Mass action ratio or reaction quotient Q for a reaction can be calculated using the law of mass actionl,
A(g)+B(g)⇔C(g)+D(g)
Q=[C][D][A][B]
The value of Q decides whether the reaction is at equilibrium or not.
At equilibrium, Q=K
For non-equilibrium process Q≠K
When Q>K, reaction will be favoured in backward direction and when Q<K, it will be favoured in forward direction. In a reaction mixture containing H2,N2 and NH3 at partial pressure of 2 atm, 1 atm and 3 atm respectively, the value of Kp at 725 K is 4.28×10−5 atm−2. In which direction the net reaction will go ?
N2(g)+3H2(g)⇔2NH3(g)
Forward
Backward
No net reaction
Direction cannot be predicated
The correct Answer is:B
Step by step video, text & image solution for Mass action ratio or reaction quotient Q for a reaction can be calculated using the law of mass actionl, A(g)+B(g)hArrC(g)+D(g) Q=([C][D])/([A][B]) The value of Q decides whether the reaction is at equilibrium or not. At equilibrium, Q=K For non-equilibrium process QneK When QgtK, reaction will be favoured in backward direction and when QltK, it will be favoured in forward direction. In a reaction mixture containing H_(2),N_(2) and NH_(3) at partial pressure of 2 atm, 1 atm and 3 atm respectively, the value of K_(p) at 725 K is 4.28xx10^(-5) "atm"^(-2). In which direction the net reaction will go ? N_(2)(g)+3H_(2)(g)hArr2NH_(3)(g) by Chemistry experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
Write a relation between DeltaG and Q and deifine the meaning of each term and answer the following : Why a reaction proceeds forward when QltK and no net reaction occure when Q=K . Explain the effect of increase in presure in terms of reaction quotient Q for the reaction : CO(g)+3H_2(g)hArrCH_4(g)+H_2O(g)
View SolutionIn the reaction
PCl5(g)⇔PCi3(g)+Ci2(g)
a graph in plotted to show the variation of rate of forward and backward reactions against time. Which of the following is correc?
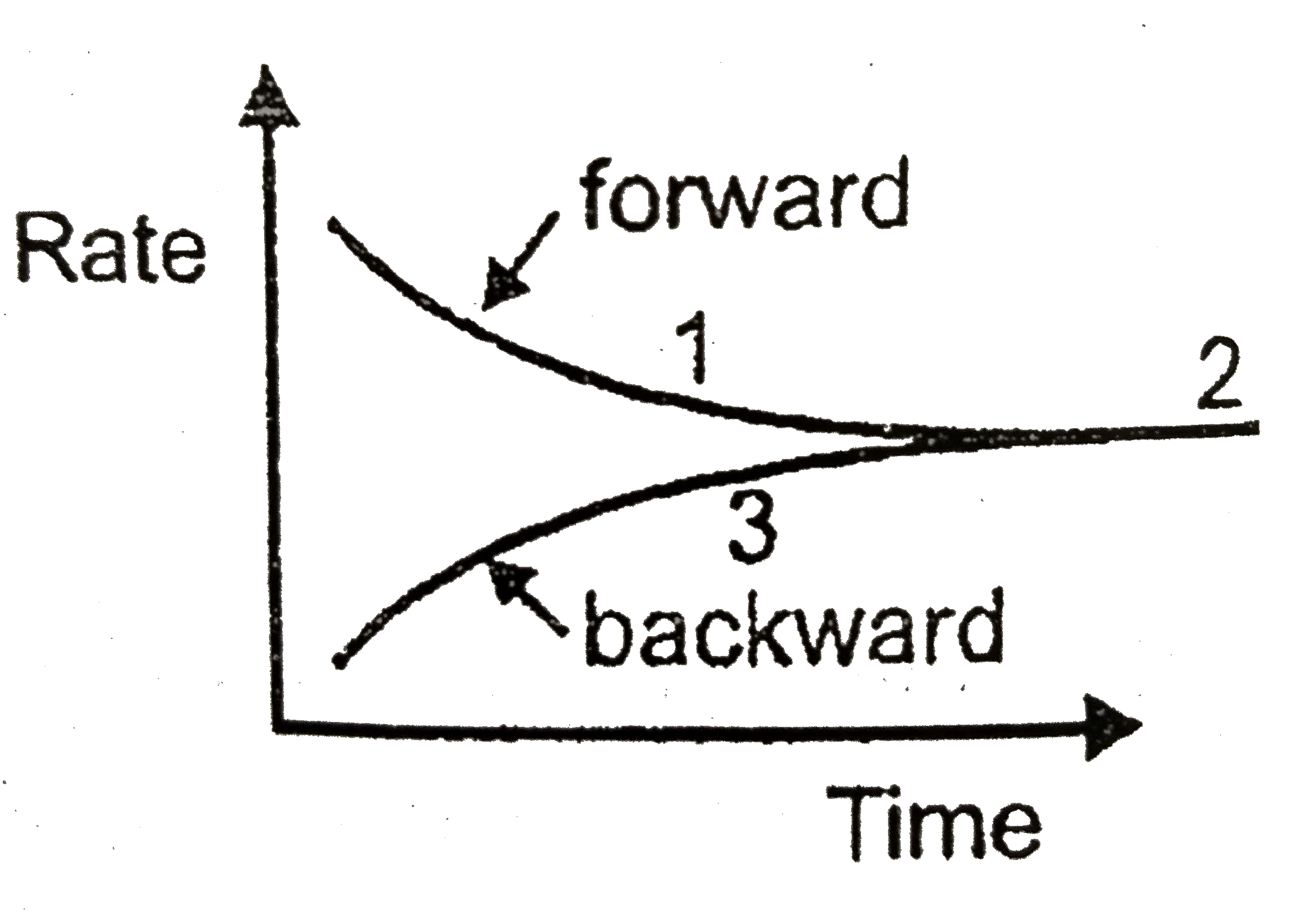
Q>KQ=KQ<K
View SolutionThe equilibrium constant for a reaction is K, and the reaction quotient is Q . For a particular reaction mixture , the ration (K)/(Q) is 0.33. this means that:
View SolutionMass action ratio or reaction quotient Q for a reaction can be calculated using the law of mass action A(g)+B(g)↔C(g)+D(g)Q=[C][D][A][B]. The value of Q decides whether the reaction is at equilibrium or not. At equilibrium, Q = K. For non equilibrium process, Q≠K. When Q>K, reaction will favour backward direction and when Q<K, it will favour forward direction.
The reaction quotient Q for : N2(g)+3H2(g)↔2NH3(g) is given by Q=[NH3]2[N2][H2]3. lhe reaction will proceed in backward direction, when :
View SolutionMass action ratio or reaction quotient Q for a reaction can be calculated using the law of mass action A(g)+B(g) harr C(g) + D(g) Q=([C][D])/([A][B]) . The value of Q decides whether the reaction is at equilibrium or not. At equilibrium, Q = K. For non equilibrium process, Q ne K . When Q gt K , reaction will favour backward direction and when Q lt K , it will favour forward direction. For the reaction : 2A + B harr 3C at 298 K, K_c = 49 A 3L vessel contains 2,1 and 3 moles of A, B and C respectively. The reaction at the same temperature:
View SolutionMass action ratio or reaction quotient Q for a reaction can be calculated using the law of mass action A(g)+B(g) harr C(g) + D(g) Q=([C][D])/([A][B]) . The value of Q decides whether the reaction is at equilibrium or not. At equilibrium, Q = K. For non equilibrium process, Q ne K . When Q gt K , reaction will favour backward direction and when Q lt K , it will favour forward direction. In a reaction mixture containing H_2 , N_2 and NH_3 at partial pressure of 2 atm, and 3 atm respectively, the value of K_p at 725 K is 4.28 xx 10^(-5) atm^(-2) . In which direction the net reaction will go ? N_(2(g)) + 3H_(2(g)) harr 2NH_(3(g))
View SolutionMass action rato or reaction quotient Q for a reaction can be calculate using the law of masss action
A(g)+B(g)⇔C(g)+D(g)
Q=[C][D][A][B]
The value of Q decides whether the reaction is at equilibrium or not.
At equilibrium, Q=K
For an equilibrium process, Q≠K
when Q>K, reaction will favour backward direction and when Q<K, it will favour direction.
Answer the following questions:
The reaction quotient Q for:
O2(g)+2H2(g)⇔2H2O(g)
is given by Q=[H2O]2[O2][H2]2. The reaction will proceed in backward direction, when
View SolutionMass action rato or reaction quotient Q for a reaction can be calculate using the law of masss action A(g)+B(g) hArr C(g)+D(g) Q=([C][D])/([A][B]) The value of Q decides whether the reaction is at equilibrium or not. At equilibrium, Q=K For an equilibrium process, Q ne K when Q gt K , reaction will favour backward direction and when Q lt K , it will favour direction. Answer the following questions: For the reaction: 2A+B hArr 3C at 298 K, K_(c)=40 A 4L vessel contains 2, 1, and 4 mol of A, B and c, respectively. The reaction at the same temperature
View Solution
