CuSO4+2KCN→CuCN⏐↓+(CN)2↑⏐+K2SO4
For precipitate formation reaction
For precipitate dissolution reaction
For precipitate exchange reaction
For no reaction
The correct Answer is:a
To analyze the reaction given in the question, we will break down the steps involved in determining the type of reaction that occurs when copper(II) sulfate reacts with potassium cyanide.
1. Identify the Reactants and Products:
- The reactants are copper(II) sulfate (CuSO₄) and potassium cyanide (KCN).
- The products are copper(I) cyanide (CuCN), cyanogen (CN₂), and potassium sulfate (K₂SO₄).
2. Write the Balanced Chemical Equation:
- The balanced equation is:
CuSO4+2KCN→CuCN+CN2+K2SO4
3. Determine the Formation of Precipitate:
- A precipitate is an insoluble solid that forms when two solutions are mixed.
- In this reaction, CuCN is formed, which is a solid precipitate. The downward arrow indicates that it is a precipitate.
4. Identify the Type of Reaction:
- Since a precipitate (CuCN) is formed from the reactants (CuSO₄ and KCN), this reaction is classified as a precipitation formation reaction.
- The other options (precipitation dissolution, precipitation exchange, and no reaction) do not apply here because:
- There is no initial precipitate in the reactants.
- There is no dissolution of a solid.
- There is no exchange of precipitates.
5. Conclusion:
- The correct classification of the reaction is a precipitation formation reaction.
Final Answer:
The reaction CuSO4+2KCN→CuCN+CN2+K2SO4 is a precipitation formation reaction.
- The reactants are copper(II) sulfate (CuSO₄) and potassium cyanide (KCN).
- The products are copper(I) cyanide (CuCN), cyanogen (CN₂), and potassium sulfate (K₂SO₄).
- The balanced equation is:
CuSO4+2KCN→CuCN+CN2+K2SO4
- A precipitate is an insoluble solid that forms when two solutions are mixed.
- In this reaction, CuCN is formed, which is a solid precipitate. The downward arrow indicates that it is a precipitate.
- Since a precipitate (CuCN) is formed from the reactants (CuSO₄ and KCN), this reaction is classified as a precipitation formation reaction.
- The other options (precipitation dissolution, precipitation exchange, and no reaction) do not apply here because:
- There is no initial precipitate in the reactants.
- There is no dissolution of a solid.
- There is no exchange of precipitates.
- The correct classification of the reaction is a precipitation formation reaction.
The reaction CuSO4+2KCN→CuCN+CN2+K2SO4 is a precipitation formation reaction.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- TYPES OF REACTIONSBook:VK JAISWAL ENGLISHChapter:TYPES OF REACTIONSExercise:LEVEL 2
Explore 194 Videos
- TYPES OF REACTIONSBook:VK JAISWAL ENGLISHChapter:TYPES OF REACTIONSExercise:LEVEL 3
Explore 36 Videos
- s-BLOCK ELEMENTSBook:VK JAISWAL ENGLISHChapter:s-BLOCK ELEMENTSExercise:SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS
Explore 2 Videos
Similar Questions
Which of the following metal nitrate produces gaseous product when reacts with KCN solution?
View Solution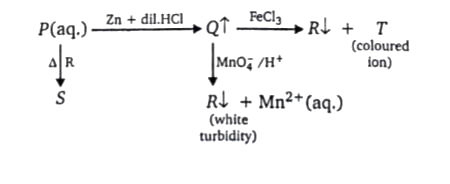
Q. Species P and S are respectively:
View Solution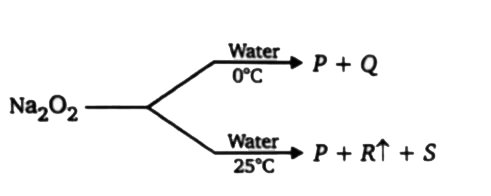
Calculate sum of bond order between same bonded atoms in Q and R compounds.
View SolutionCuSO4+2KCN→CuCN⏐↓+(CN)2↑⏐+K2SO4
View SolutionCd(CN)2⏐⏐↓+2KCN→K2[Cd(CN)4]
View SolutionCuSO4+2KI→CuI⏐⏐ ⏐↓+12I2+K2SO4
View SolutionBaSO_(3)darr+H_(2)SO_(4) to BaSO_(4) darr+SO_(2)uarr+H_(2)O
View SolutionK2[Cd(CN)4]+H2S→CdS⏐⏐↓+2KCN+2HCN
View SolutionCd(CN)2⏐⏐↓+2KCN→K2[Cd(CN)4]
View SolutionBaSO3↓+H2SO4→BaSO4↓+SO2↑+H2O
View SolutionK2[Cd(CN)4]+H2S→CdS⏐⏐↓+2KCN+2HCN
View Solution2KI+CuSO4→CuI⏐⏐ ⏐↓+12I2+K2SO4
View SolutionCuSO4+2KCN→CuCN⏐↓+(CN)2↑⏐+K2SO4
View SolutionCd(CN)2⏐⏐↓+2KCN→K2[Cd(CN)4]
View SolutionCuSO4+2KI→CuI⏐⏐ ⏐↓+12I2+K2SO4
View Solution
