A transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density p floats in a transparent liquid of density 2ρ kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of curvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an object is placed a 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If 'h' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is 32and that of the liquid is 43 .Answer the following questions.
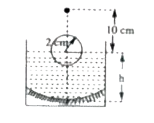
The image formed by transparent solid sphere (measured from the bottom point of the sphere) is nearly equal to
2cm
5cm
6cm
9cm
The correct Answer is:B
Topper's Solved these Questions
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:LECTURE SHEET (EXERCISE-II (LEVEL-II (ADVANCED) MATRIX MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS))
Explore 2 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:LECTURE SHEET (EXERCISE-II (LEVEL-II (ADVANCED) INTEGER TYPE QUESTIONS))
Explore 2 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:LECTURE SHEET (EXERCISE-II (LEVEL-II (ADVANCED) STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS))
Explore 46 Videos
- ELEMENTS OF VECTORSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:ELEMENTS OF VECTORSExercise:QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWERS
Explore 9 Videos
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:PRACTICE EXERCISE
Explore 98 Videos
Similar Questions
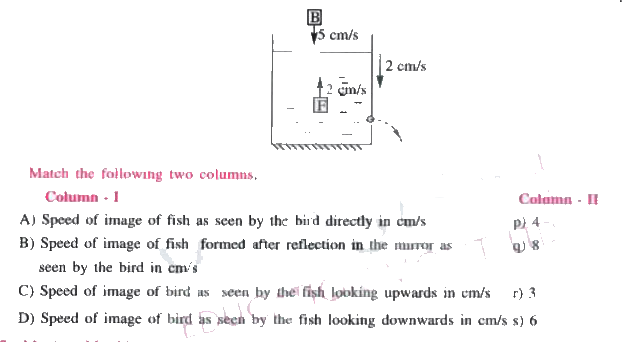
A bird 'B' in air is diving vertically downwards over a water tank with speed 5 cm/s. Base of the tank is silvered. A fish 'F' in the tank is rising vertically upwards along the same line with speed 2 cm/s. Water level is lowered at the rate of 2 cm/s. Take μwater = 4/3
View SolutionA beam of light falls on a glass plate (μ = 3/2) of thickness 6.0 cm at an angle of 60∘. Find the deflection of the beam on passing through the plate. [in cm].
View SolutionLet the x-y plane be the boundary between two transparent media. Medium 1 in Z≥0 has a refractive index of √2 and medium 2 with z < 0 has a refractive index of √3. A ray of light in medium 1 given by the vector →A=6√3i+8√3j−10ˆk is incident on the plane of separation. The angle of refraction in medium 2 is
View SolutionFind the components of vector ¯¯¯A=2ˆi+3ˆj along the directions of ˆi+ˆjandˆi−ˆj
View SolutionA force of 50 N acts on a body of mass 10 kg at rest. Its velocity after 5 seconds if the same force acts, is
View SolutionA transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density rho floats in a transparent liquid of density 2rho kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with radius of curvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it concave mirror as shown in the figure. When an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere C, its final image coincides with it. Find h (as shown in the figure ), the height of the liquid surface in the beaker from the apex of the bottom. Consider the paraxial rays only. The refractive index of the sphere is 3//2 and that of the liquid is 4//3.
View SolutionA small object is enclosed in a transparent solid sphere of radius 8 cm. the object is situated at 2 cm from the centre of the sphere. If its image appears to be at 3.2 cm from the nearest side, then the refractive index of the material of the sphere is
View SolutionA transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density p floats in a transparent liquid of density 2 rho kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of curvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an object is placed a 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If 'h' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is 3/2 and that of the liquid is 4/3 .Answer the following questions. The image formed by the top spherical portion of sphere is (as measured from top of spherical ball)
View SolutionA transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density p floats in a transparent liquid of density 2 rho kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of curvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an object is placed a 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If 'h' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is 3/2 and that of the liquid is 4/3 .Answer the following questions. The value of h is (nearly equal to)
View Solutionकोई वस्तु अवतल दर्पण के सम्मुख 20 सेमी दूरी पर रखी है यदि दर्पण की वक्रता त्रिज्या 20 सेमी हो तो उसका प्रतिबिम्ब बनेगा
View Solutionएक 100 सेमी वक्रता त्रिज्या वाले अवतल दर्पण से 25 सेमी की दूरी पर एक वस्तु रखी है। उसके प्रतिबिम्ब की स्थिति तथा प्रक्रति होगी
View SolutionA transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density rho floats in a transparent liquid of density 2rho kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with radius of curvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it concave mirror as shown in the figure. When an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere C, its final image coincides with it. Find h (as shown in the figure ), the height of the liquid surface in the beaker from the apex of the bottom. Consider the paraxial rays only. The refractive index of the sphere is 3//2 and that of the liquid is 4//3.
View SolutionAn object of height 5 cm is placed 2 m in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm. The size of image is
View SolutionFind the distance of the image, when an object is placed on the principal axis at a distance of 10 cm in front of a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 8 cm.
View SolutionFind the distance of the image when an object is placed on the principal axis at a distance of 10 cm in front of a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 8 cm.
View Solution

