A square-shaped conducting wire loop of dimension a moving parallel to the x-axis approaches a square region of size b (a<b) where a uniform magnetic field B exists pointing into the plane of the paper (see figure). As the loop passes through this region, the plot correctly depicting its speed (v) as a function of x is




The correct Answer is:B
Step by step video, text & image solution for A square-shaped conducting wire loop of dimension a moving parallel to the x-axis approaches a square region of size b (a lt b) where a uniform magnetic field B exists pointing into the plane of the paper (see figure). As the loop passes through this region, the plot correctly depicting its speed (v) as a function of x is by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
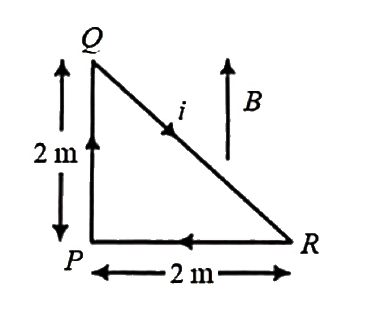
A loop PQR carries a current i=2A as shown in the figure. A uniform magnetic field B = 2T exists in space parallel to the plane of the loop . The magnetic torque on the loop is
View SolutionA square loop of a conducting material of side l and resistance r is dragged through a uniform magnetic field B with uniform velocity v keeping the plane of the loop perpendicular to the direction of the field. What is the current flowing through the loop?
View Solution
Knowledge Check
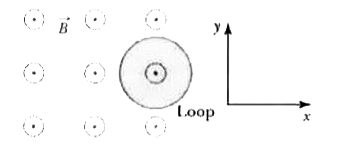
A square-shaped wire loop of mass m, resistance R and side 'a' moving with speed v0, parallel to the x-axis, enters a region of uniform magnetic field B, which is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The speed of the loop changes with distance x (x<a) in the filed, as
Av0−B2a2RmBv0−B2a22RmCv0−B2aRmDv0A conducting rod AB moves parallel to x-axis in a uniform magnetic field pointing perpendicular and into the plane of paper. The end A of the rod
 Agets positively chargedBgets negatively chargedCremains neutralDgets positively charged first and then negatively charged
Agets positively chargedBgets negatively chargedCremains neutralDgets positively charged first and then negatively chargedA square loop of side L, resistance R placed in a uniform magnetic field B acting normally to the plane of the loop. If we attempt to pull it out of the field with a constant velocity v, then the power needed is
ABRlvBB2l2v2RCBl2v2RDBvlR
A wire loop carrying current I is placed in the x−y plane as shown in the figure. If an external uniform magnetic field →B=Bˆi is switched on, then the torque acting on the loop is
View SolutionA circular loop of wire is positioned half in and half out of a square region of uniform magnetic field directed in the +z direction, out of the paper, as shown in the following figure. To induce a counterclockwise current in this loop
View SolutionA square loop of side a and resistance B is moved in the region of uniform magnetic field B (loop remaining completely inside field), with a velocity v through a distance x. The work done is
View SolutionA square loop of side a and resistance R is moved in the region of uniform magnetic field B(loop remaining completely insidefield), with a velocity v through a distance x. The work done is:
View SolutionA rigid wire loop of square shape having side of length L and resistance R is moving along the x-axis with a constant velocity v0 in the plane of the paper. At t=0 , the right edge of the loop enters a region of length 3L where there is a uniform magnetic field B0 into the plane of the paper, as shown in the figure. For sufficiently large v0, the loop eventually crosses the region. Let x be the location of the right edge of the loop. Let v(x),IxandFx represent the velocity of the loop, current in the loop, and force on the loop, respectively, as a function of x. Counter-clockwise curren is taken as positive.
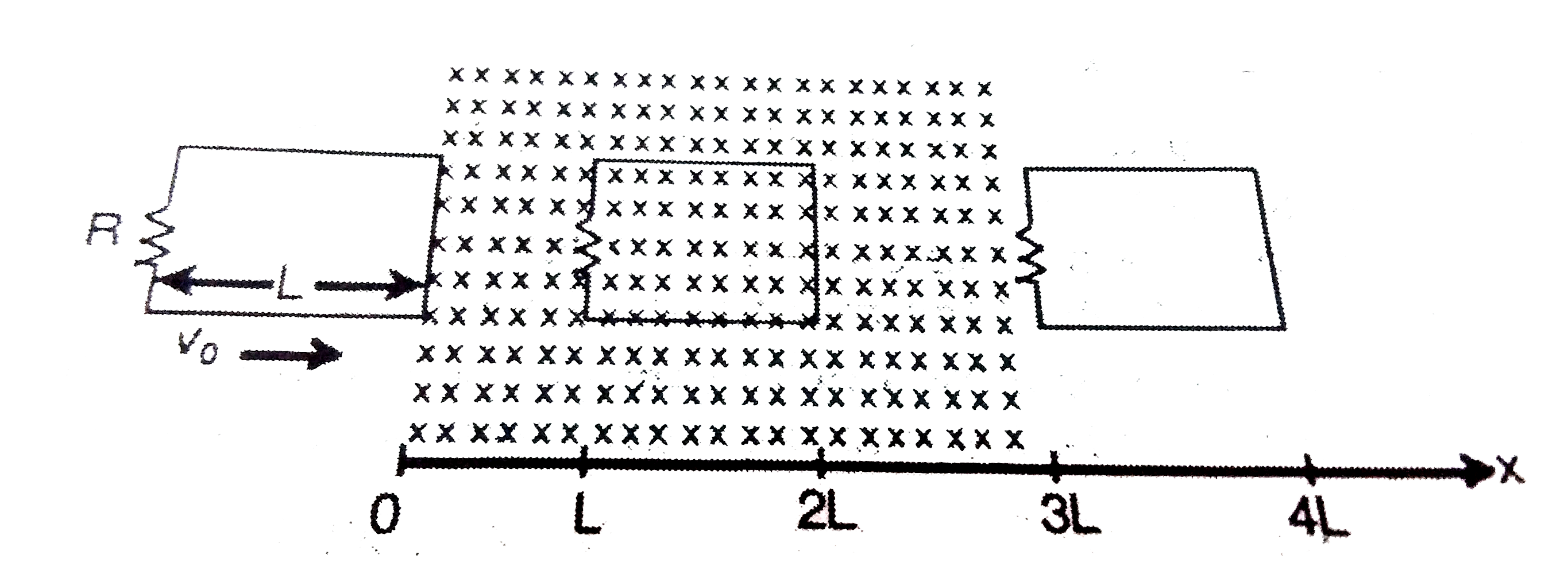
Which of the following schematic plots (s) is are correct ? (Ignore gravity )
View Solution
