Draw Energy Diagram for exothermic reaction and Explain effect of catalyst.
Step-by-Step Solution
Step 1: Draw the Axes
- Begin by drawing a vertical line (y-axis) and a horizontal line (x-axis).
- Label the y-axis as "Potential Energy" and the x-axis as "Progress of Reaction".
Hint: The y-axis represents energy levels, while the x-axis shows the progression of the reaction from reactants to products.
Step 2: Indicate Reactants and Products
- On the y-axis, mark a point for the energy level of the reactants (higher energy) and a point for the energy level of the products (lower energy).
- Draw a horizontal line connecting the two points to represent the energy change.
Hint: In an exothermic reaction, the products have lower energy than the reactants, indicating that energy is released.
Step 3: Draw Activation Energy for Forward Reaction
- Draw a curve starting from the reactant energy level that peaks at a transition state (the highest point) and then drops down to the product energy level.
- The height of the peak represents the activation energy (Ea) required for the forward reaction.
Hint: Activation energy is the minimum energy required for the reactants to collide and form products.
Step 4: Draw Activation Energy for Backward Reaction
- From the product energy level, draw another curve that peaks at a transition state and returns to the reactant energy level.
- This peak represents the activation energy for the backward reaction.
Hint: The backward activation energy is typically higher than the forward activation energy in an exothermic reaction.
Step 5: Indicate ΔH
- Mark the difference in energy between the reactants and products as ΔH (enthalpy change).
- This value should be negative, indicating energy release.
Hint: ΔH is the energy released during the reaction, which is characteristic of exothermic processes.
Step 6: Introduce the Catalyst
- Draw a dotted line parallel to the original activation energy curve for the forward reaction to represent the effect of a catalyst.
- This dotted line should have a lower peak than the original activation energy curve.
Hint: A catalyst lowers the activation energy, making it easier for the reaction to occur.
Step 7: Explain the Effect of Catalyst
- Describe how the catalyst provides an alternative pathway for the reaction with a lower activation energy.
- Mention that this results in an increased rate of reaction, as more reactant molecules can overcome the lower energy barrier.
Hint: The presence of a catalyst does not change the overall energy change (ΔH) of the reaction; it only speeds up the process.
Summary
- An energy diagram for an exothermic reaction shows reactants at a higher energy level than products, with activation energies for both forward and backward reactions.
- A catalyst lowers the activation energy, thus increasing the reaction rate without altering the overall energy change of the reaction.
- Begin by drawing a vertical line (y-axis) and a horizontal line (x-axis).
- Label the y-axis as "Potential Energy" and the x-axis as "Progress of Reaction".
- On the y-axis, mark a point for the energy level of the reactants (higher energy) and a point for the energy level of the products (lower energy).
- Draw a horizontal line connecting the two points to represent the energy change.
- Draw a curve starting from the reactant energy level that peaks at a transition state (the highest point) and then drops down to the product energy level.
- The height of the peak represents the activation energy (Ea) required for the forward reaction.
- From the product energy level, draw another curve that peaks at a transition state and returns to the reactant energy level.
- This peak represents the activation energy for the backward reaction.
- Mark the difference in energy between the reactants and products as ΔH (enthalpy change).
- This value should be negative, indicating energy release.
- Draw a dotted line parallel to the original activation energy curve for the forward reaction to represent the effect of a catalyst.
- This dotted line should have a lower peak than the original activation energy curve.
- Describe how the catalyst provides an alternative pathway for the reaction with a lower activation energy.
- Mention that this results in an increased rate of reaction, as more reactant molecules can overcome the lower energy barrier.
- An energy diagram for an exothermic reaction shows reactants at a higher energy level than products, with activation energies for both forward and backward reactions.
- A catalyst lowers the activation energy, thus increasing the reaction rate without altering the overall energy change of the reaction.
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Energy of activation of an exothermic reaction reaction is _____.
AzeroBnegativeCpositiveDcan't be predictedSTATEMENT-1 : A catalyst enhances the rate of a reaction
and
STATEMENT-2 : The energy of activation of the reaction is lowered in presence of a catalyst.ASTATEMENT-1 is True, STATEMENT-2 is True, STATEMENT-2 is correct explanation for STATEMENT-1BSTATEMENT-1 is True, STATEMENT-2 is True, STATEMENT-2 is NOT a correct explanation for STATEMENT-1CSTATEMENT-1 True, STATEMENT-2 is FalseDSTATEMENT-1 is False, STATEMENT-2 is TrueOn the velocity in a reversible reaction, the correct explanation of the effect of catalyst is.
AIt provides a new reaction path of low activation energyBIt increases the kinetic energy of reacting moleculesCIt displaces the equilibrium state on right sideDIt decreases the velocity of backward reaction
Why is repiration considered an exothermic reaction ? Explain.
View SolutionGiven the following graph.
(a) Calculate ΔH for the reaction and energy of activation for the forward and backward reaction.
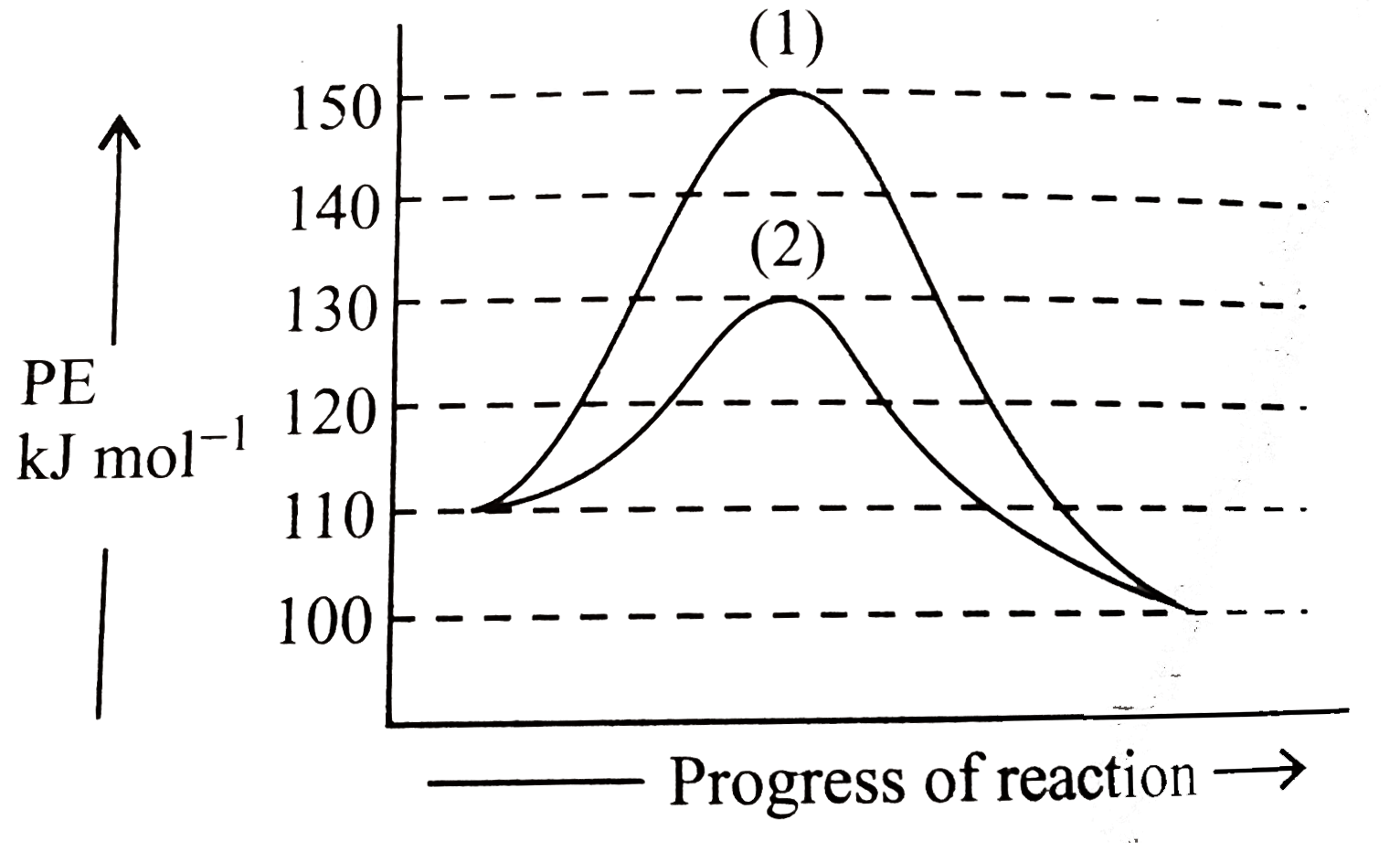
(b) Curve (2) is the energy profile in the presence of a catalyst. What is the energy of activation for the two reaction in the presence of a catalyst?
( c) Will the catalyst change the extent of the reaction?
View SolutionFrom the given figure:
i) Calculate ΔE for the reaction and energy of activation for the forward reaction and energy of activation for the backward reaction.
ii) The dotted curve is in the presence of a catalyst, what is the energy of activation for the two reactions in the presence of the catalyst?
iii) will the catalyst change the extent of the reaction?

View SolutionWhy is respiration considered an exothermic reaction? Explain.
View SolutionDraw an energy profile diagram for a three step reaction in which first step is slowest and last step is fastest. (Assume that reaction is exothermic)
View Solution
