Match Column -I with Column -II :
Column -I Column-II
(A) Ph of water ( p ) 12pKw
( B ) Ph of a salt of strong acid and strong base ( q) pH=12[pKw+pKa+logc]
(C ) Ph of a salt of weak acid and strong base ( r ) pH=12[pKw+pKa−pKb]
(D) Ph of a salt of weak acid and weak base (s) 7
where Ka,Kb are dissociation constants of weak acid and weak base and Kw= Ionic product of water.
The correct Answer is:(A→p,s),(B→p,s),(C→q),(D→r)
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ATOMIC STRUCTUREBook:FIITJEEChapter:ATOMIC STRUCTUREExercise:SINGLE INTEGER TYPE QUESTIONS
Explore 8 Videos
- ATOMIC STRUCTUREBook:FIITJEEChapter:ATOMIC STRUCTUREExercise:ILLUSTRATION 1.
Explore 30 Videos
- ATOMIC STRUCTUREBook:FIITJEEChapter:ATOMIC STRUCTUREExercise:COMPEREHENSION-IV
Explore 3 Videos
- ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDESBook:FIITJEEChapter:ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDESExercise:NUMERICAL BASED QUESTIONS
Explore 1 Video
- CARBOHYDRATES, AMINO ACIDS, POLYMERS AND PRACTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRYBook:FIITJEEChapter:CARBOHYDRATES, AMINO ACIDS, POLYMERS AND PRACTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRYExercise:EXERCISE
Explore 4 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Match the Column I and Column II.,B
 AA-p, B-q, C-r, D-sBA-q, B-r, C-s. D-pCA-r, B-q, C-p, D-pDA-r, B-s, C-p, D-q
AA-p, B-q, C-r, D-sBA-q, B-r, C-s. D-pCA-r, B-q, C-p, D-pDA-r, B-s, C-p, D-qMatch the Column I and Column II.,B
 AA-p, B-q, C-r, D-sBA-q, B-r, C-s. D-pCA-r, B-q, C-p, D-pDA-r, B-s, C-p, D-q
AA-p, B-q, C-r, D-sBA-q, B-r, C-s. D-pCA-r, B-q, C-p, D-pDA-r, B-s, C-p, D-qMatch the two columns (Column-I & Column-II)
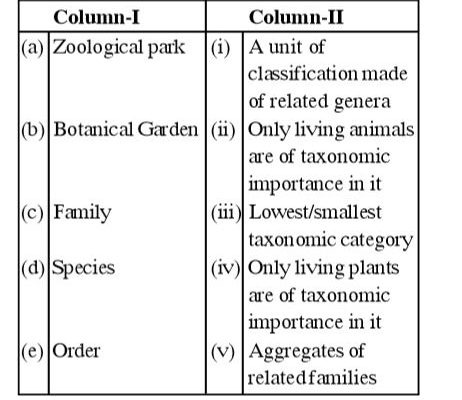 Aa-ii, b-iv, c-i, d-iii, e-vBa-i, b-ii, c-iii, d-iv, e-vCa-v, b-iv, c-iii, d-ii, e-iDa-iii, b-v, c-ii, d-i, e-iv
Aa-ii, b-iv, c-i, d-iii, e-vBa-i, b-ii, c-iii, d-iv, e-vCa-v, b-iv, c-iii, d-ii, e-iDa-iii, b-v, c-ii, d-i, e-iv
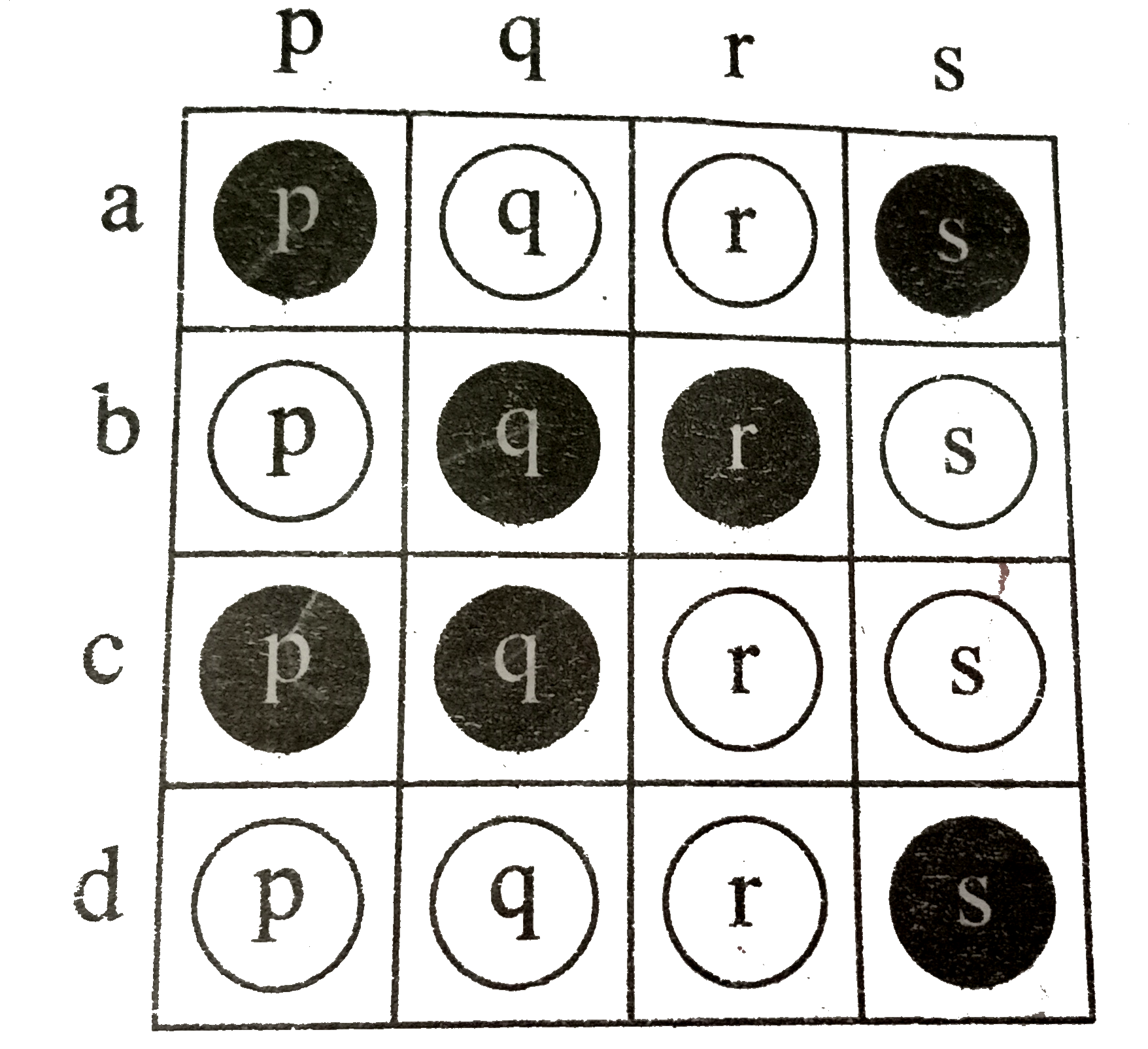
Match the column I with column II and with column III.
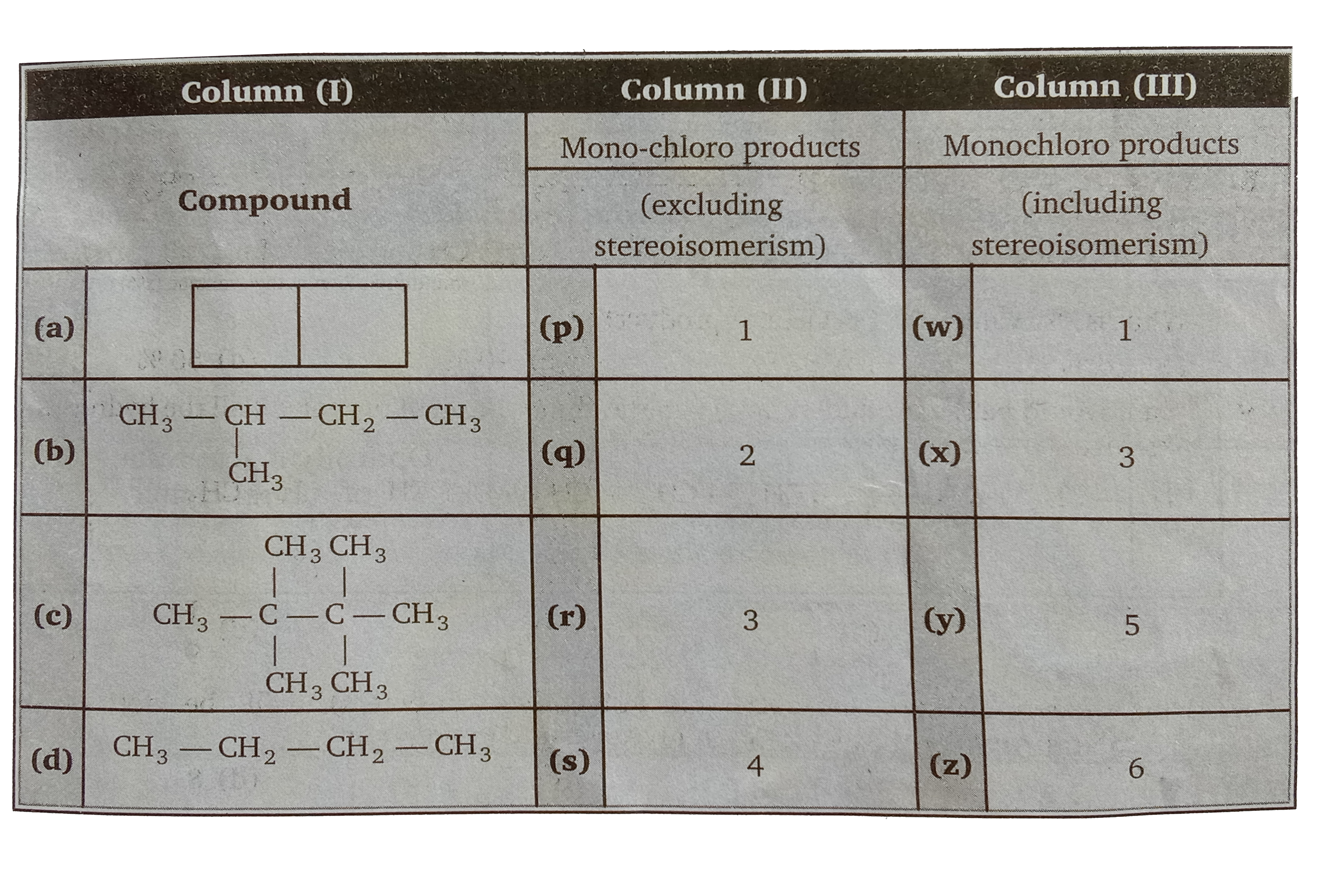
View SolutionMatch the two columns (Column-I & Column-II)

View SolutionWhen a salt reacts with water resulting into formation of acidic or basic solution, the process is referred to as salt hydrolysis. The pH of salt solution can be calculated using the following equations.
pH=12(pKw+pKa+logC) for salt of weak acid and strong base.
pH=12(pKw−pKb−logC) for salt of weak base and strong acid.
pH=12(pKw+pKa−pKb) for salt of weak acid and weak base
equal volume of 0.1M solution of weak acid HA is titrated with 0.1M NaOH solution till the end point pKa for acid is 6 and degree of hydroglysis is less compared to 1.The pH of the resultant solution at the end point is
View SolutionWhen a salt reacts with water resulting into formation of acidic or basic solution, the process is referred to as salt hydrolysis. The pH of salt solution can be calculated using the following equations.
pH=12(pKw+pKa+logC) for salt of weak acid and strong base.
pH=12(pKw−pKb−logC) for salt of weak base and strong acid.
pH=12(pKw+pKa−pKb) for salt of weak acid and weak base
pKb of NH3 is 4.74 and pKb of A−,B−and C− are 4,5 and 6 respectively. Aqueous solution of 0.01 M has pH in the increasing order.
View SolutionWhen a salt reacts with water to form acidic or basic solution , the process is called hydrolysis . The pH of salt solution can be calculated using the following relations :
pH=12[pKw+pKa+logc] (for salt of weak acid and strong base .)
pH=12[pKw−pKb−logc] (for salt of weak base and strong acid ) .
pH=12[pKw+pKa−pKb] (for weak acid and weak base ).
where 'c' represents the concentration of salt .
When a weak acid or a weak base not completely neutralized by strong base or strong acid
respectively , then formation of buffer takes place . The pH of buffer solution can be calculated using the following relation :
pH=pKa+log.[Salt][Acid],pOH=pKb+log.[Salt][Base]
Answer the following questions using the following data :
pKa=4.7447,pKb=4.7447,pKw=14
When 100 mL of 0.1 M NH4OH is added to 50 mL of 0.1M HCl solution , the pH is
View Solution


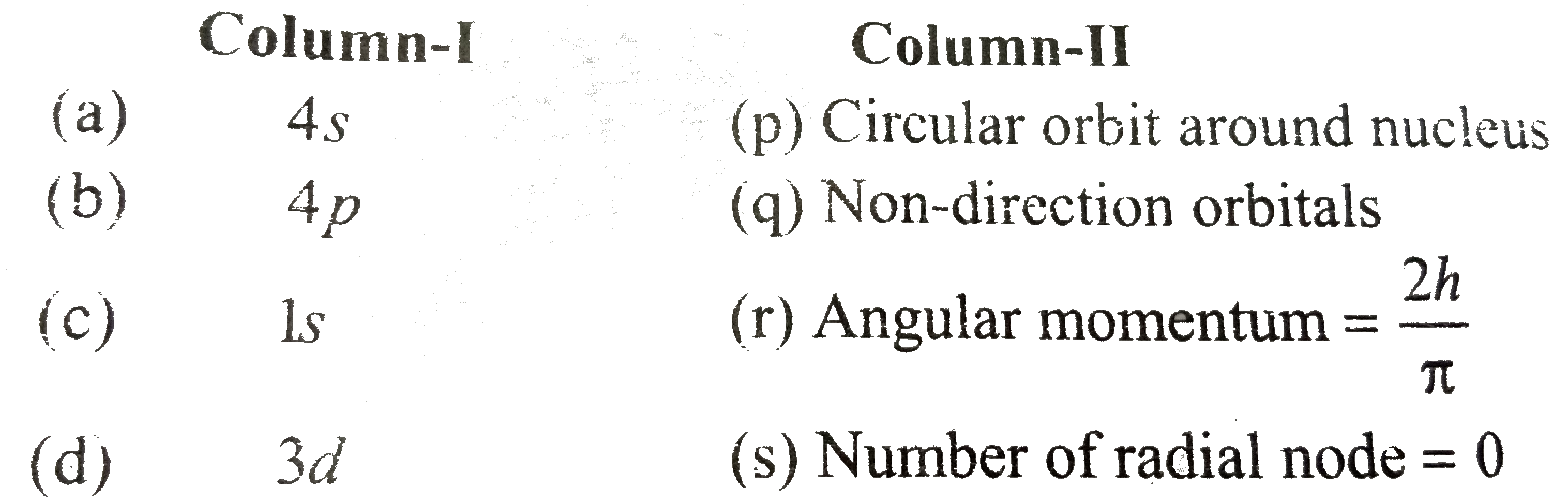 .
. 