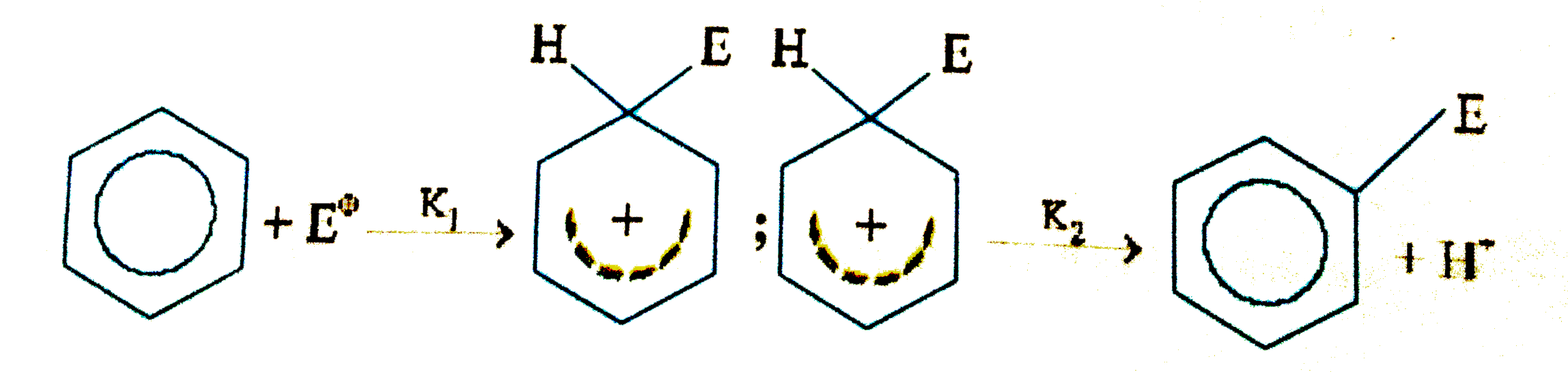
A general mechanism for aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction is. (K1 and K2 are rate constant for the forward reaction) also C-D bond in harder to break than a C-H bond, and consequently reaction in which C-D bond broken proceed more slowly than the reaction in which C-H bond are broken. However experimetns reveal that nitration of C6H6andC6D6 proceeds at equal rates while the same is not true for sulphonation of C6H6 and C6D6.
Q. When one of the carbons of benzene is labelled (C14), in which case we expect greater yield of the product obtained at labelled carbon.
Nitration
Sulphonation
Both have equal chance
It depends on temperature.
The correct Answer is:C
Both in nitration and sulphonation have equal chance of greater yield of products obtained at labelled carbon.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- BENZENEBOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - BENZENEEXERCISE - Level-6
121 Videos
- BENZENEBOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - BENZENEEXERCISE - Level-2 (H.W)
12 Videos
- ATOMIC STRUCTUREBOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - ATOMIC STRUCTUREEXERCISE - All Questions
685 Videos
- CARBONYL COMPOUNDSBOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - CARBONYL COMPOUNDSEXERCISE - LEVEL -VI
99 Videos
Similar Questions
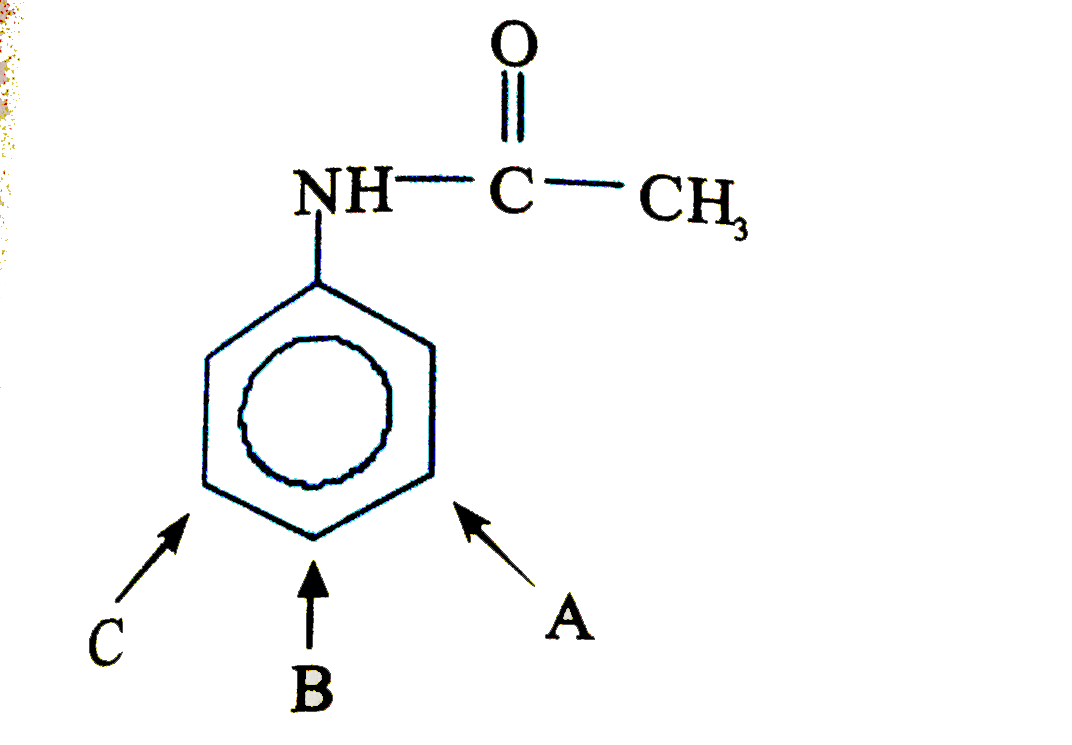
Identify the position where electrophilic aromatic substitution EAS) is most favourable
View SolutionIdentify the aromaic species in the following
View SolutionFind the e/m value of α-particle (He+2) w.r.t H-atom?
View SolutionIn the Cannizzaro reaction given below:
2Ph−CHOΘOH−−→Ph−CH2OH+PhCO−2 the slowest step is:
View SolutionDeuterium is the isotope of hydrogen of mass number 2 , with a proton and a neutron in its nucleus. The chemistry of deuterium is nearly identical to the chemistry of hydrogen, except that C-D bond is slightly (5.0 "KJ" //"mole") stonger than the C-H bond. Reaction rates tend to be slower if a C-D bond as opposed to a C-H bond is broken in a rate limiting step. This effect on the rate is called a kinetic isotope effect. CH_(3)-overset(O) overset(||)(C)-CH_(3)overset(D_(2)O,D^(+))toX
View SolutionC6H6→C6H12ΔH=−204KJ heat of hydrognentaion of each C=C bond in benzene
View SolutionThe enthalpy change for the reaction, C2H6(g)→2C(g)+6H(g) is X kJ. The bond energy of C-H bond is :
View SolutionA general mechanism for aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction is. ( K_(1) and K_(2) are rate constant for the forward reaction) also C-D bond in harder to break than a C-H bond, and consequently reaction in which C-D bond broken proceed more slowly than the reaction in which C-H bond are broken. However experimetns reveal that nitration of C_(6)H_(6) and C_(6)D_(6) proceeds at equal rates while the same is not true for sulphonation of C_(6)H_(6) and C_(6)D_(6) . Q. In the nitration reaction
View SolutionA general mechanism for aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction is. ( K_(1) and K_(2) are rate constant for the forward reaction) also C-D bond in harder to break than a C-H bond, and consequently reaction in which C-D bond broken proceed more slowly than the reaction in which C-H bond are broken. However experimetns reveal that nitration of C_(6)H_(6) and C_(6)D_(6) proceeds at equal rates while the same is not true for sulphonation of C_(6)H_(6) and C_(6)D_(6) . Q. What can be inferred regarding mechanism of sulphonation of C_(6)H_(6) and C_(6)D_(6)
View Solution(A) Rate of nitration of benzene and hexadeuterobenzene are different.
(R) C-H bond is stronger than C-D bond.
View SolutionAssertion. Rates of nitration of benzene and hexadeuterobenzene are different. Reason. C-H bond is stronger than C-D bond.
View SolutionThe bond enthalpy of C - C, C = C, H - H and C - H bonds are 350,600,400 and 410 kJ · mol-1 respectively. The enthalpy change for reaction
C2H4(g)+H2(g)→C2H6(g) is
View Solution(A) in creaking of akances C-C bond is broken but not C-H bond (R ) Bond energy fo c-C bond is less than C-H bond .
View SolutionStatement-1 : Rate of nitration is C6H6≅C6D6≅C6T6
Statement-2 : Formation of wheland intermediate is rate determining step in nitration of benzene, not the breaking of C–H or C–D bond.
View SolutionThe enthalpy change for the reaction C_(2)H_(6(g)) rarr 2C_((g)) + 6H_((g)) is x kJ. The bond energy of C-H bond is:
View Solution

