Explain the formation of covalent bond in hydrogen molecule (H2).
The atomic number of hydrogen is 1, hence its electronic configuration is K1.
Thus, hydrogen has one electron in its K shell.
It requires one more electron to fill the K shell.
So, two hydrogen atoms share their electrons to form a molecule of hydrogen, H2.
As a result, each hydrogen atom to attain the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas helium, which has two electrons in its K shell.
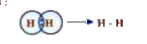
Here, these two valence electrons are depicted by dots or crosses is shown as follows:

The shared pair of electrons forms a single covalent bond between the two hydrogen atoms. A single covalent bond is also represented by a short line between the two atoms, is shown as follows :
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDSBOOK - KUMAR PRAKASHANCHAPTER - CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDSEXERCISE - ACTIVITY
22 Videos
- CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDSBOOK - KUMAR PRAKASHANCHAPTER - CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDSEXERCISE - TEXTUAL EXERCISE
14 Videos
- ACID , BASES AND SALTBOOK - KUMAR PRAKASHANCHAPTER - ACID , BASES AND SALTEXERCISE - Activity
47 Videos
- CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS BOOK - KUMAR PRAKASHANCHAPTER - CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS EXERCISE - PRACTICAL SKILL BASED QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
5 Videos
Similar Questions
Make a list of ten things you have used or consumed since morning.
Compile this list with the lists made by your classmates and then sort the items into the adjascent table.
If there are items which are made up of more than one material, put them into both the relevant columns.
View SolutionEthane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has…
View SolutionState the function of an indicator.
View SolutionWhat would happen if you add zinc coated iron nail into the solution of copper sulphate ? Give reason for your prediction.
View SolutionExplain the formation of H2 molecule on the basis of valance bond theory.
View SolutionThe covalent radius of hydrogen is 0.37A0. The bond length in H2 molecule is
View SolutionExplain formation of covalent bond by the electron structure of hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen molecules.
View Solutionसंयोजकता आबन्ध सिद्धान्त के आधार पर H2 अणु के विरचन (निर्माण) कि व्याख्या कीजिए ।
View SolutionCovalent bond formation in H2 involves ________ overlap.
View SolutionExplain the formation H2 molecule on the basis of Valence Bond theory.
View SolutionExplain the bond formation of hydrogen molecule.
View SolutionExplain the bond formation of hydrogen molecule.
View SolutionExplain the formation of hydrogen molecule (H2) by covalent bond.
View SolutionExplain the formation of covalent bonds in water molecule (H2O).
View SolutionExplain the formation of covalent bonds in ammonia molecule (NH3).
View Solution
