Write the equation for relationship of rate constant and temperature.
To express the relationship between the rate constant (k) and temperature (T), we can use the Arrhenius equation. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how to write this equation:
Step 1: Understand the Components of the Arrhenius Equation
The Arrhenius equation is a mathematical expression that describes how the rate constant (k) of a reaction depends on temperature (T). The equation is given by:
k=Ae−EaRT
Where:
- k = rate constant
- A = frequency factor (also known as the pre-exponential factor)
- Ea = activation energy (the minimum energy required for a reaction to occur)
- R = universal gas constant (approximately 8.314 J/(mol·K))
- T = temperature in Kelvin
Step 2: Write the Arrhenius Equation
Using the components defined above, we can write the Arrhenius equation as follows:
k=Ae−EaRT
Step 3: Interpret the Equation
This equation indicates that the rate constant k increases with an increase in temperature T and/or a decrease in activation energy Ea. The exponential term e−EaRT shows that as temperature increases, the value of −EaRT becomes less negative, leading to a larger value of k.
Final Answer
The equation that describes the relationship between the rate constant and temperature is the Arrhenius equation:
k=Ae−EaRT
---
The Arrhenius equation is a mathematical expression that describes how the rate constant (k) of a reaction depends on temperature (T). The equation is given by:
- k = rate constant
- A = frequency factor (also known as the pre-exponential factor)
- Ea = activation energy (the minimum energy required for a reaction to occur)
- R = universal gas constant (approximately 8.314 J/(mol·K))
- T = temperature in Kelvin
Using the components defined above, we can write the Arrhenius equation as follows:
This equation indicates that the rate constant k increases with an increase in temperature T and/or a decrease in activation energy Ea. The exponential term e−EaRT shows that as temperature increases, the value of −EaRT becomes less negative, leading to a larger value of k.
The equation that describes the relationship between the rate constant and temperature is the Arrhenius equation:
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CHEMICAL KINETICS BOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - CHEMICAL KINETICS EXERCISE - CUQ (RATE OF REACTION)
83 Videos
- CHEMICAL KINETICS BOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - CHEMICAL KINETICS EXERCISE - EXERCISE -1 (C.W) (RATE OF REACTION & FACTORS)
14 Videos
- CHEMICAL KINETICS BOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - CHEMICAL KINETICS EXERCISE - EVALUATE YOURSELF - 6
4 Videos
- CARBOXYLIC ACIDBOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - CARBOXYLIC ACIDEXERCISE - All Questions
288 Videos
- CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFEBOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFEEXERCISE - ASSERTION & REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
10 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Which of the following graph is incorrect for variation of rate constant (K) with temperature for a reaction obeying Arrhenius equation ?
A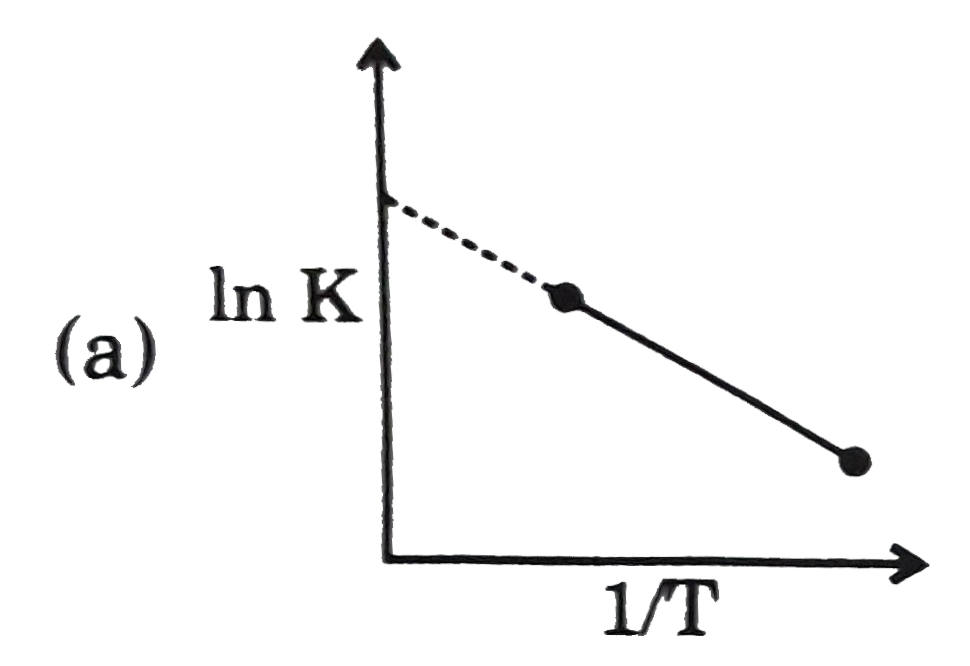 B
B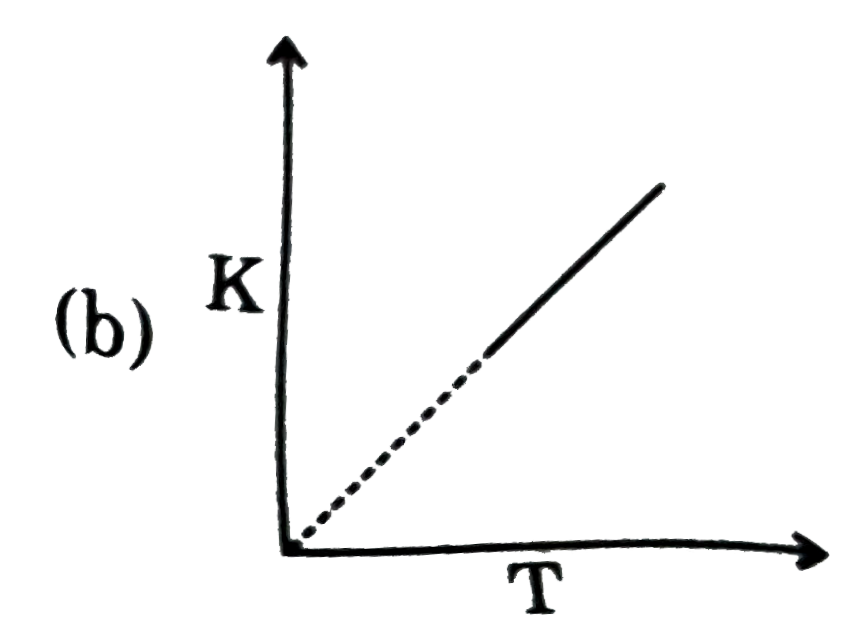 C
C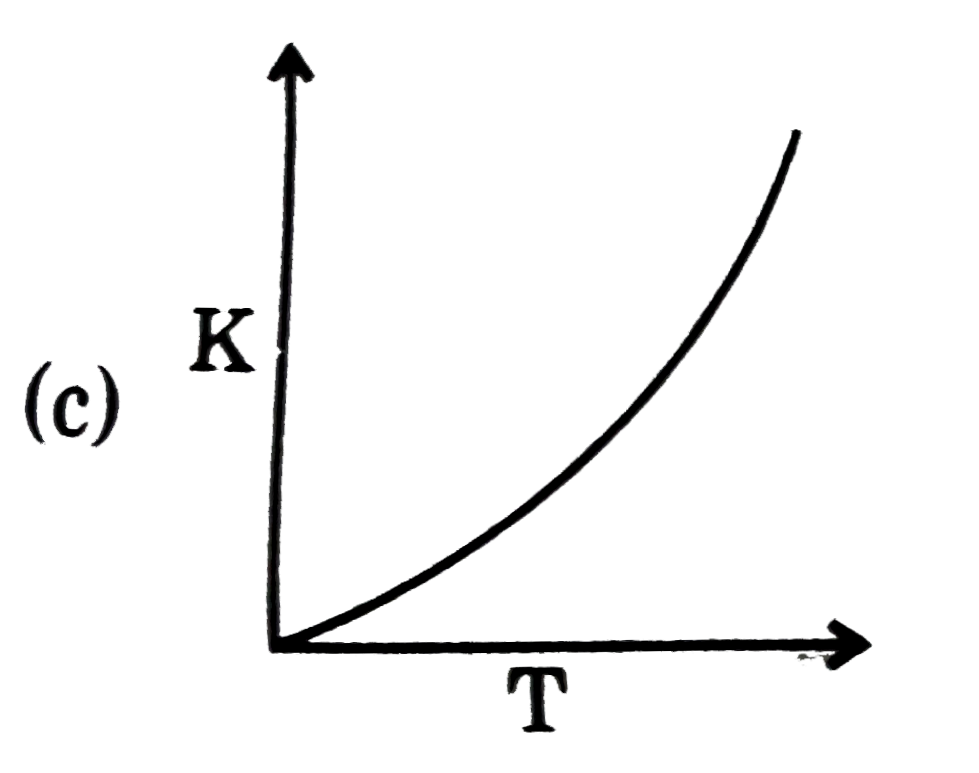 D
D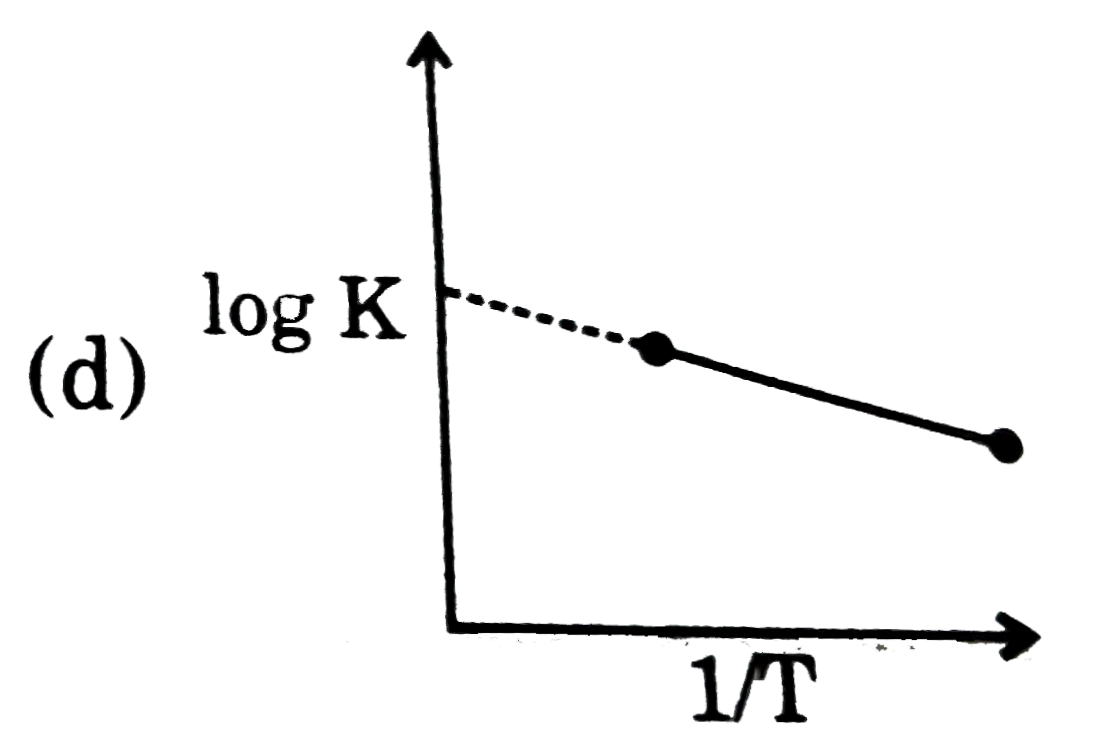
Arrhenius equation is :
k=Ae−E/RT
Which of the following graphs represents the variation of rate constant k against temperatureT ?A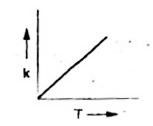 B
B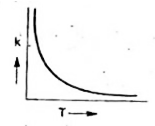 C
C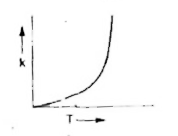 D
D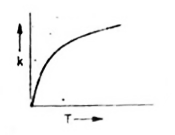
The variation of rate constant with temperature can be explained by Arrhenius equation. However , the can be explained by Activation energy is found to be temperature dependent/In such casesdinKdT=EaRT2 should be used to predict variation of rate constant with tempreature. On the basic of this information , answer the question that follow :
Which if the following statement is not correct ?ATemperature coefficient of a reaction at high temperature will be lessBReaction with no activation energy will have no change in rate constant due to temperatureCThe factor by which catalyst increase rate constant will be same at all the temperatureDGreater the activation energy, more sanitive will the rate constant be cecause of temperature
State the Arrhenius equation for the rate constant of a reaction.
View SolutionWrite the equation showing the relationship between equivalent and concentrate of a storng electrolyte.
View SolutionVarious Solved Numerical Questions on Arrhenius Equation || Variation OF Rate Constant with Temperature || Variation OF Equilibrium Constant with Temperature
View SolutionDerive the relationship between rate constant and half-life period of a first order reaction.
View SolutionThe rate of chemical reaction are strongly affected by temperature . Arrhenius (1889) gave following relation between rate contant and temperature .
k=Ae−Ea/RT .....(i)
This equation is called Arrhenius equation. The constant 'A' is caleld Arrhenius of pre-exponential factor. Logarithm of equation (i) given :
log10k=log10AEa2.3030RT .....(ii)
The rate constant for a reaction is .
log10sec−1=14−1.25×104KT .....(iii)
At what temperature, rate constant of the reaction is equal to the pre-exponenntial factor ?
View Solution

