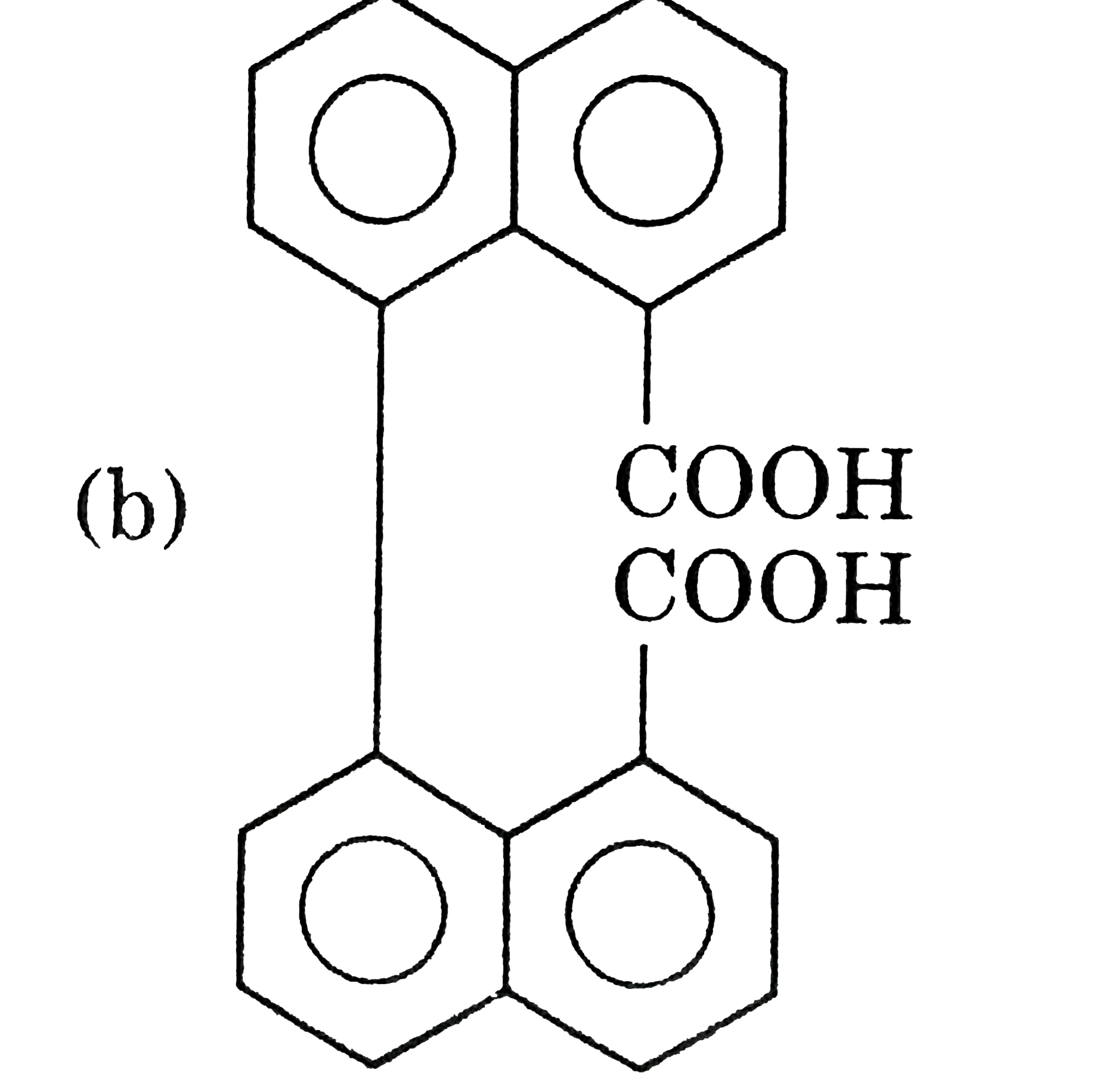 C
C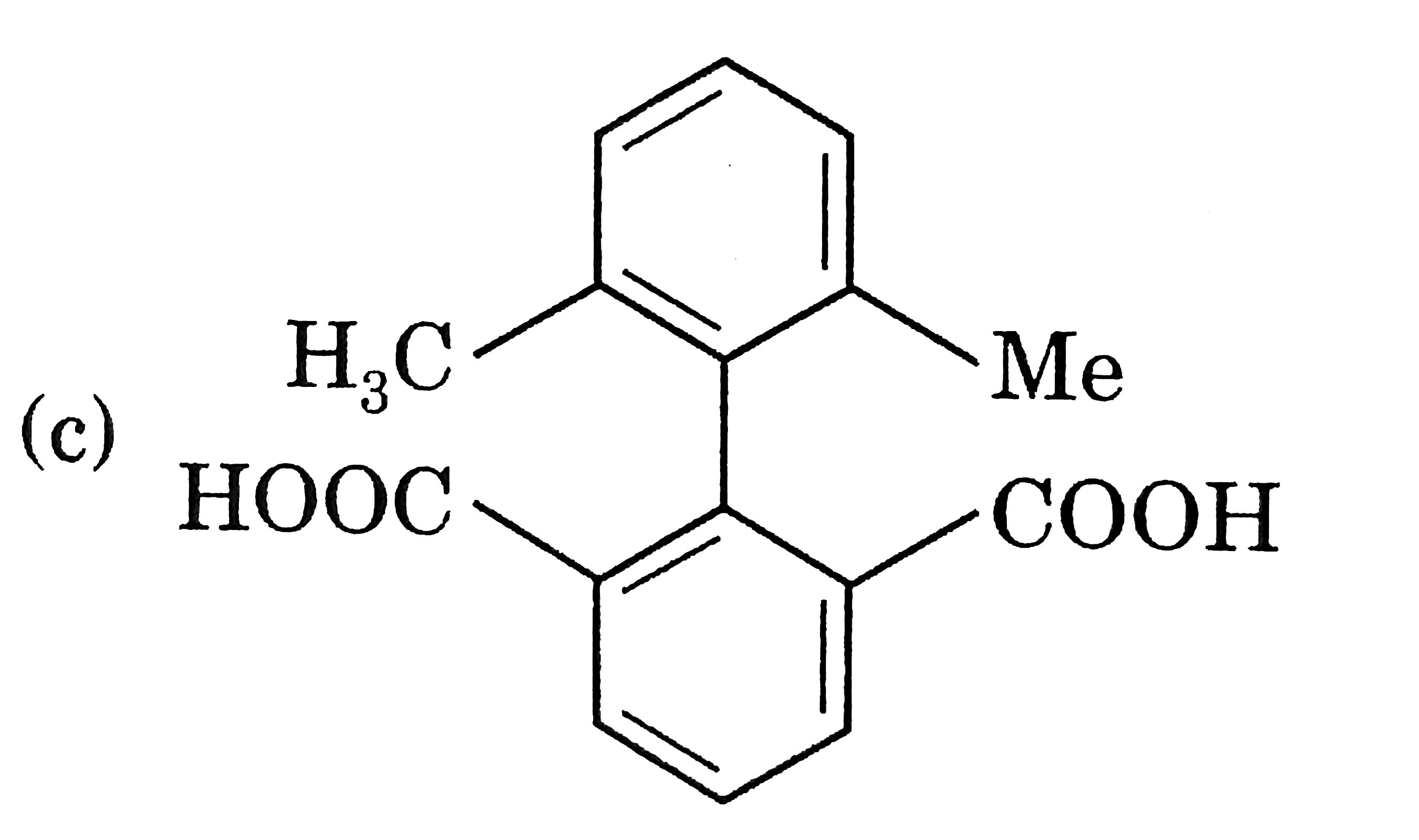 D
D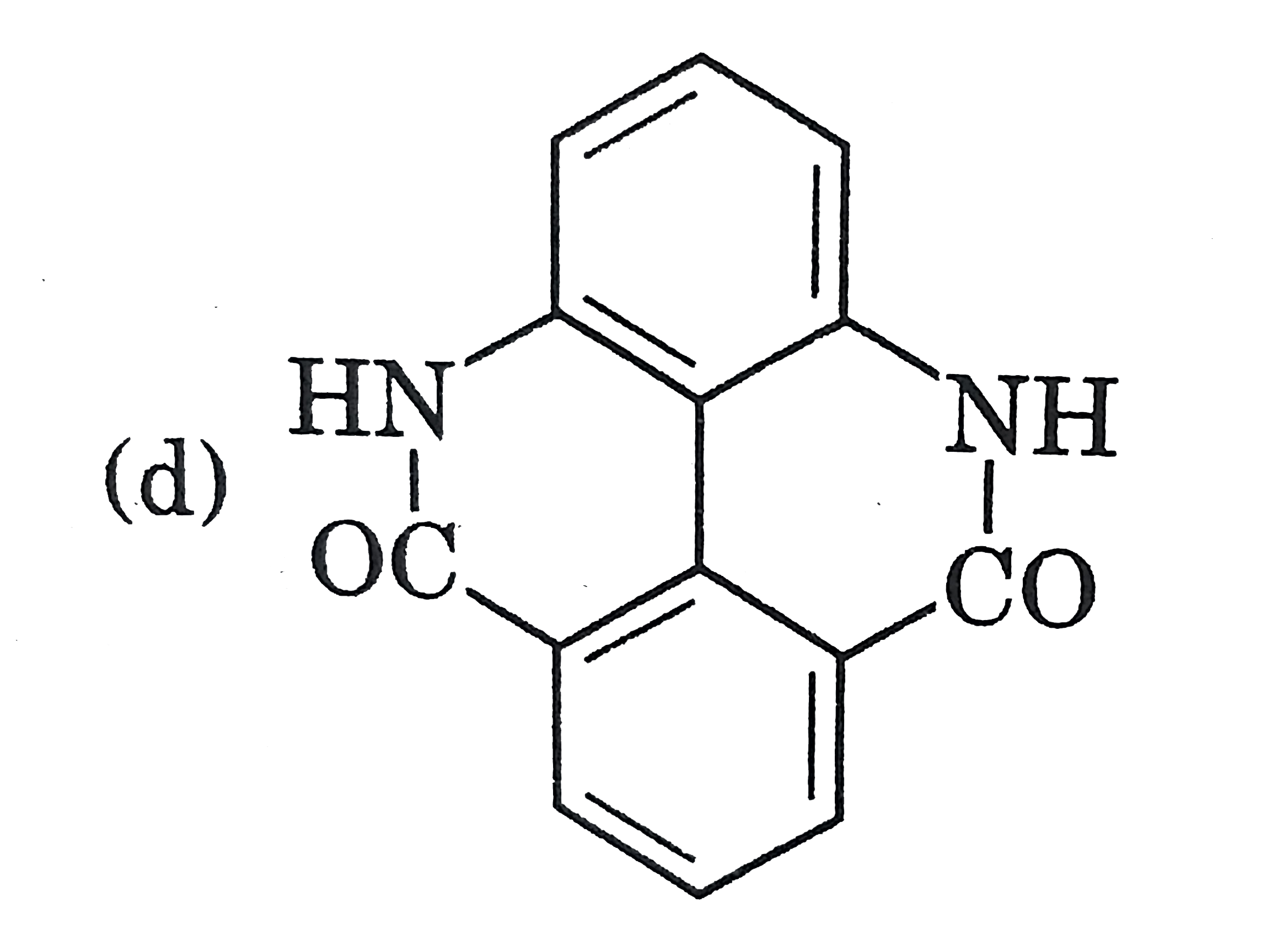
Select the optically active compound among the following:
A B
B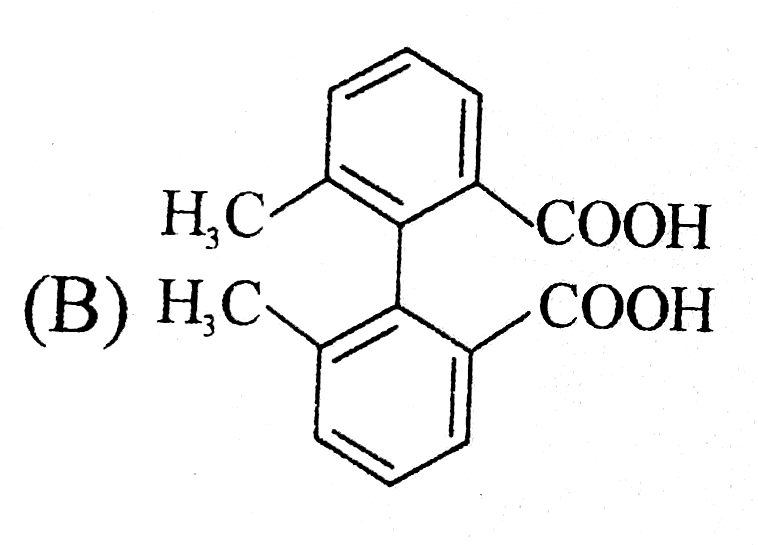 C
C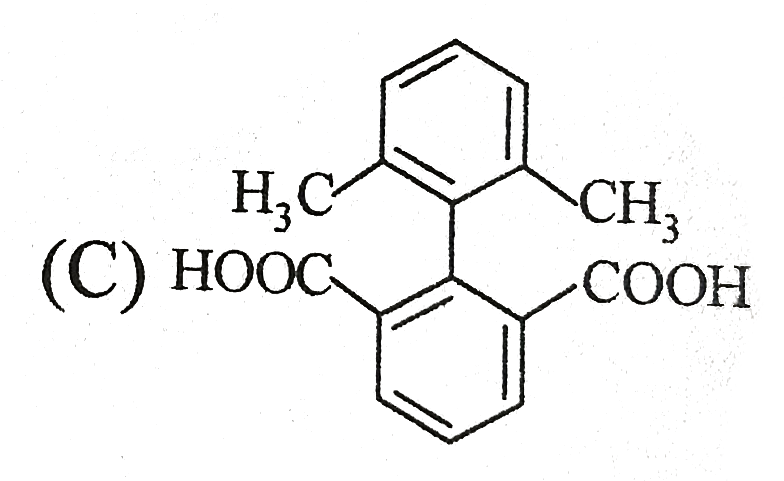 D
D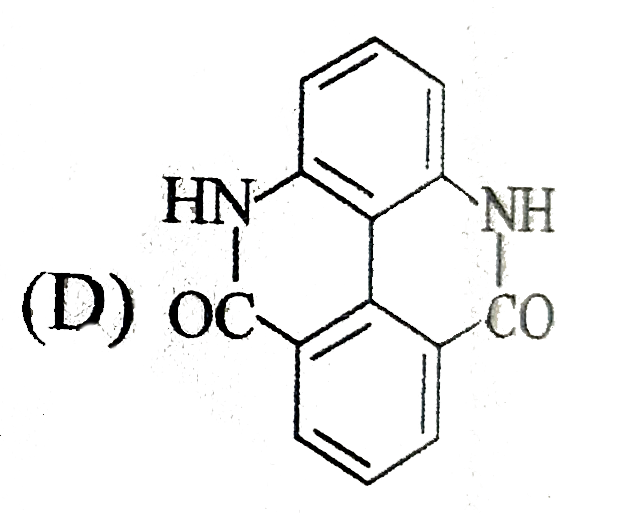
The optically active co-ordination complex ion among the following is
View SolutionThe optically active co-ordination complex ion among the following is
View SolutionAmong the following compounds, the optically active alkane having the lowest molecular mass is:
View SolutionAmong the following the optically inactive compound is :
View SolutionAmong the following the optically inactive compound is :
View Solution
