Nuclear charge actually experienced by an electron is termed as effective nuclear charge. The effective nuclear charge Z∗ actuall ydepends on type of shell and orbital in which electron is actually present. The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is
s>p>d>f (for the same value of n)
The phenomenon in which penultimate shell electrons act as screen or sheild in between nucleus and valence shell electrons and thereby reducing nuclear charge is known as shielding effect. the penultimate shell electrons repel the valence shell electron to keep them loosely held with nucleus. it is thus evident that more is the shielding effect, lesser is the effective nuclear charge and lesser is the ionization energy.
Q. Ionzation enegy is not influenced by:
Size of atom
Effective nuclear charge
Electrons present in inner shell
Change in entropy
The correct Answer is:D
To answer the question regarding which factors do not influence ionization energy, we can analyze the factors mentioned in the video transcript and provide a step-by-step explanation.
1. Understanding Ionization Energy:
- Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from the outermost shell of an atom. It is influenced by various factors, including atomic size, effective nuclear charge, and the presence of inner shell electrons.
2. Factors Influencing Ionization Energy:
- Size of Atom: Larger atoms have electrons that are farther from the nucleus, making it easier to remove an electron. Therefore, atomic size does influence ionization energy.
- Effective Nuclear Charge: A higher effective nuclear charge means a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons, making it harder to remove an electron. Thus, effective nuclear charge influences ionization energy.
- Electrons Present in Inner Shell: Inner shell electrons can shield the valence electrons from the full effect of the nuclear charge. This shielding effect reduces the effective nuclear charge felt by the outermost electrons, thus influencing ionization energy.
3. Factor Not Influencing Ionization Energy:
- Entropy: Entropy refers to the degree of randomness or disorder in a system. It is a thermodynamic property that does not directly affect the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. Therefore, entropy does not influence ionization energy.
Conclusion:
From the analysis, we conclude that ionization energy is not influenced by entropy.
- Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from the outermost shell of an atom. It is influenced by various factors, including atomic size, effective nuclear charge, and the presence of inner shell electrons.
- Size of Atom: Larger atoms have electrons that are farther from the nucleus, making it easier to remove an electron. Therefore, atomic size does influence ionization energy.
- Effective Nuclear Charge: A higher effective nuclear charge means a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons, making it harder to remove an electron. Thus, effective nuclear charge influences ionization energy.
- Electrons Present in Inner Shell: Inner shell electrons can shield the valence electrons from the full effect of the nuclear charge. This shielding effect reduces the effective nuclear charge felt by the outermost electrons, thus influencing ionization energy.
- Entropy: Entropy refers to the degree of randomness or disorder in a system. It is a thermodynamic property that does not directly affect the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. Therefore, entropy does not influence ionization energy.
From the analysis, we conclude that ionization energy is not influenced by entropy.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- PERIODIC PROPERTIESBOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - PERIODIC PROPERTIESEXERCISE - ONE OR MORE ANSWERS IN/ARE CORRECT
94 Videos
- PERIODIC PROPERTIESBOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - PERIODIC PROPERTIESEXERCISE - MATCHTHE COLUMN
11 Videos
- PERIODIC PROPERTIESBOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - PERIODIC PROPERTIESEXERCISE - Level 2
101 Videos
- p-BLOCK ELEMENTSBOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - p-BLOCK ELEMENTSEXERCISE - SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS
35 Videos
- QUALITATIVE INORGANIC ANALYSISBOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - QUALITATIVE INORGANIC ANALYSISEXERCISE - SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS
3 Videos
Similar Questions
Assign the position of the element having outer electronic configuration,
(A) ns2np2 (n=6)
(B) (n−1)d2ns2 (n=4)
(C) (n−2)f7(n−1)d−1ns2 (n=6)
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
View Solution
View SolutionA compound contains atom A, B and C . The oxidation number of A is +2, of B is +5 and C is -2. The possible formula of the compound is
View SolutionIn phosphorus acid, If X is number of non-bonding electron pairs. Y is number of σ-bonds and Z is number of π-bonds. Then calculate value of "YxZ-X".
View SolutionFind number of basic radicals among the following cations, which can form soluble complex on adding excess of NH4 solution.
Cd2+(aq.),Pb2+(aq.),Ni2+(aq.),Mn2+(aq.),Zn2+(aq.),Ag+(aq.),Hg2+(aq.),Fe3+(aq.),Mg2+(aq.)
View SolutionNuclear charge actually experienced by an electron is termed as effective nuclear charge The effective nuclear Z∗ actually depends on type of shell and orbital in which electron is actually present. The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate is .s>p>d>f (for the same value of n)
The phenomenon in which penulitmate shell electrons act as screen or shield in between nucleus adn valence shell electrons and there by reducing nuclear charge is known as sheilding effect. The penultimate shell electrons repel the valence shell electron to keep them loosely held with nucleus . It is thus evident that more is the shielding effect, lesser is the effective nuclear charge and lesser is the ionizatio energy.
Which of the following is not concerned to effective nuclear charge?
View SolutionNuclear charge actually experienced by an electron is termed as effective nuclear charge The effective nuclear Z∗ actually depends on type of shell and orbital in which electron is actually present. The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate is .s>p>d>f (for the same value of n)
The phenomenon in which penulitmate shell electrons act as screen or shield in between nucleus adn valence shell electrons and there by reducing nuclear charge is known as sheilding effect. The penultimate shell electrons repel the valence shell electron to keep them loosely held with nucleus . It is thus evident that more is the shielding effect, lesser is the effective nuclear charge and lesser is the ionizatio energy.
Ionization energy is not influenced by :
View SolutionAccording to I.C slater effective nuclear charge, Z∗, due to screening, is not exactly equal to the actual nuclear charge Z of the nucleus of the atom. Z∗ depends on the type of orbitals in which the electron is housed, and on the ability of other electrons in more penetrating orbitals to screen the electron in question from the nucleus.
The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is s>p>f . The effective nuclear charge Z∗ due to screening is given by Z∗=Z−σ, where Z is the atomic atomic number and σ is the slater screening constant values 0<σ<Z
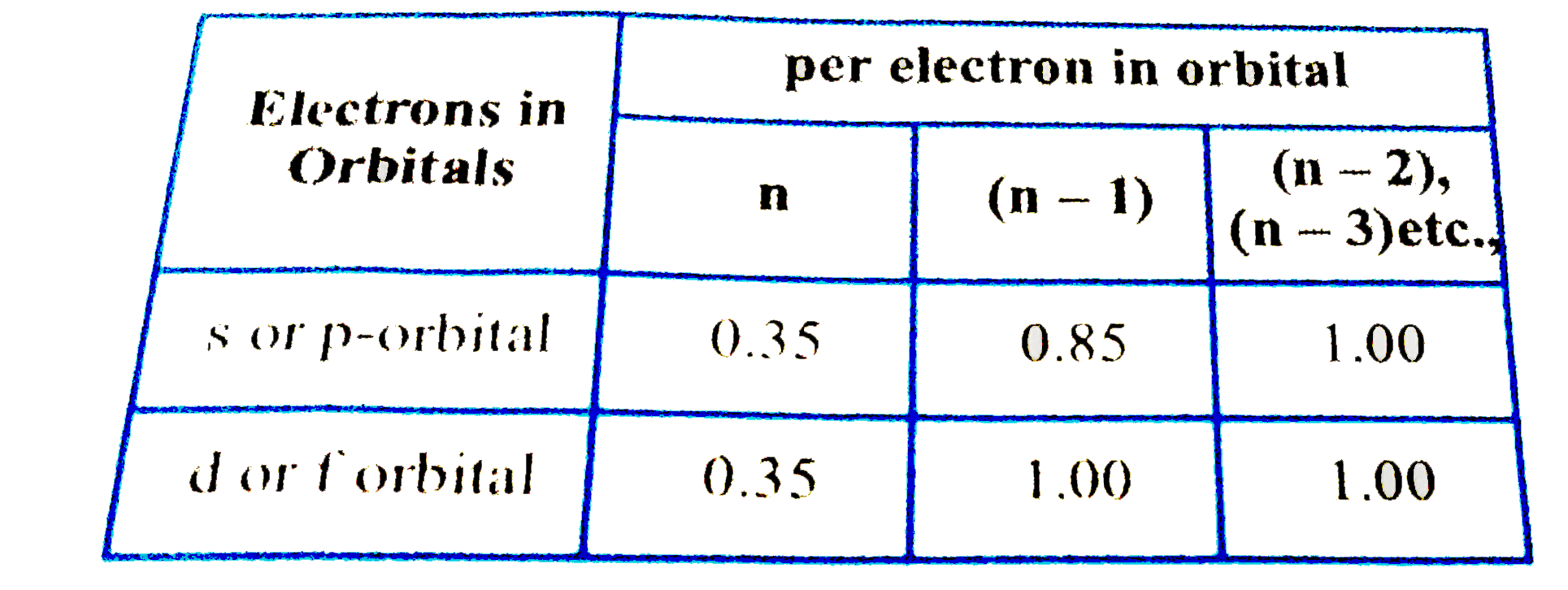
Screening effect of one electron in the outermost orbitals, is not considered in calculate of σ.
What is the value of Z∗ for Rb(37) ?
View SolutionAccording to I.C slater effective nuclear charge, Z∗, due to screening, is not exactly equal to the actual nuclear charge Z of the nucleus of the atom. Z∗ depends on the type of orbitals in which the electron is housed, and on the ability of other electrons in more penetrating orbitals to screen the electron in question from the nucleus.
The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is s>p>f . The effective nuclear charge Z∗ due to screening is given by Z∗=Z−σ, where Z is the atomic atomic number and σ is the slater screening constant values 0<σ<Z
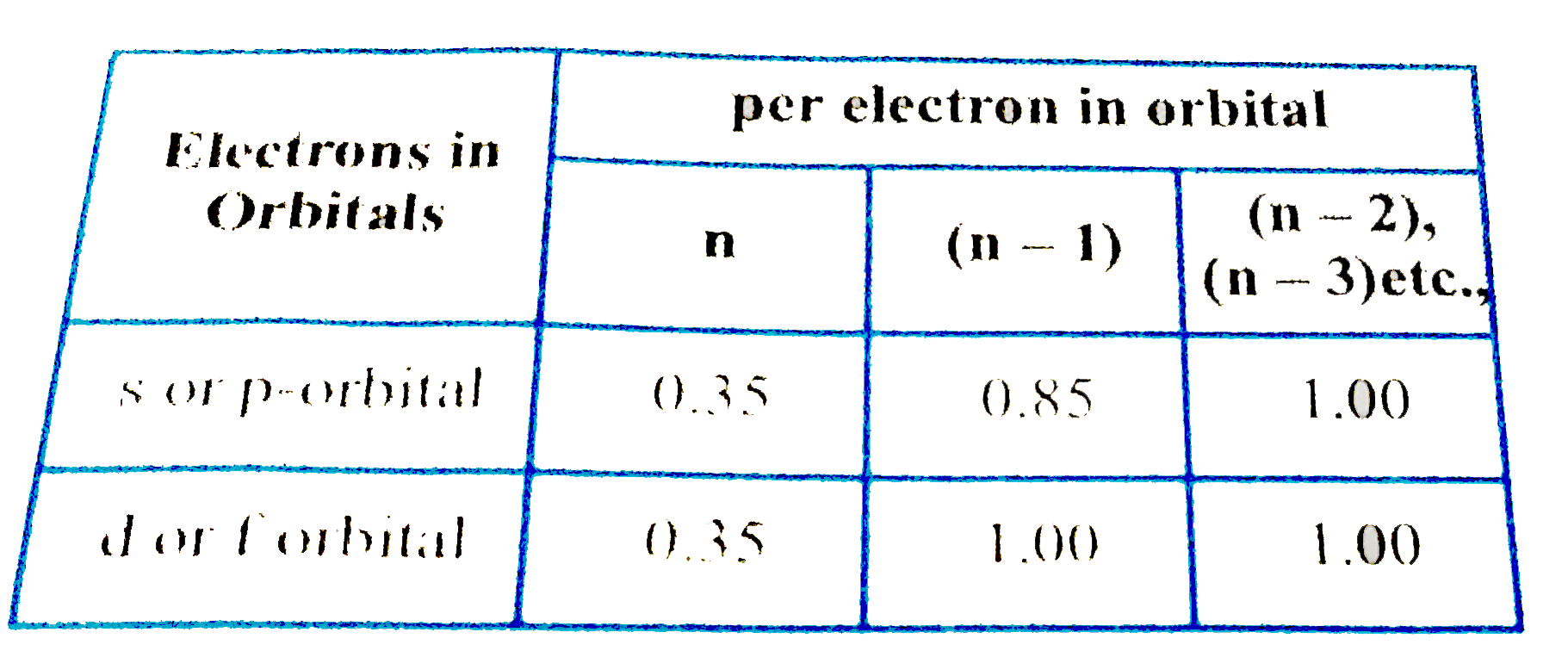
Screening effect of one electron in the outermost orbitals, is not considered in calculate of σ.
what is Z∗ for Cu(29) ?
View SolutionNuclear charge actually experienced by an electron is termed as effective nuclear charge The effective nuclear Z^(**) actually depends on type of shell and orbital in which electron is actually present. The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate is . s gt p gt d gt f (for the same value of n) The phenomenon in which penulitmate shell electrons act as screen or shield in between nucleus adn valence shell electrons and there by reducing nuclear charge is known as sheilding effect. The penultimate shell electrons repel the valence shell electron to keep them loosely held with nucleus . It is thus evident that more is the shielding effect, lesser is the effective nuclear charge and lesser is the ionizatio energy. In which of the following valence electron experience maximum effective nuclear charge?
View SolutionAccording to I.C slater effective nuclear charge, Z^(**) , due to screening, is not exactly equal to the actual nuclear charge Z of the nucleus of the atom. Z^(**) depends on the type of orbitals in which the electron is housed, and on the ability of other electrons in more penetrating orbitals to screen the electron in question from the nucleus. The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is s gt p gt f . The effective nuclear charge Z^(**) due to screening is given by Z^(**)=Z-sigma , where Z is the atomic atomic number and sigma is the slater screening constant values 0 lt sigma lt Z Screening effect of one electron in the outermost orbitals, is not considered in calculate of sigma . What is the value of Z^(**) for Rb(37) ?
View SolutionAccording to I.C slater effective nuclear charge, Z∗, due to screening, is not exactly equal to the actual nuclear charge Z of the nucleus of the atom. Z∗ depends on the type of orbitals in which the electron is housed, and on the ability of other electrons in more penetrating orbitals to screen the electron in question from the nucleus.
The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is s>p>f . The effective nuclear charge Z∗ due to screening is given by Z∗=Z−σ, where Z is the atomic atomic number and σ is the slater screening constant values 0<σ<Z
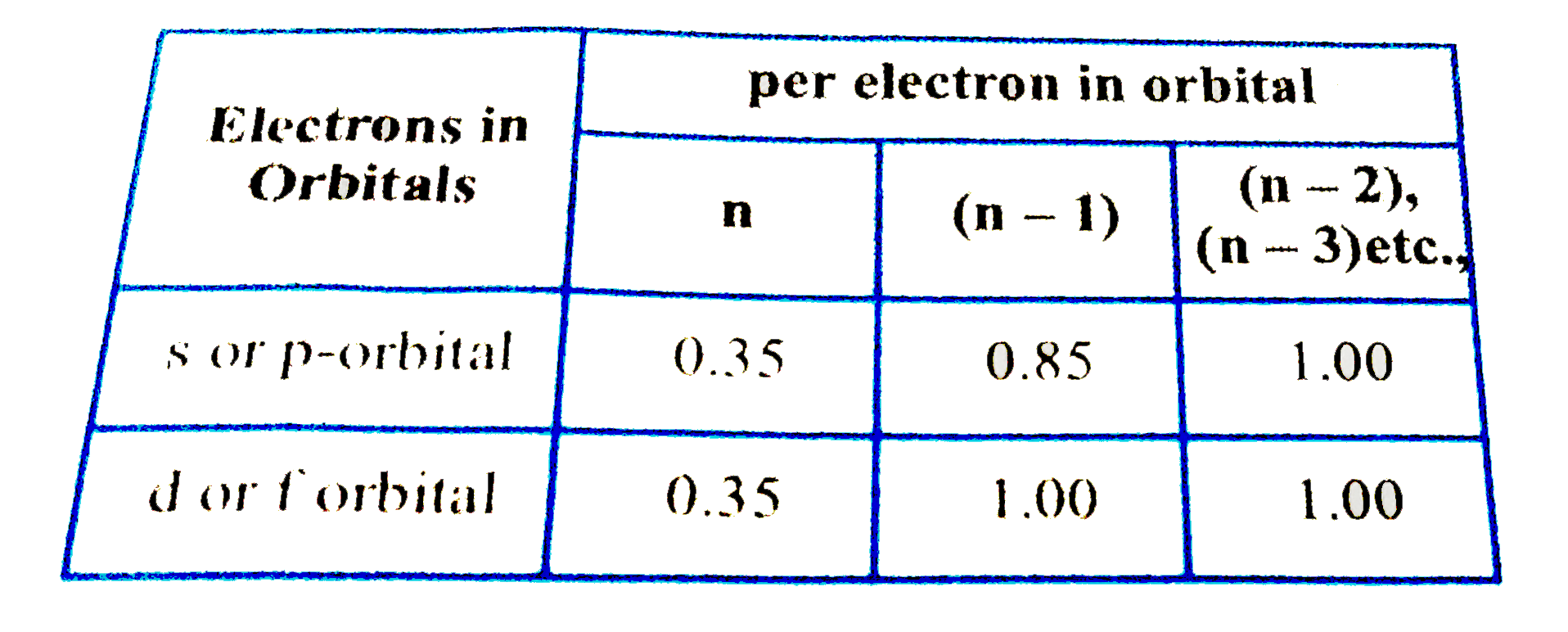
Screening effect of one electron in the outermost orbitals, is not considered in calculate of σ.
In which of the following cases the concept of Z∗ is applicable?
View SolutionNuclear charge actually experienced by an electron is termed as effective nuclear charge. The effective nuclear charge Z∗ actuall ydepends on type of shell and orbital in which electron is actually present. The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is
s>p>d>f (for the same value of n)
The phenomenon in which penultimate shell electrons act as screen or sheild in between nucleus and valence shell electrons and thereby reducing nuclear charge is known as shielding effect. the penultimate shell electrons repel the valence shell electron to keep them loosely held with nucleus. it is thus evident that more is the shielding effect, lesser is the effective nuclear charge and lesser is the ionization energy.
Q. Which of the following valence electron experience maximum effective nuclear charge?
View SolutionNuclear charge actually experienced by an electron is termed as effective nuclear charge. The effective nuclear charge Z∗ actuall ydepends on type of shell and orbital in which electron is actually present. The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is
s>p>d>f (for the same value of n)
The phenomenon in which penultimate shell electrons act as screen or sheild in between nucleus and valence shell electrons and thereby reducing nuclear charge is known as shielding effect. the penultimate shell electrons repel the valence shell electron to keep them loosely held with nucleus. it is thus evident that more is the shielding effect, lesser is the effective nuclear charge and lesser is the ionization energy.
Q. Ionzation enegy is not influenced by:
View SolutionNuclear charge actually experienced by an electron is termed as effective nuclear charge. The effective nuclear charge Z^(**) actuall ydepends on type of shell and orbital in which electron is actually present. The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is s gt p gt d gt f (for the same value of n) The phenomenon in which penultimate shell electrons act as screen or sheild in between nucleus and valence shell electrons and thereby reducing nuclear charge is known as shielding effect. the penultimate shell electrons repel the valence shell electron to keep them loosely held with nucleus. it is thus evident that more is the shielding effect, lesser is the effective nuclear charge and lesser is the ionization energy. Q. Which of the following valence electron experience maximum effective nuclear charge?
View SolutionNuclear charge actually experienced by an electron is termed as effective nuclear charge. The effective nuclear charge Z∗ actuall ydepends on type of shell and orbital in which electron is actually present. The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is
s>p>d>f (for the same value of n)
The phenomenon in which penultimate shell electrons act as screen or sheild in between nucleus and valence shell electrons and thereby reducing nuclear charge is known as shielding effect. the penultimate shell electrons repel the valence shell electron to keep them loosely held with nucleus. it is thus evident that more is the shielding effect, lesser is the effective nuclear charge and lesser is the ionization energy.
Q. Which of the following is not concerned to effective nuclear charge?
View Solution

