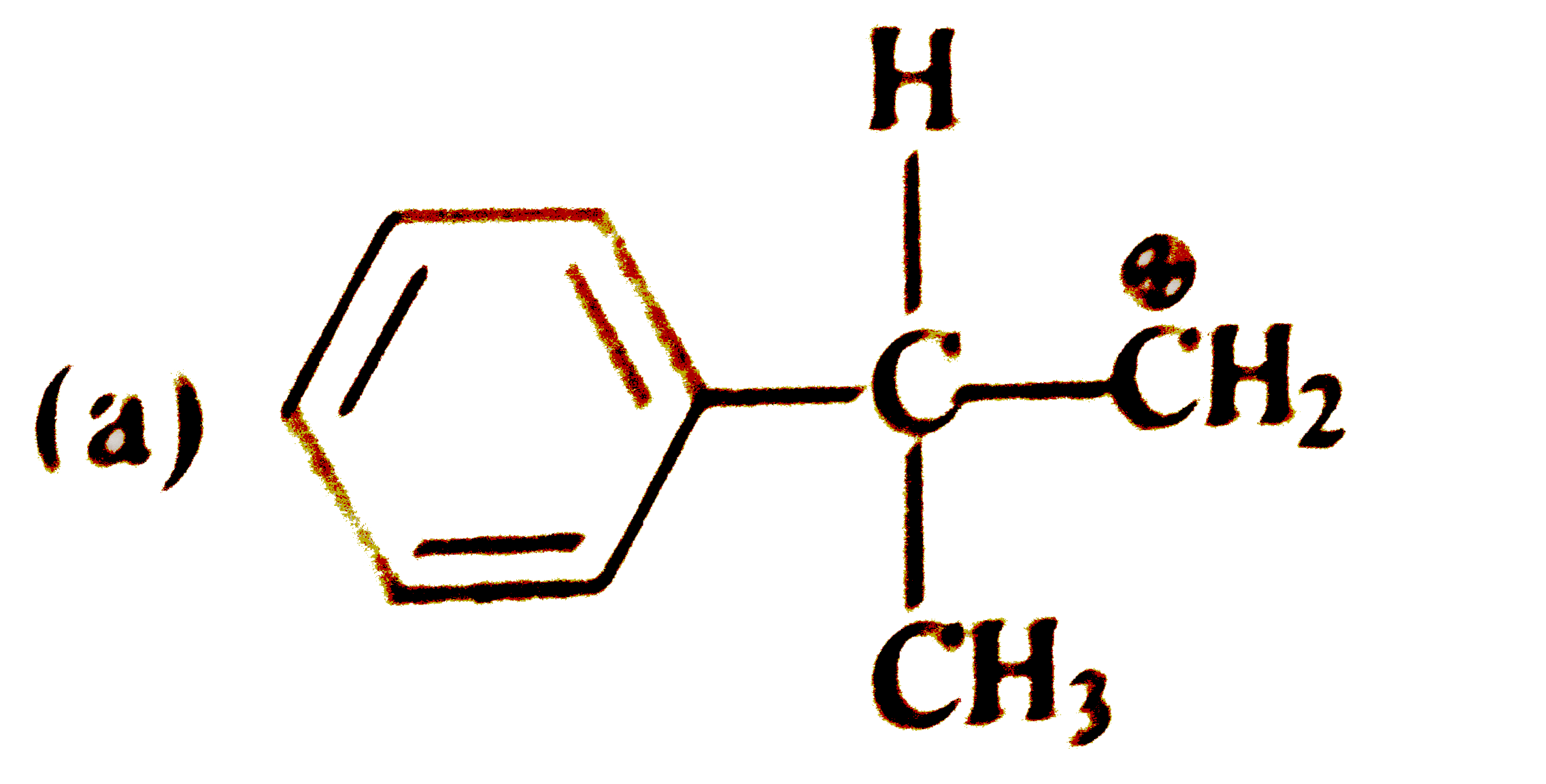
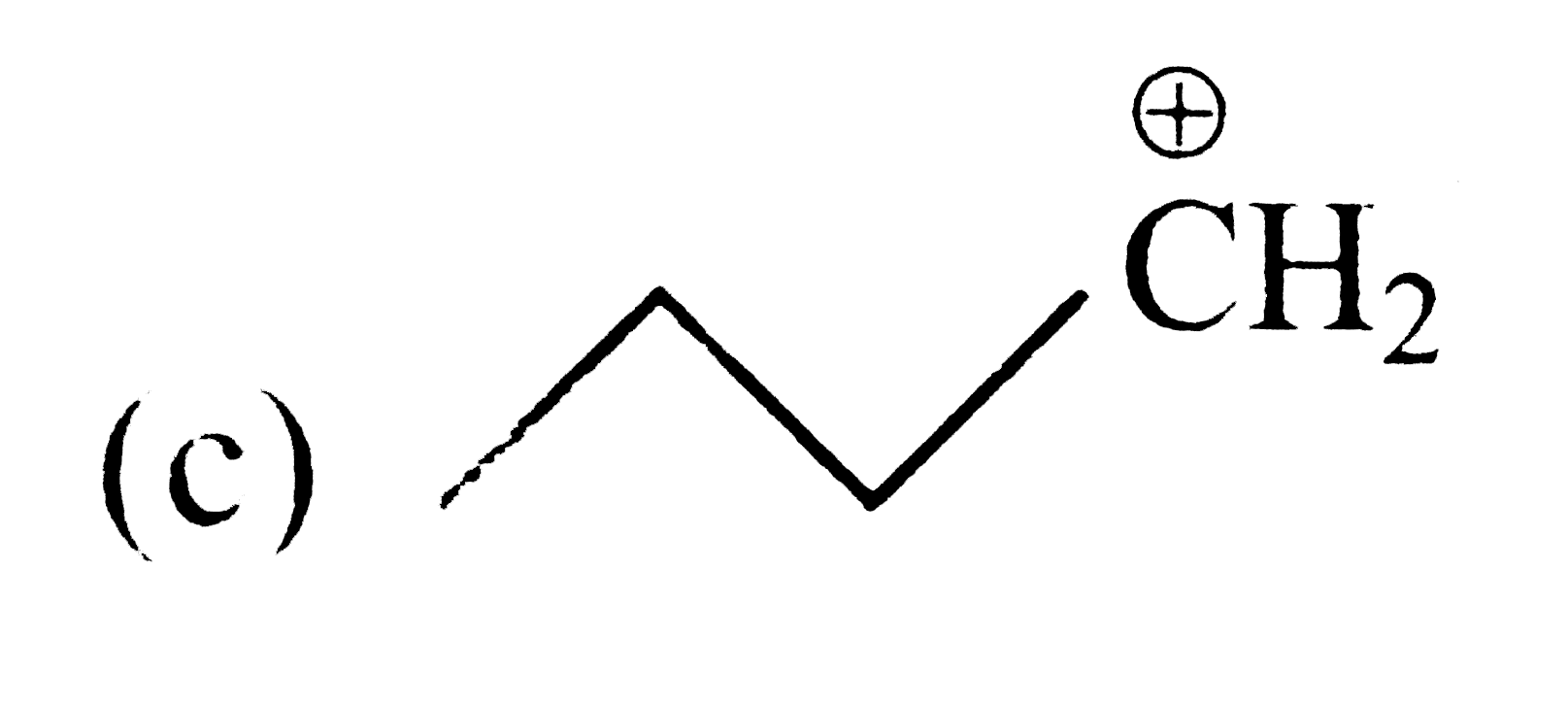
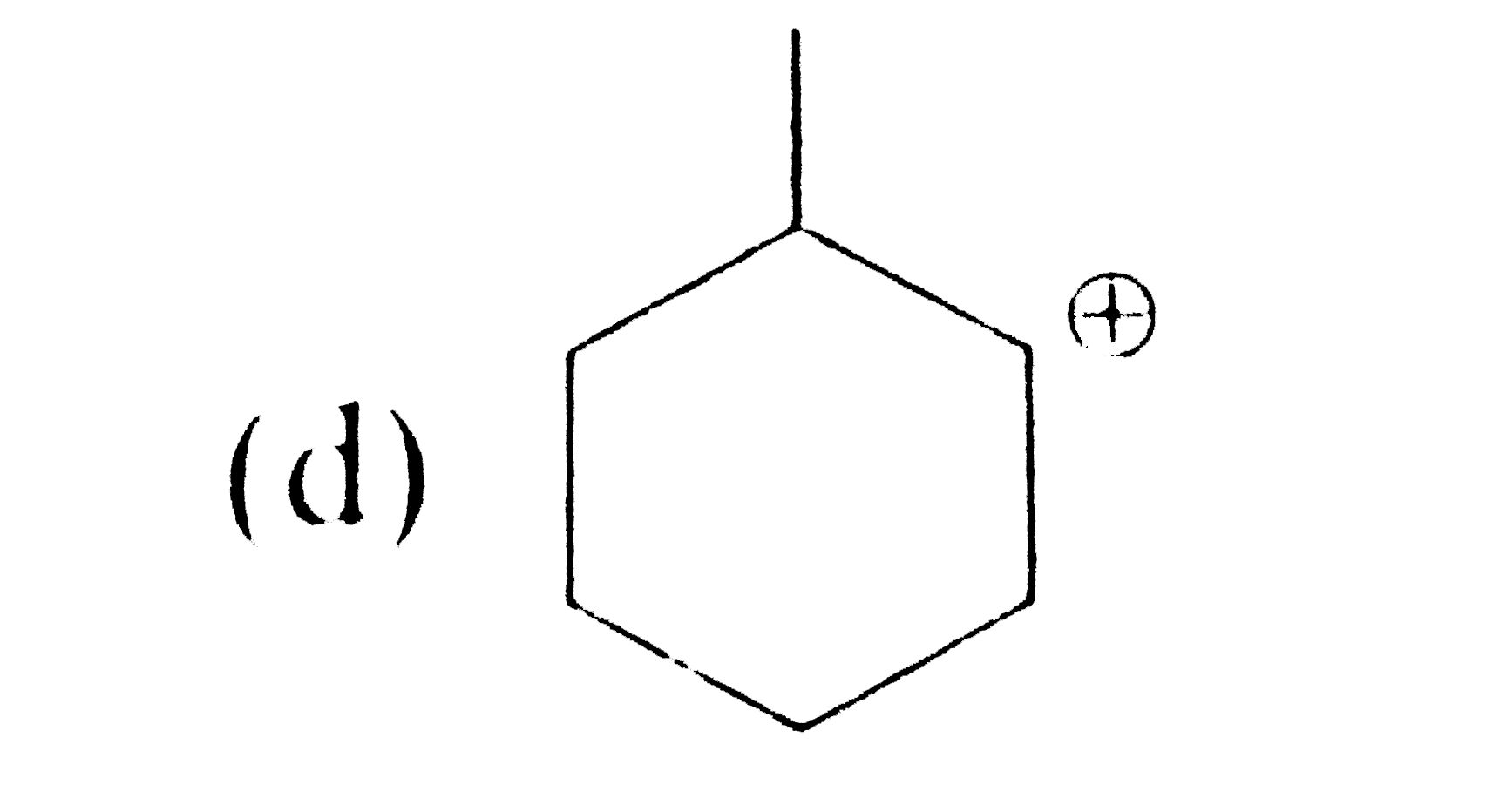
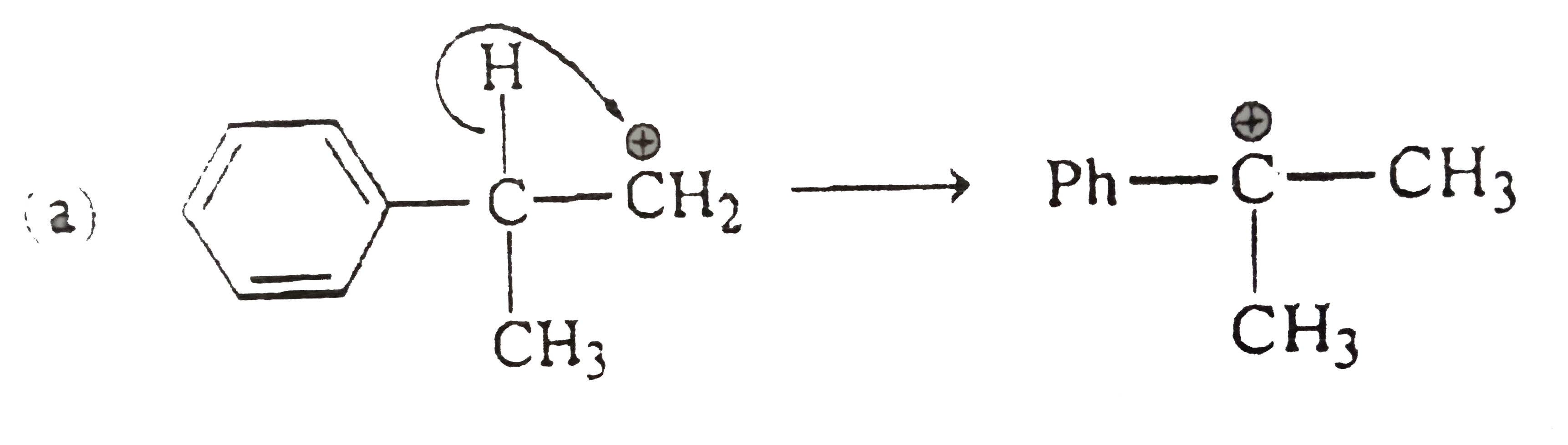Under common reaction conditions, a carboncation rearranges to another carbocation of equal or greater stability. For example secondary carbocation will rearrange to a tertiary carbocation. It will not rearrange to a less stable primary carbocation. This generalization is not absolute, and because there is not is a high energy barrier to the rearrangement of carbocations, rearrangement to a less stable cation can occur if it offers the chance to forme a more stable product.
In which of the following cations rearrangement takes place most rapidly?
A
B
CH3H∣C∣CH3−⊕CH2
C
D
Video Solution
Text Solution
The correct Answer is:A
|
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Under common reaction conditions, a carboncation rearranges to another carbocation of equal or greater stability. For example secondary carbocation will rearrange to a tertiary carbocation. It will not rearrange to a less stable primary carbocation. This generalization is not absolute, and because there is not is a high energy barrier to the rearrangement of carbocations, rearrangement to a less stable cation can occur if it offers the chance to forme a more stable product.
In the following cation , H/CH3 that is most likely to migarte to the positively charged carbon is :
H3C1−2H∣C∣OH−3⊕C∣H−4H∣C∣CH3−5CH3ACH3atC−4BHatC−4CCH3atC−2DHatC−2Most stable carbocation is:
ACH3−+CH2B+CH2CHCl2C+CH2CH2ClD+CH2−CH2NO2Most stable carbocation is:
A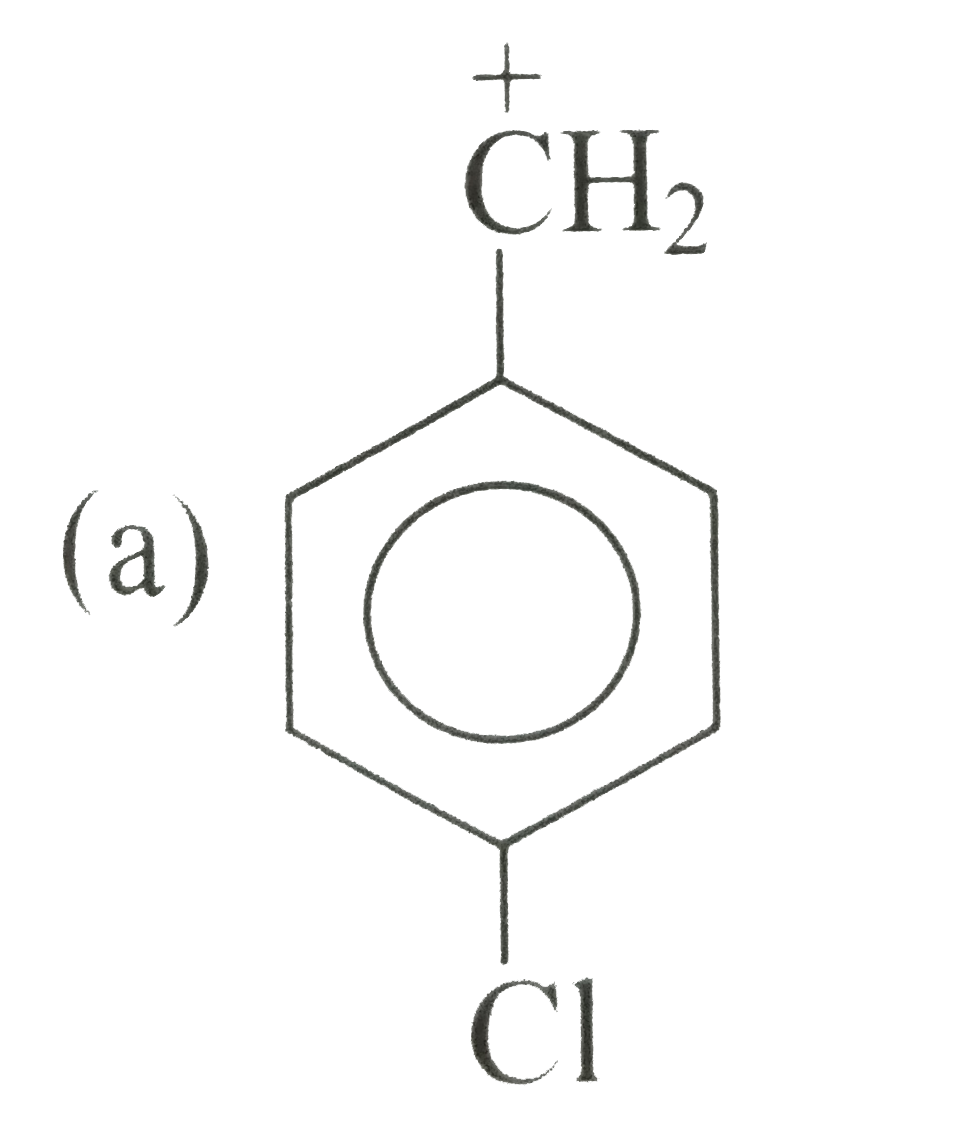 B
B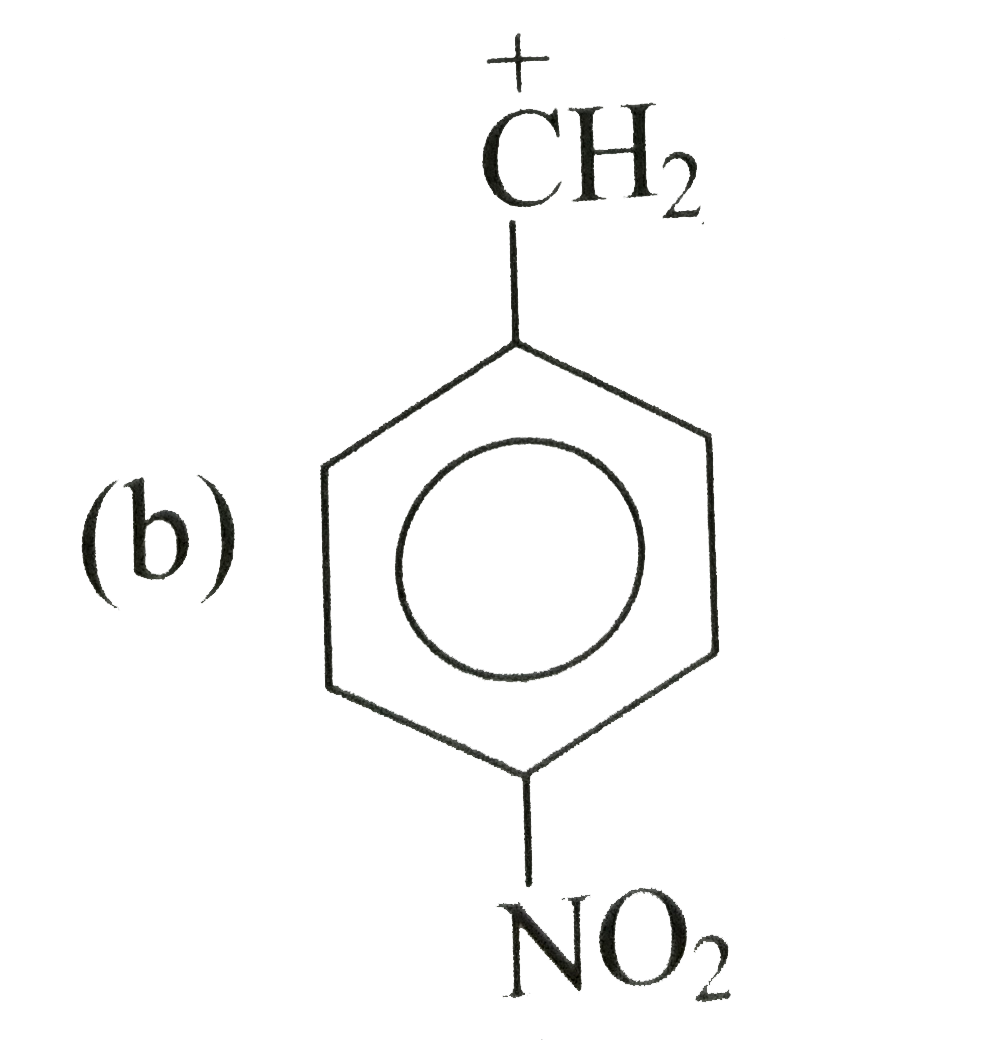 C
C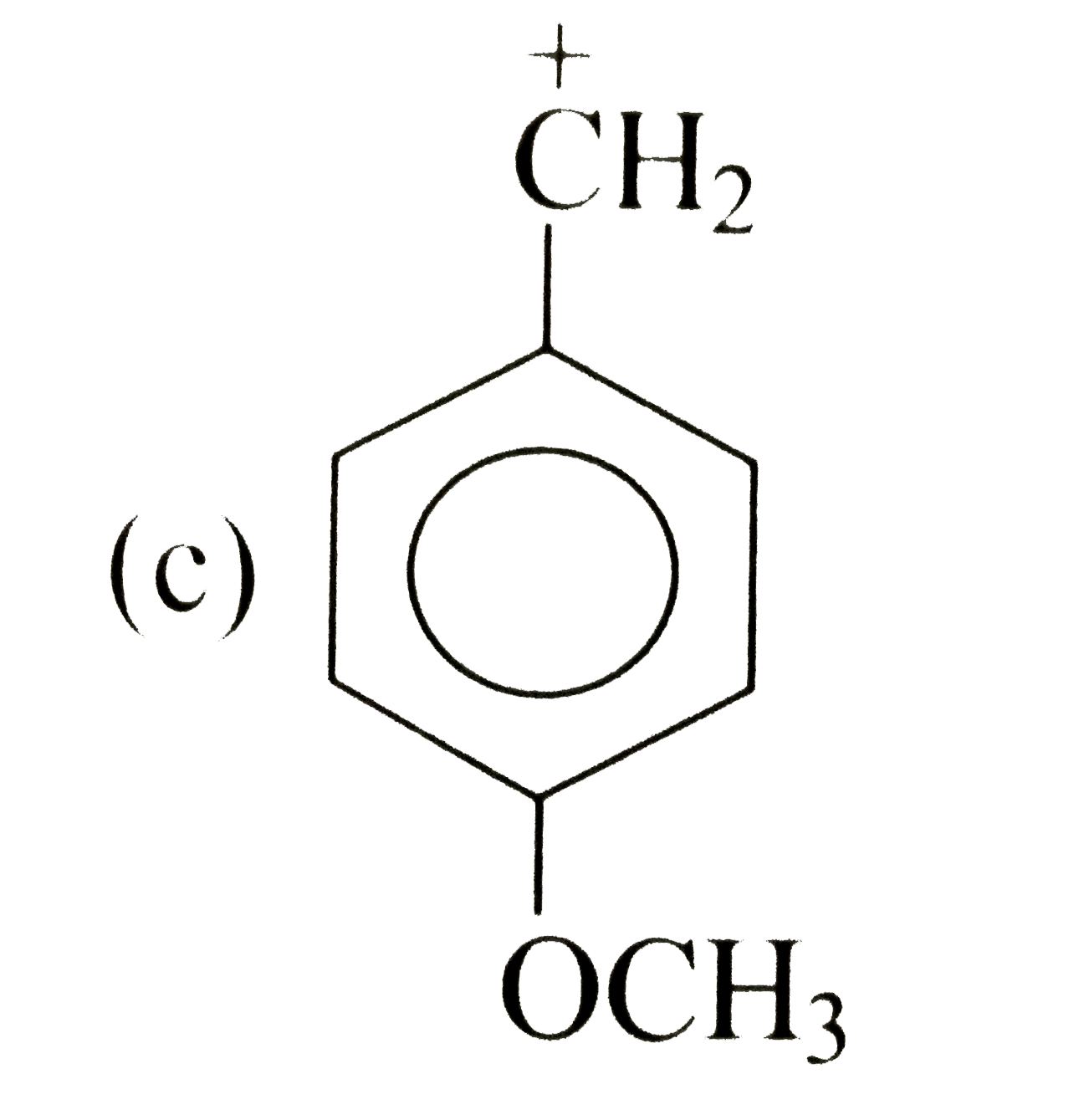 D
D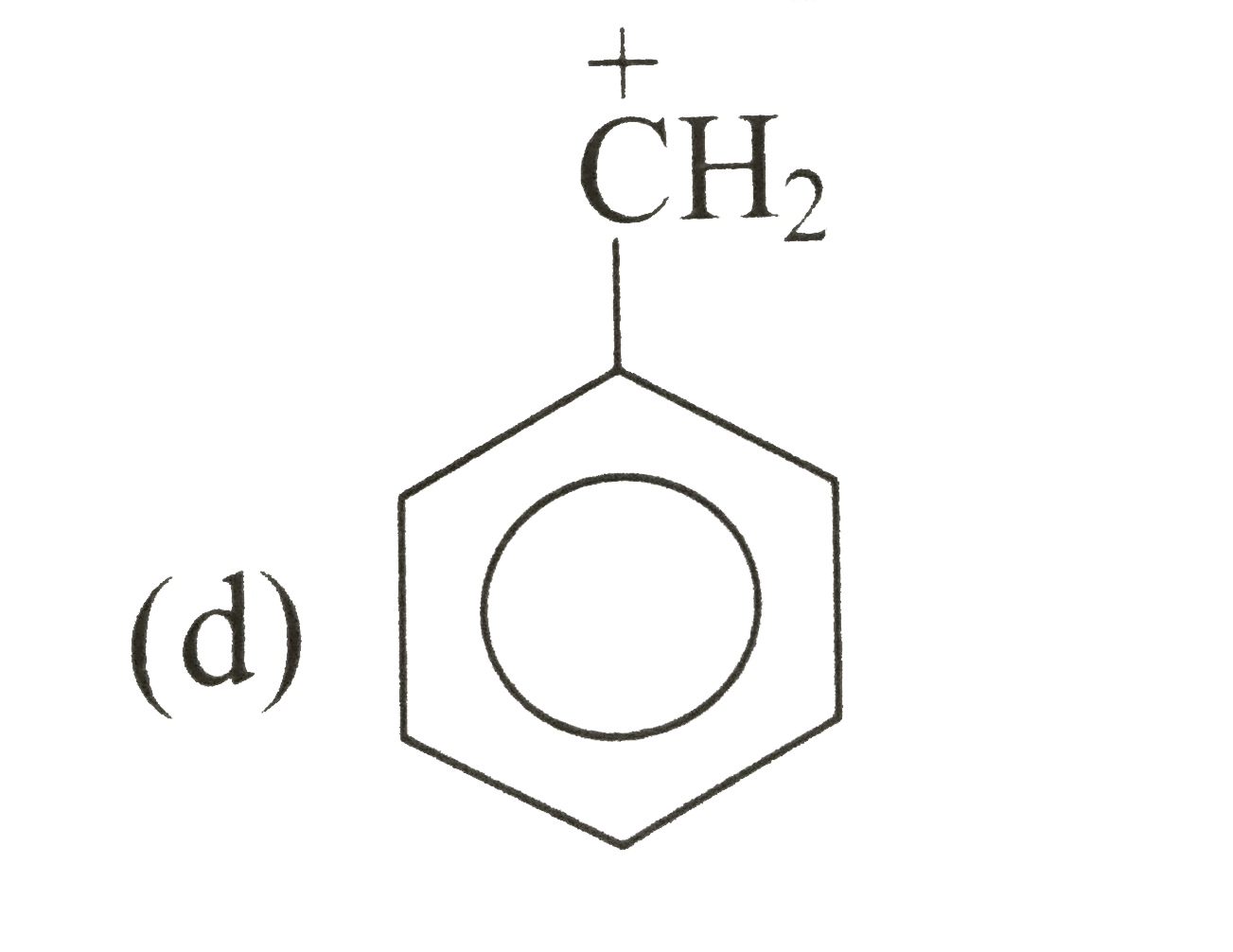
Carbocation Rearrangement 1
View SolutionBenzyl carbocation is more stable than ethyl carbocation. Justify.
View SolutionMost stable carbocation is:
View SolutionWhich of the following carbocations would not likely rearrange to more stable carbocation ?
View SolutionThe most stable carbocation is :
View Solution