Draw energy profile diagrams for exothermic and endothermic reactions.
(i) Energy charges during the formation of a product.
(ii) Comparison of energy of the reactant and product in case of endothermic and exothermic reactions.
(iii) relation among the energy of the reactant, product and activation energy.
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Draw an energy profile diagram for a three step reaction in which first step is slowest and last step is fastest. (Assume that reaction is exothermic)
A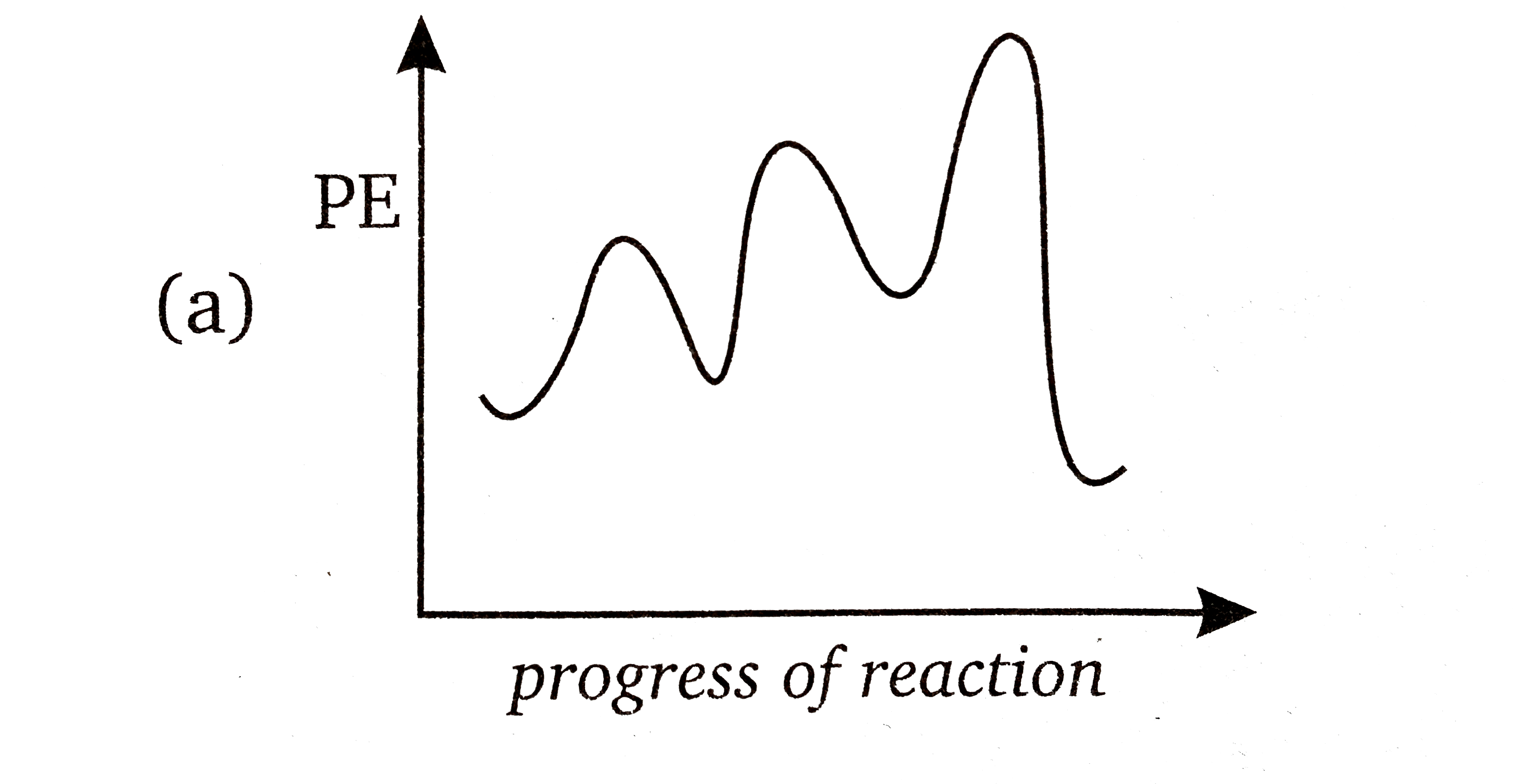 B
B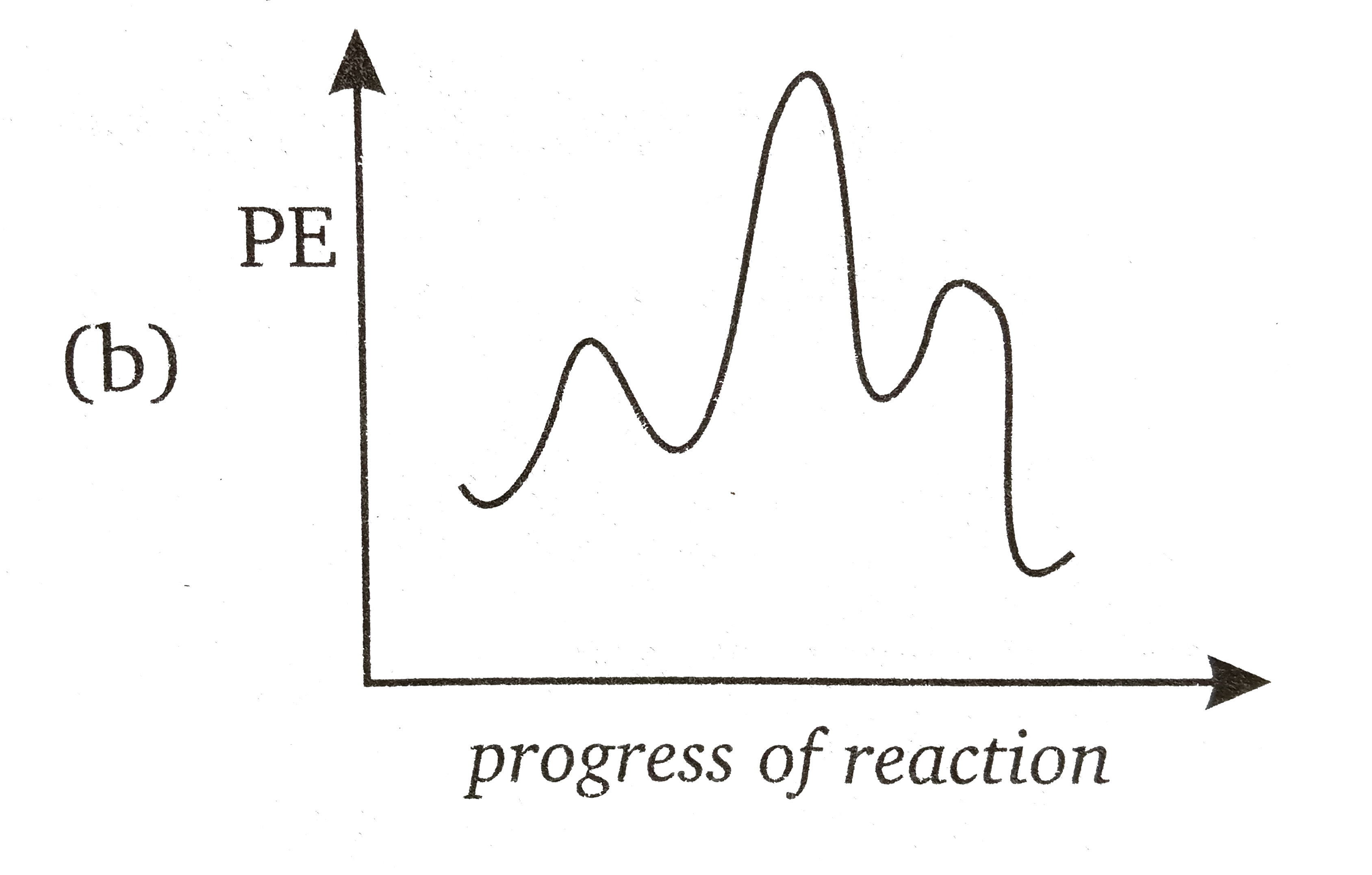 C
C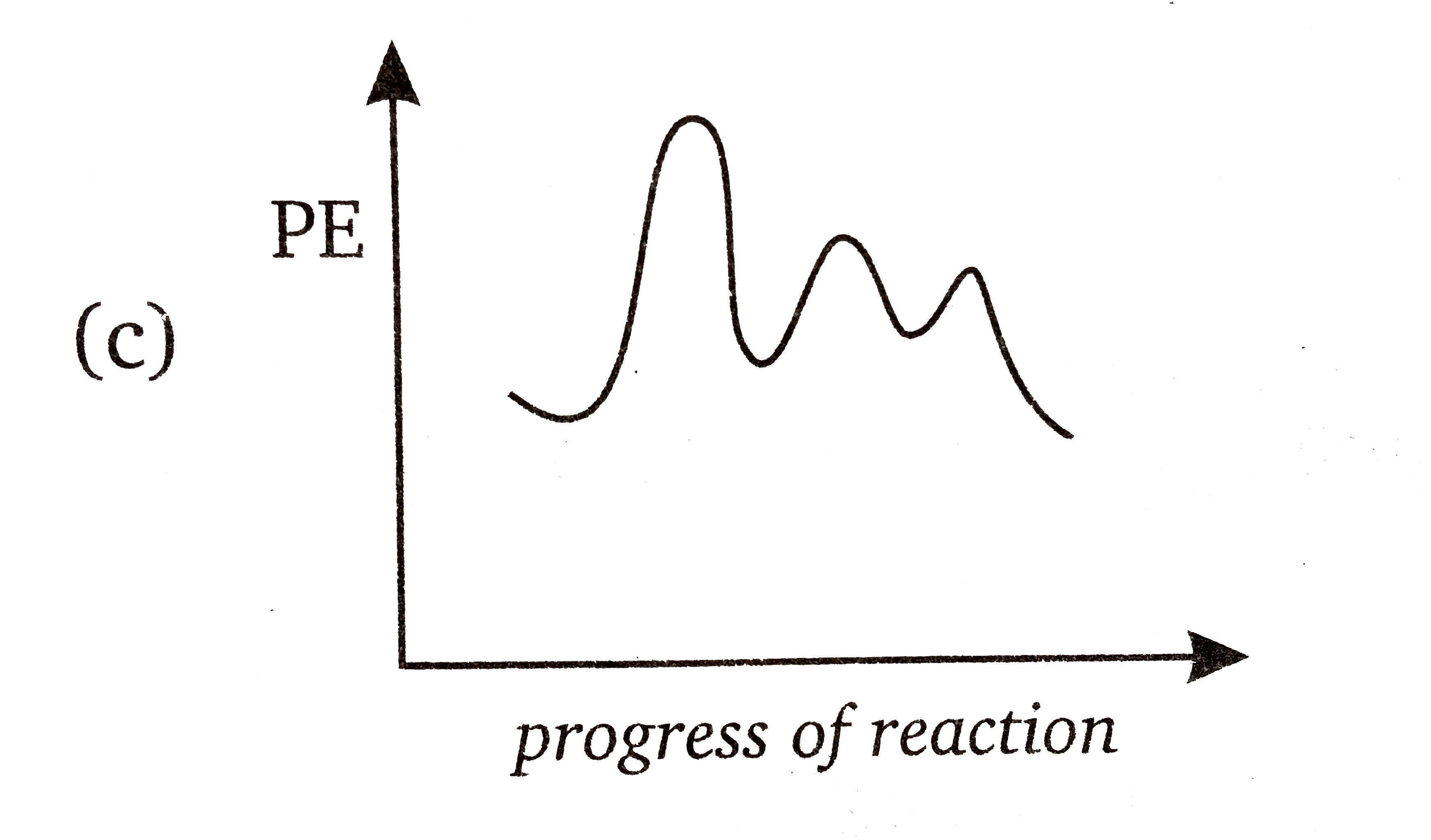 DNone of these
DNone of these
Energy profile diagram for an exothermic reaction. A1−−→B2−−→C3−−→D, is given below the step/s which is/are not rate determining for forward reaction?AA→BBB→CCC→DDcan't be predictedThe energy profile diagrams are very important tool through which, we predict lot of things, like the amount of activation energy of the catalysed and uncatalysed reaction as well as for the backward reaction and forward reaction. Thershold energy of the catalysed and uncatalysed reaction. The graphs representing the energy profile diagram for catalysed and uncatalysed reactions are given below :

The graph of the lower energy barrier is the energy profile diagram for the catalysed reaction adn of the higher barrier is the energy profile diagram of uncatalysed reaction.
From the graph, it is clear that EafandEab are the activation energy of the respectively. EafandEab are the activation energy of the catalysed forward and backward reaction respectvely
The reaction which occurs by absorption of heat is known as endothermic reaction and by release of heat is known as exothermic reaction
For exothermic reaction, ΔH is negative and for endothermic reaction, ΔH is positive
From Arrhenius equation, we know that k=Ae−Ea/RT where k is rate constant which signifies effective number of collisions. A is known as Arrehnius constant, or maximum rate constant of frequency factor which signifies maximum number of collisions with proper orientation of reacting species per mole per second.
The catalysed reaction occurs at 500 K and the uncatalysed reaction occurs at 800 K in such way so that the rate of catalysed reaction and uncatalysed reaction becomes equal as well as the catalyst lower down the energy barrier by 60 J.
Answer the following questions on the basis of above paragraph
From the given above information, what will be threshold energy for the catalysed reaction. If the normal energy of the reactant is 40 JA170 JB200 JC140 JD180 J
The energy profile diagrams are very important tool through which, we predict lot of things, like the amount of activation energy of the catalysed and uncatalysed reaction as well as for the backward reaction and forward reaction. Thershold energy of the catalysed and uncatalysed reaction. The graphs representing the energy profile diagram for catalysed and uncatalysed reactions are given below :
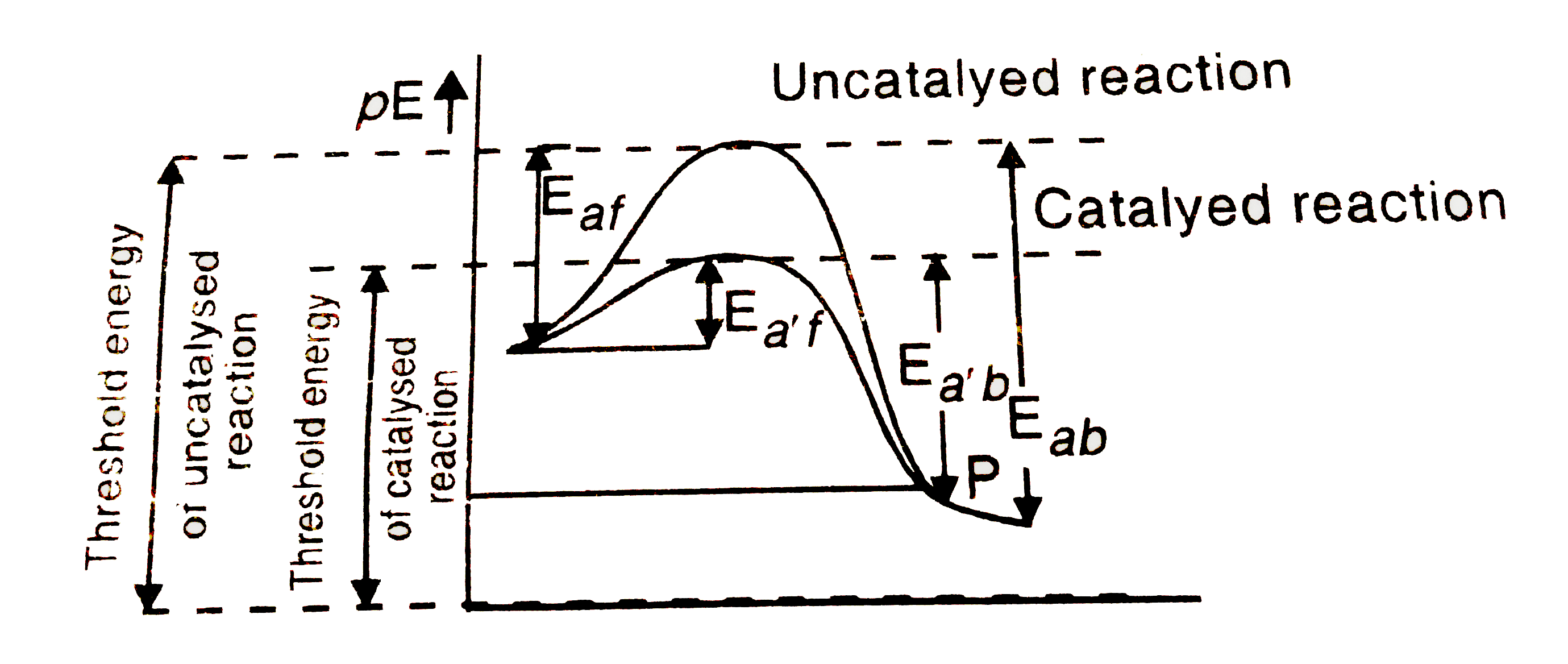
The graph of the lower energy barrier is the energy profile diagram for the catalysed reaction adn of the higher barrier is the energy profile diagram of uncatalysed reaction.
From the graph, it is clear that EafandEab are the activation energy of the respectively. EafandEab are the activation energy of the catalysed forward and backward reaction respectvely
The reaction which occurs by absorption of heat is known as endothermic reaction and by release of heat is known as exothermic reaction
For exothermic reaction, ΔH is negative and for endothermic reaction, ΔH is positive
From Arrhenius equation, we know that k=Ae−Ea/RT where k is rate constant which signifies effective number of collisions. A is known as Arrehnius constant, or maximum rate constant of frequency factor which signifies maximum number of collisions with proper orientation of reacting species per mole per second.
The catalysed reaction occurs at 500 K and the uncatalysed reaction occurs at 800 K in such way so that the rate of catalysed reaction and uncatalysed reaction becomes equal as well as the catalyst lower down the energy barrier by 60 J.
Answer the following questions on the basis of above paragraph
From the above information given inthe compreshension, if the normal energy of the reactant is 50 J and that of the product is 20 J. then what will be the activation energy of the uncatalysed backward reaction ?
View SolutionThe energy profile diagrams are very important tool through which, we predict lot of things, like the amount of activation energy of the catalysed and uncatalysed reaction as well as for the backward reaction and forward reaction. Thershold energy of the catalysed and uncatalysed reaction. The graphs representing the energy profile diagram for catalysed and uncatalysed reactions are given below :
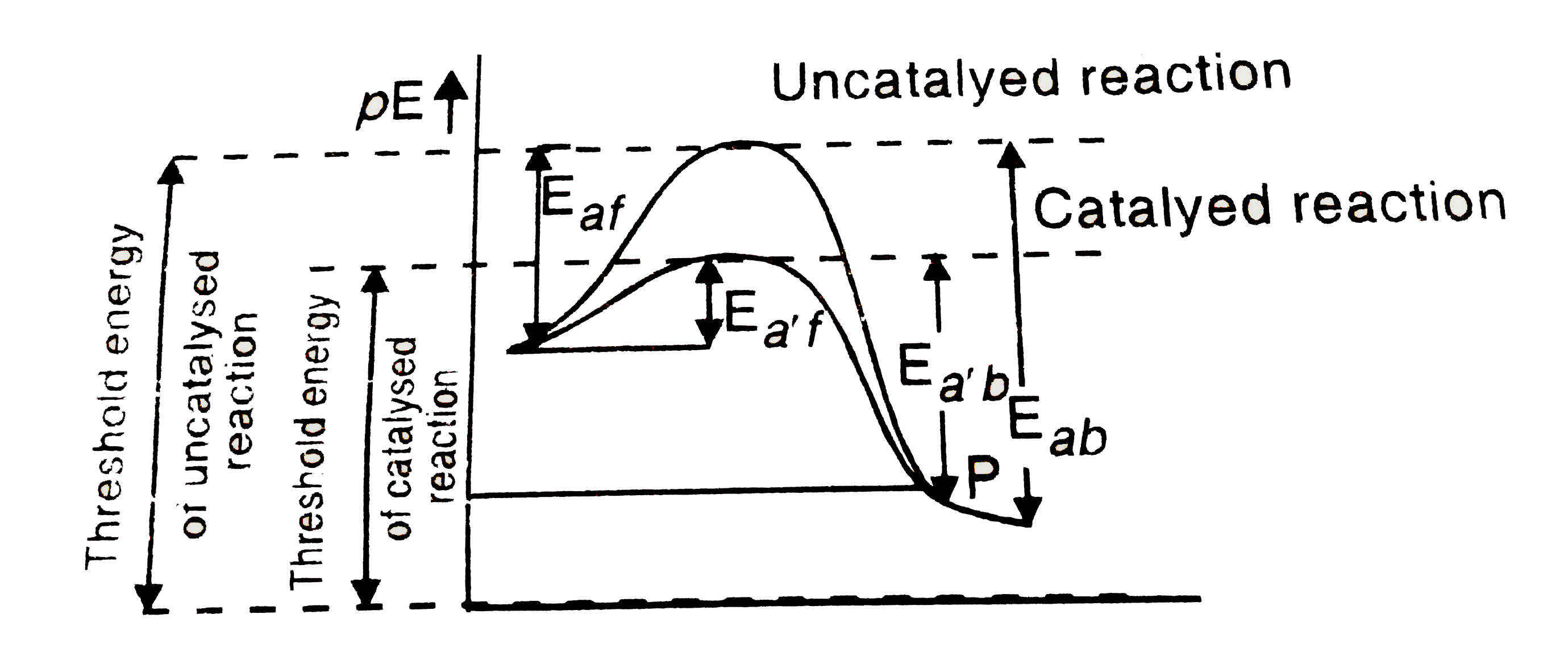
The graph of the lower energy barrier is the energy profile diagram for the catalysed reaction adn of the higher barrier is the energy profile diagram of uncatalysed reaction.
From the graph, it is clear that EafandEab are the activation energy of the respectively. EafandEab are the activation energy of the catalysed forward and backward reaction respectvely
The reaction which occurs by absorption of heat is known as endothermic reaction and by release of heat is known as exothermic reaction
For exothermic reaction, ΔH is negative and for endothermic reaction, ΔH is positive
From Arrhenius equation, we know that k=Ae−Ea/RT where k is rate constant which signifies effective number of collisions. A is known as Arrehnius constant, or maximum rate constant of frequency factor which signifies maximum number of collisions with proper orientation of reacting species per mole per second.
The catalysed reaction occurs at 500 K and the uncatalysed reaction occurs at 800 K in such way so that the rate of catalysed reaction and uncatalysed reaction becomes equal as well as the catalyst lower down the energy barrier by 60 J.
Answer the following questions on the basis of above paragraph
From the given above information what will be the threshold energy for the uncatalysed reaction, if the normal energy of the reactant is 40 J.
View SolutionThe energy profile diagrams are very important tool through which, we predict lot of things, like the amount of activation energy of the catalysed and uncatalysed reaction as well as for the backward reaction and forward reaction. Thershold energy of the catalysed and uncatalysed reaction. The graphs representing the energy profile diagram for catalysed and uncatalysed reactions are given below :
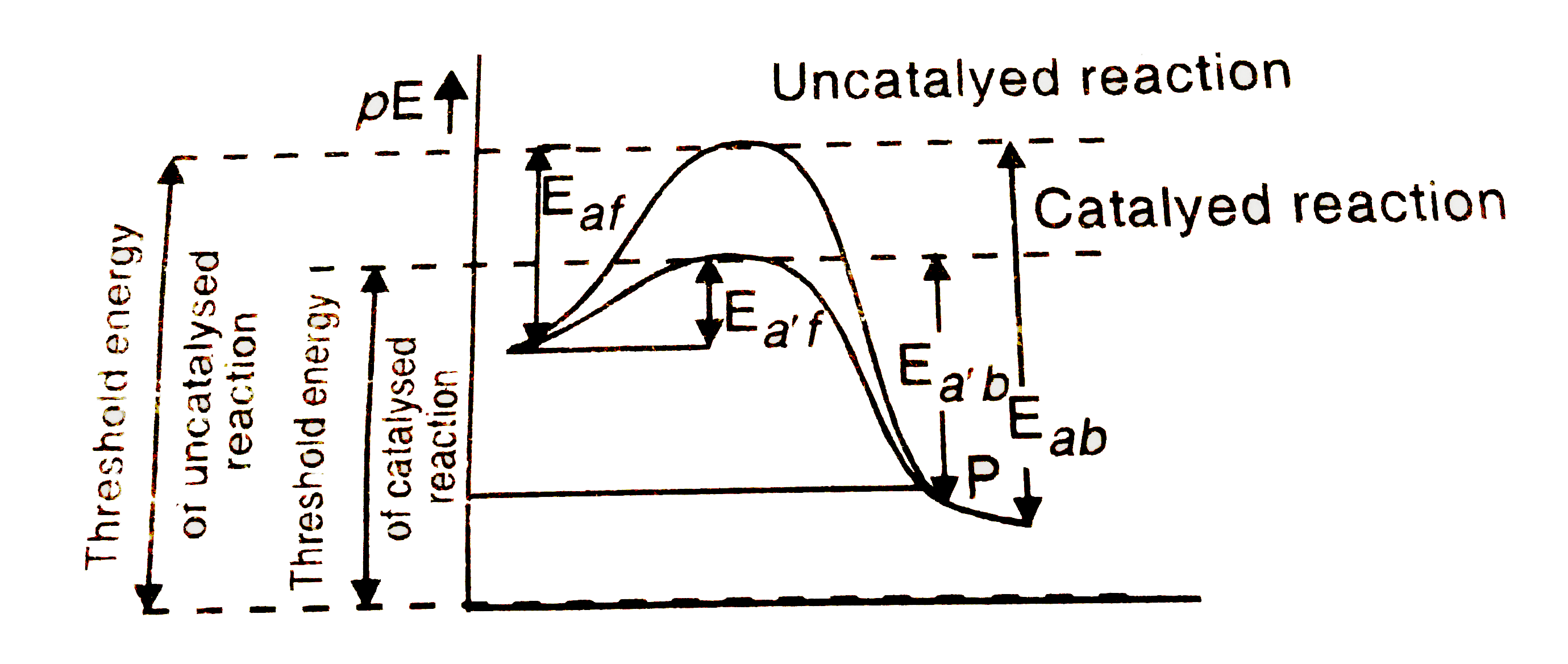
The graph of the lower energy barrier is the energy profile diagram for the catalysed reaction adn of the higher barrier is the energy profile diagram of uncatalysed reaction.
From the graph, it is clear that EafandEab are the activation energy of the respectively. EafandEab are the activation energy of the catalysed forward and backward reaction respectvely
The reaction which occurs by absorption of heat is known as endothermic reaction and by release of heat is known as exothermic reaction
For exothermic reaction, ΔH is negative and for endothermic reaction, ΔH is positive
From Arrhenius equation, we know that k=Ae−Ea/RT where k is rate constant which signifies effective number of collisions. A is known as Arrehnius constant, or maximum rate constant of frequency factor which signifies maximum number of collisions with proper orientation of reacting species per mole per second.
The catalysed reaction occurs at 500 K and the uncatalysed reaction occurs at 800 K in such way so that the rate of catalysed reaction and uncatalysed reaction becomes equal as well as the catalyst lower down the energy barrier by 60 J.
Answer the following questions on the basis of above paragraph
What percentage fraction of the molecule will cross over the energy barrier at 2000 K temperature for 36.848 kJ activation energy ? (Given R = 8 J mol−1K−1)
View SolutionThe energy profile diagrams are very important tool through which, we predict lot of things, like the amount of activation energy of the catalysed and uncatalysed reaction as well as for the backward reaction and forward reaction. Thershold energy of the catalysed and uncatalysed reaction. The graphs representing the energy profile diagram for catalysed and uncatalysed reactions are given below :
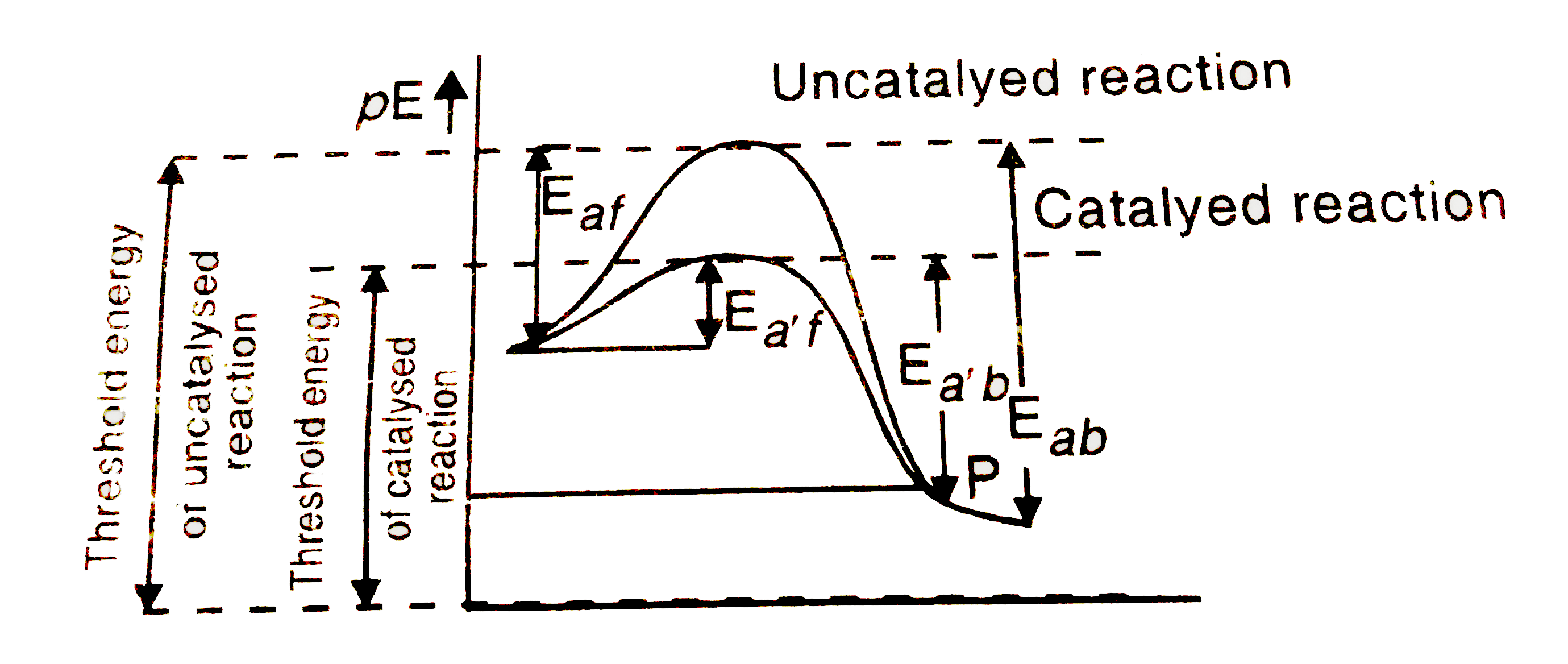
The graph of the lower energy barrier is the energy profile diagram for the catalysed reaction adn of the higher barrier is the energy profile diagram of uncatalysed reaction.
From the graph, it is clear that EafandEab are the activation energy of the respectively. EafandEab are the activation energy of the catalysed forward and backward reaction respectvely
The reaction which occurs by absorption of heat is known as endothermic reaction and by release of heat is known as exothermic reaction
For exothermic reaction, ΔH is negative and for endothermic reaction, ΔH is positive
From Arrhenius equation, we know that k=Ae−Ea/RT where k is rate constant which signifies effective number of collisions. A is known as Arrehnius constant, or maximum rate constant of frequency factor which signifies maximum number of collisions with proper orientation of reacting species per mole per second.
The catalysed reaction occurs at 500 K and the uncatalysed reaction occurs at 800 K in such way so that the rate of catalysed reaction and uncatalysed reaction becomes equal as well as the catalyst lower down the energy barrier by 60 J.
Answer the following questions on the basis of above paragraph
On the basis of question no. 4 what will be the value of threshold energy of the catalysed reactions ?
View SolutionThe energy profile diagrams are very important tool through which, we predict lot of things, like the amount of activation energy of the catalysed and uncatalysed reaction as well as for the backward reaction and forward reaction. Thershold energy of the catalysed and uncatalysed reaction. The graphs representing the energy profile diagram for catalysed and uncatalysed reactions are given below :
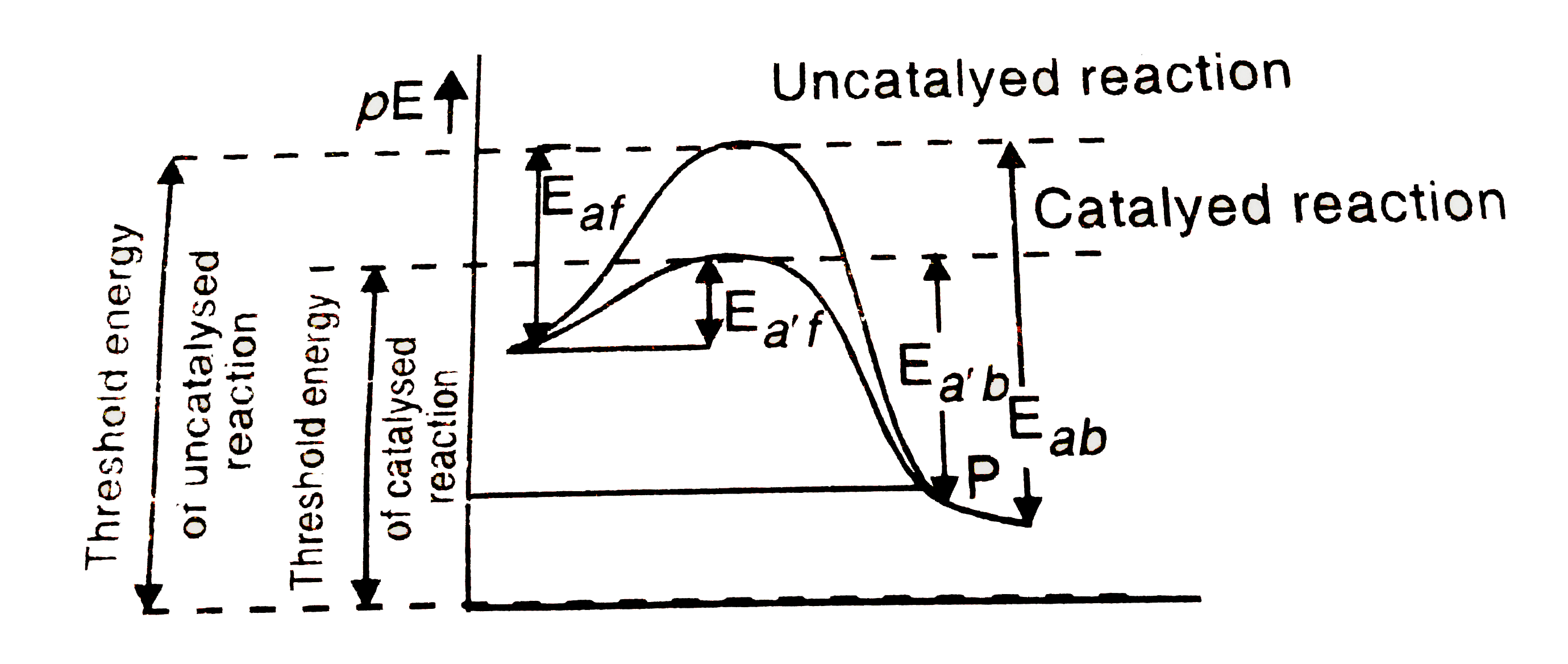
The graph of the lower energy barrier is the energy profile diagram for the catalysed reaction adn of the higher barrier is the energy profile diagram of uncatalysed reaction.
From the graph, it is clear that EafandEab are the activation energy of the respectively. EafandEab are the activation energy of the catalysed forward and backward reaction respectvely
The reaction which occurs by absorption of heat is known as endothermic reaction and by release of heat is known as exothermic reaction
For exothermic reaction, ΔH is negative and for endothermic reaction, ΔH is positive
From Arrhenius equation, we know that k=Ae−Ea/RT where k is rate constant which signifies effective number of collisions. A is known as Arrehnius constant, or maximum rate constant of frequency factor which signifies maximum number of collisions with proper orientation of reacting species per mole per second.
The catalysed reaction occurs at 500 K and the uncatalysed reaction occurs at 800 K in such way so that the rate of catalysed reaction and uncatalysed reaction becomes equal as well as the catalyst lower down the energy barrier by 60 J.
Answer the following questions on the basis of above paragraph
On the basis of question no. 4, what will be the value of threshold energy of the uncatalysed reaction ?
View Solution
