For an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P1,V1,T1 to a final state P2,V2,T1 is shown in the given figure.
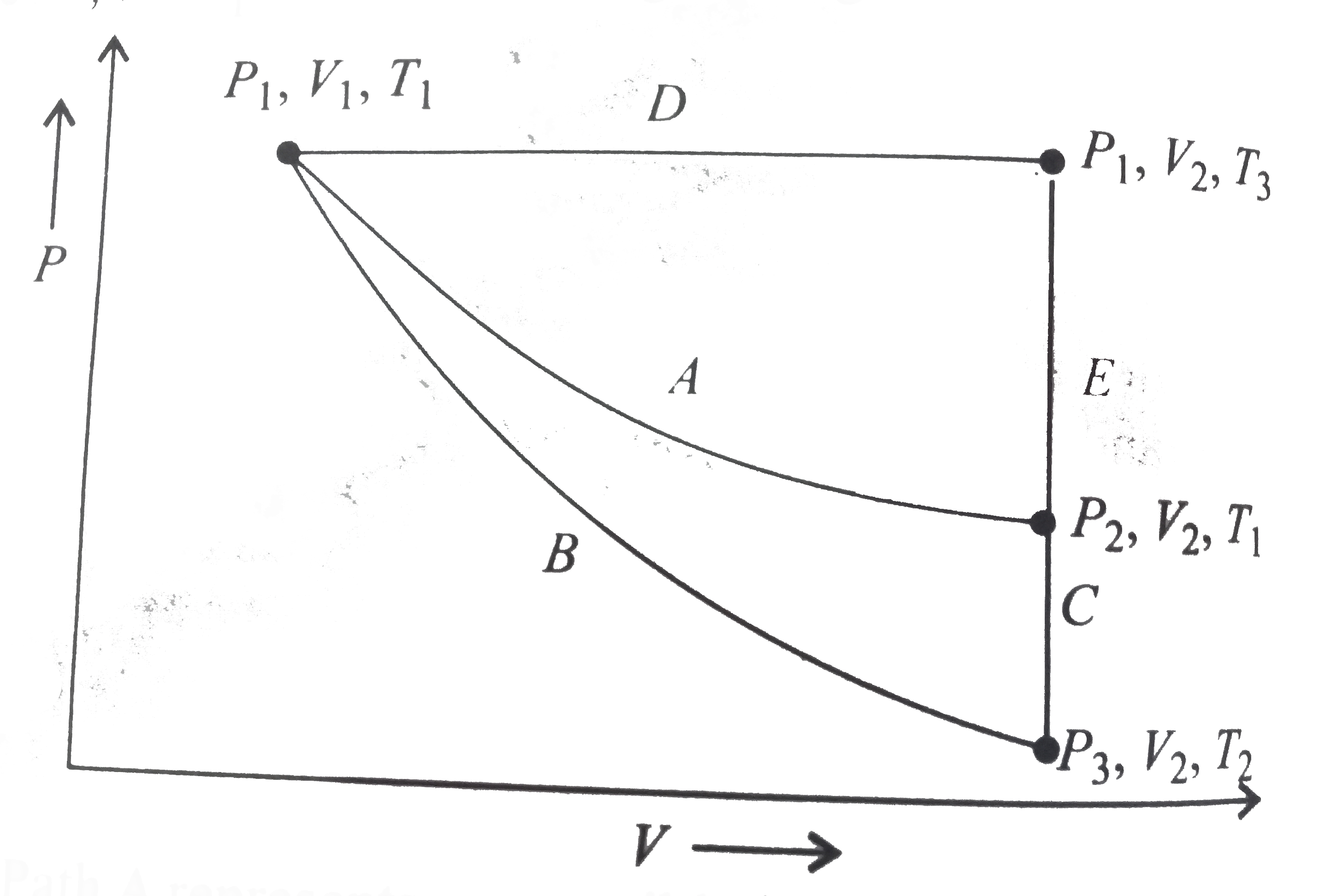
Path Arepresents a reversible isothermal expansion form P1,V1 to P2,V2, Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1→P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C)from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2,T1. Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P1(D) from P1,V1,T1 to P1,V2,T3 followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V2(E) from P1,V2,T3→P2,V2,T1.
What is ΔS for path (D+E)?
−P(V2−V1)
−nRInV2V1
+P(V2−V1)
nRInV2V1
For path (D+E)
ΔS=nRInV2V1
Topper's Solved these Questions
- THERMODYNAMICSBOOK - CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHCHAPTER - THERMODYNAMICSEXERCISE - Paragraph for Problem
1 Video
- THERMODYNAMICSBOOK - CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHCHAPTER - THERMODYNAMICSEXERCISE - Exercises (Multiple Correct)
50 Videos
- THERMODYNAMICSBOOK - CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHCHAPTER - THERMODYNAMICSEXERCISE - Exercises (Subjective)
68 Videos
- STOICHIOMETRYBOOK - CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHCHAPTER - STOICHIOMETRYEXERCISE - Archives Subjective
33 Videos
Similar Questions
Three moles of CO2 gas expands isothermally (in thermal contact with the surroundings, temperature =15.0∘C) against a fixed external pressure of 1.00 bar. The initial and final volumes of the gas are 10.0L and 30.0L, respectively. ltbr> Change in entropy of the universe is
View SolutionSelect the correct statement
View SolutionEthylene on combustion gives carbon dioxide and water. Its heat of combustion is 1410.0kJmol−1. If the heat of formation of CO2 and H2O are 393.3kJ and 286.2kJ, respectively. Calculate the heat of formation of ethylene.
View SolutionIn the analysis of 0.1 of sample of feldspar, 0.118 g of mixture of NaCl and KCl is obtained which on treatment with AgNO3 gives 0.2451 of AgCl. Calculate the precentage of Na2O and K2O in feldspar.
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P1,V1,T1 to a final state P2,V2,T1 is shown in the given figure.
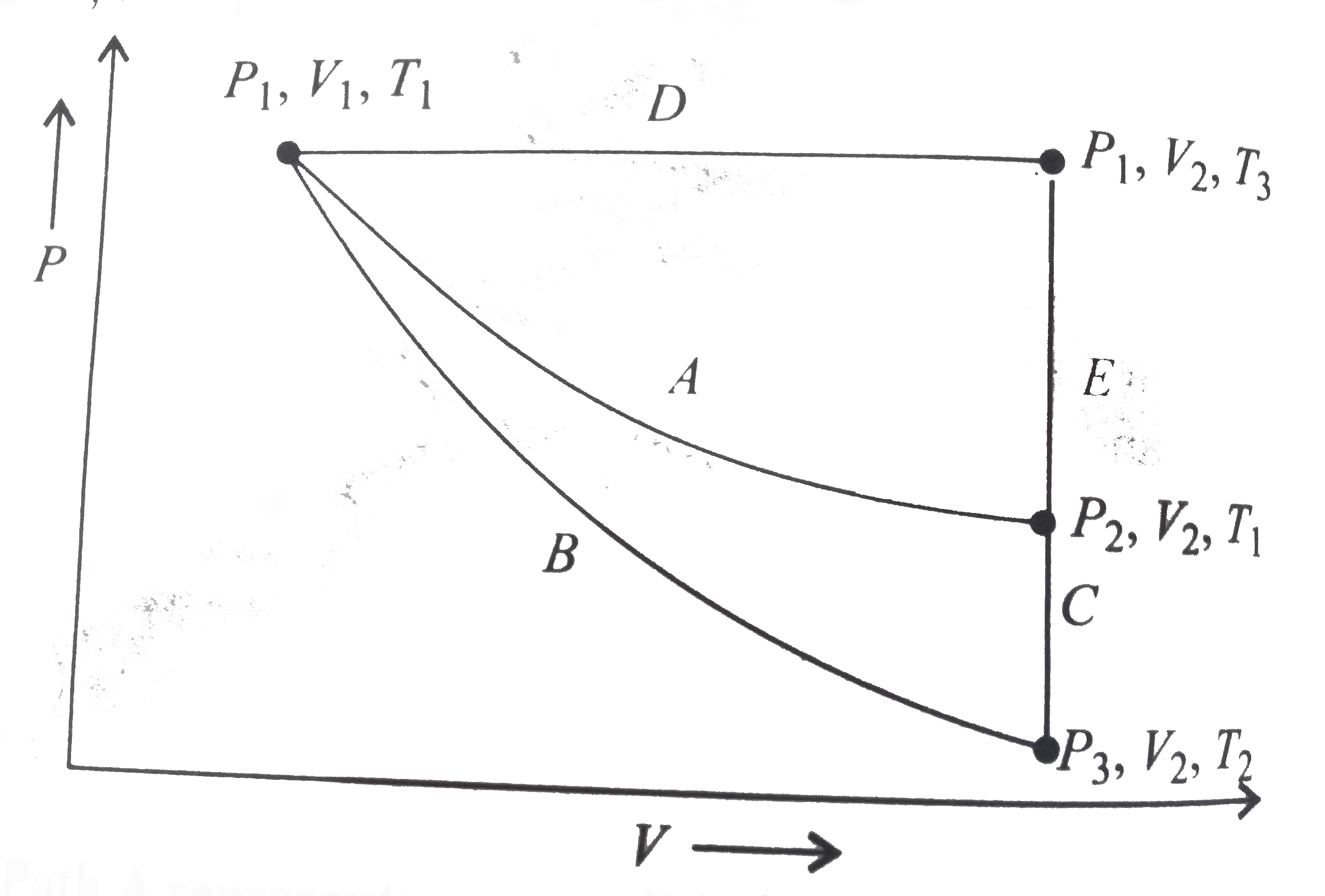
Path Arepresents a reversible isothermal expansion form P1,V1 to P2,V2, Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1→P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C)from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2,T1. Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P1(D) from P1,V1,T1 to P1,V2,T3 followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V2(E) from P1,V2,T3→P2,V2,T1.
What is qrev, for path (A)?
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P_(1), V_(1), T_(1) to a final state P_(2), V_(2),T_(1) is shown in the given figure. Path A represents a reversible isothermal expansion form P_(1),V_(1) to P_(2),V_(2) , Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1)to P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C) from P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) to P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) . Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P_(1)(D) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) to P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V_(2)(E) from P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) to P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) . What is q_(rev) , for path (B +C) ?
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P1,V1,T1 to a final state P2,V2,T1 is shown in the given figure.
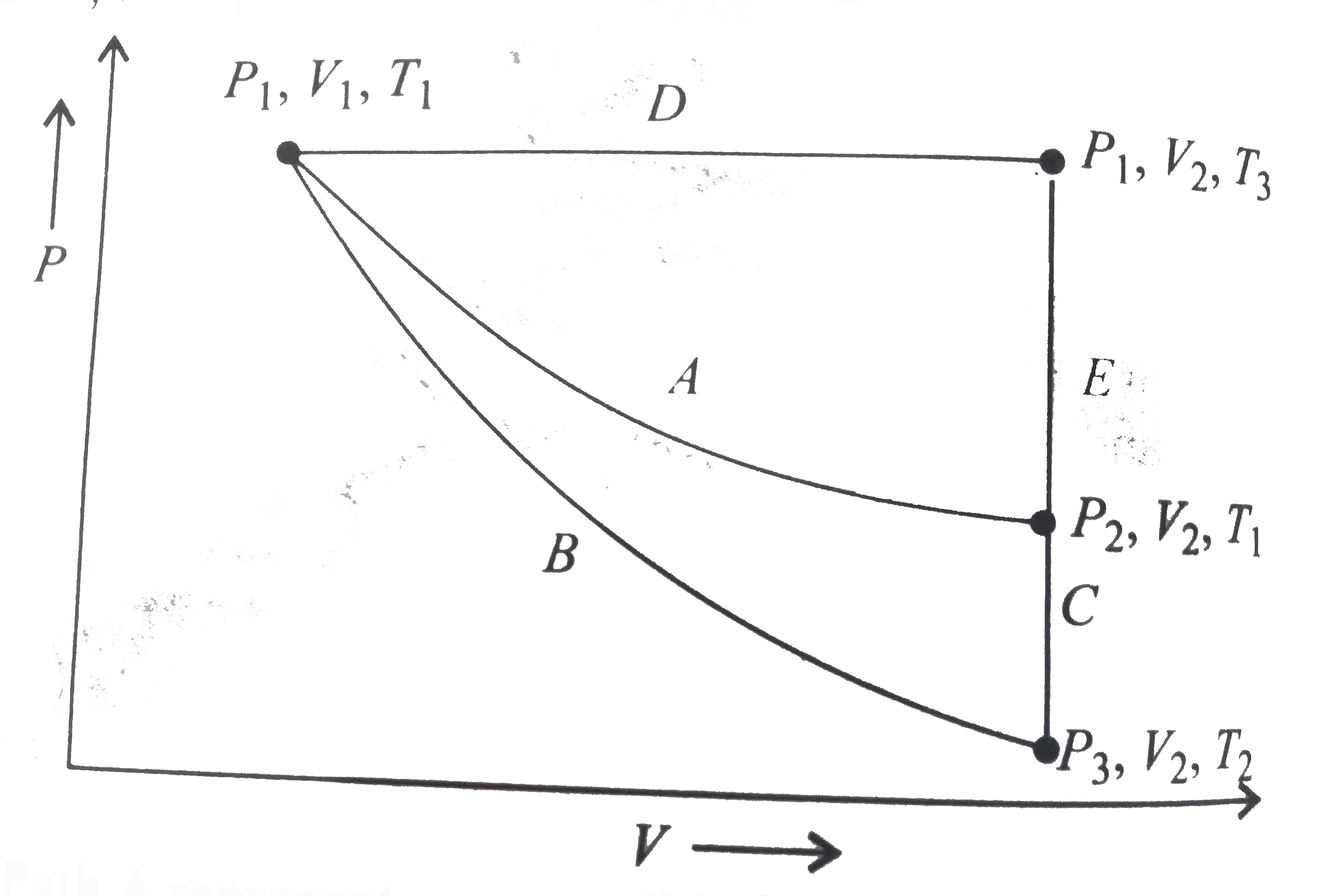
Path Arepresents a reversible isothermal expansion form P1,V1 to P2,V2, Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1→P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C)from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2,T1. Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P1(D) from P1,V1,T1 to P1,V2,T3 followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V2(E) from P1,V2,T3→P2,V2,T1.
What is ΔS for path A?
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P1,V1,T1 to a final state P2,V2,T1 is shown in the given figure.
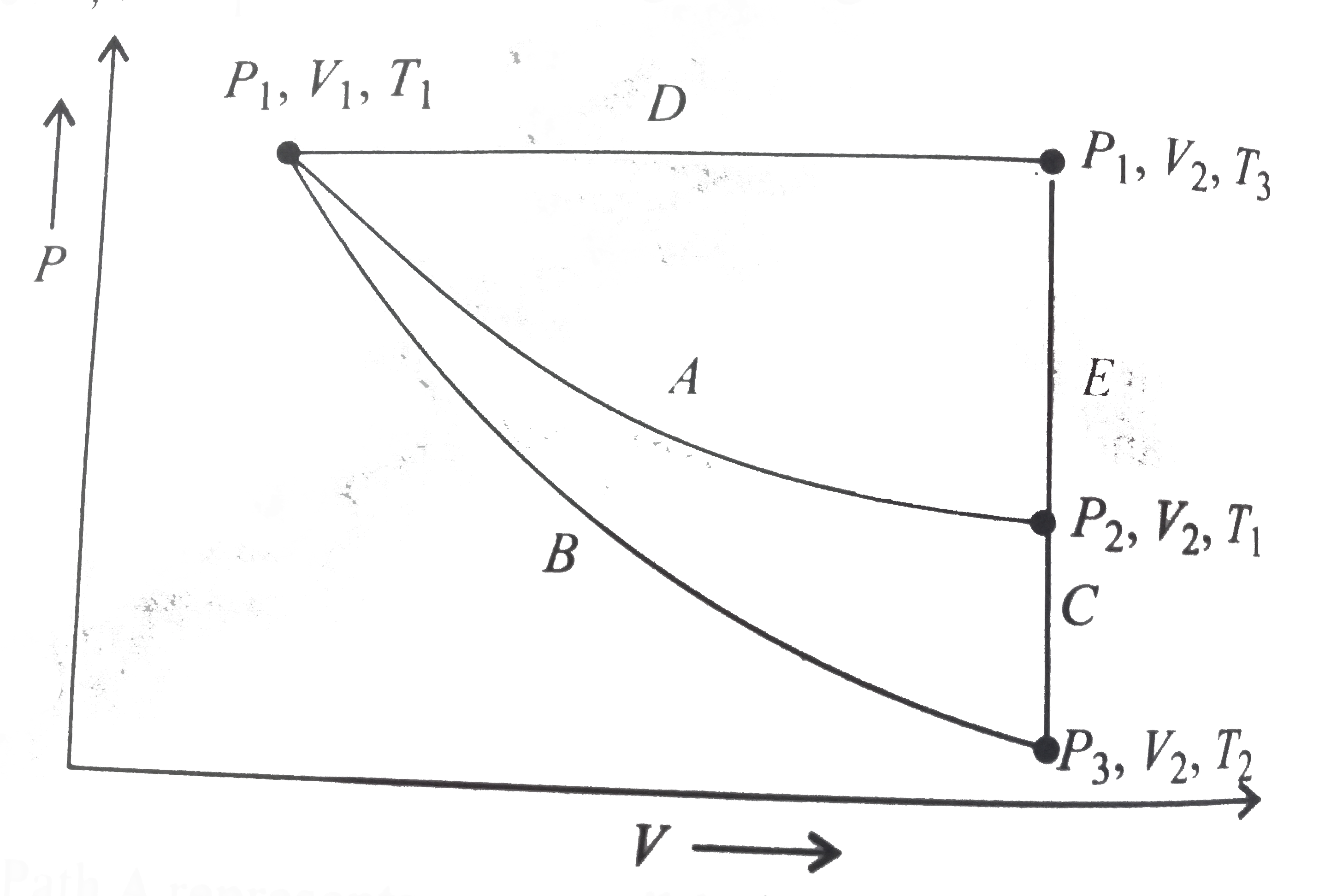
Path Arepresents a reversible isothermal expansion form P1,V1 to P2,V2, Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1→P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C)from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2,T1. Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P1(D) from P1,V1,T1 to P1,V2,T3 followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V2(E) from P1,V2,T3→P2,V2,T1.
What is qrev, for path (D+E)?
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P_(1), V_(1), T_(1) to a final state P_(2), V_(2),T_(1) is shown in the given figure. Path A represents a reversible isothermal expansion form P_(1),V_(1) to P_(2),V_(2) , Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1)to P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C) from P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) to P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) . Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P_(1)(D) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) to P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V_(2)(E) from P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) to P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) . What is DeltaS for path (D +E) ?
View SolutionAn ideal gasa undergoes through folowing cyclic procees. 1-2 : Reversible adialbatic comparession from P_(1)V_(1)T_(1)"to"P_(2)V_(2)T_(2) 2-3 : Reversible isochoric heating from P_(2)V_(2)T_(2)" to " P_(3)V_(3)T_(3) 3-4 Reversible adialbatic expansion from P_(3)V_(3)T_(3)" to " P_(4)V_(4)T_(4) 4-1 Reversible isochoric cooling from P_(4)V_(4)T_(4)" to " P_(1)V_(1)T_(1) Eefficiencyof the cycle is :
View SolutionFor an ideal monoatomic gas, an illustration of three different paths A,(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) to a final state P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) is shown in the given figure . Path A represents a reversible isothermal from P_(1)V_(1)" to "P_(2),V_(2) , path (B+C) represent a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1)" to " P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) followed by reversible heating of the gas at constant volume (C) from P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) " to " P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) . Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P_(1)(D) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) " to "P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V_(2)(E) form P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) " to "P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) What is q_("rev") for path (A)?
View SolutionFor an ideal monoatomic gas, an illustration of three different paths A,(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) to a final state P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) is shown in the given figure . Path A represents a reversible isothermal from P_(1)V_(1)" to "P_(2),V_(2) , path (B+C) represent a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1)" to " P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) followed by reversible heating of the gas at constant volume (C) from P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) " to " P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) . Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P_(1)(D) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) " to "P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V_(2)(E) form P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) " to "P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) What is DeltaS for path (A)?
View SolutionFor an ideal monoatomic gas, an illustration of three different paths A,(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P1,V1,T1 to a final state P2,V2,T1 is shown in the given figure .
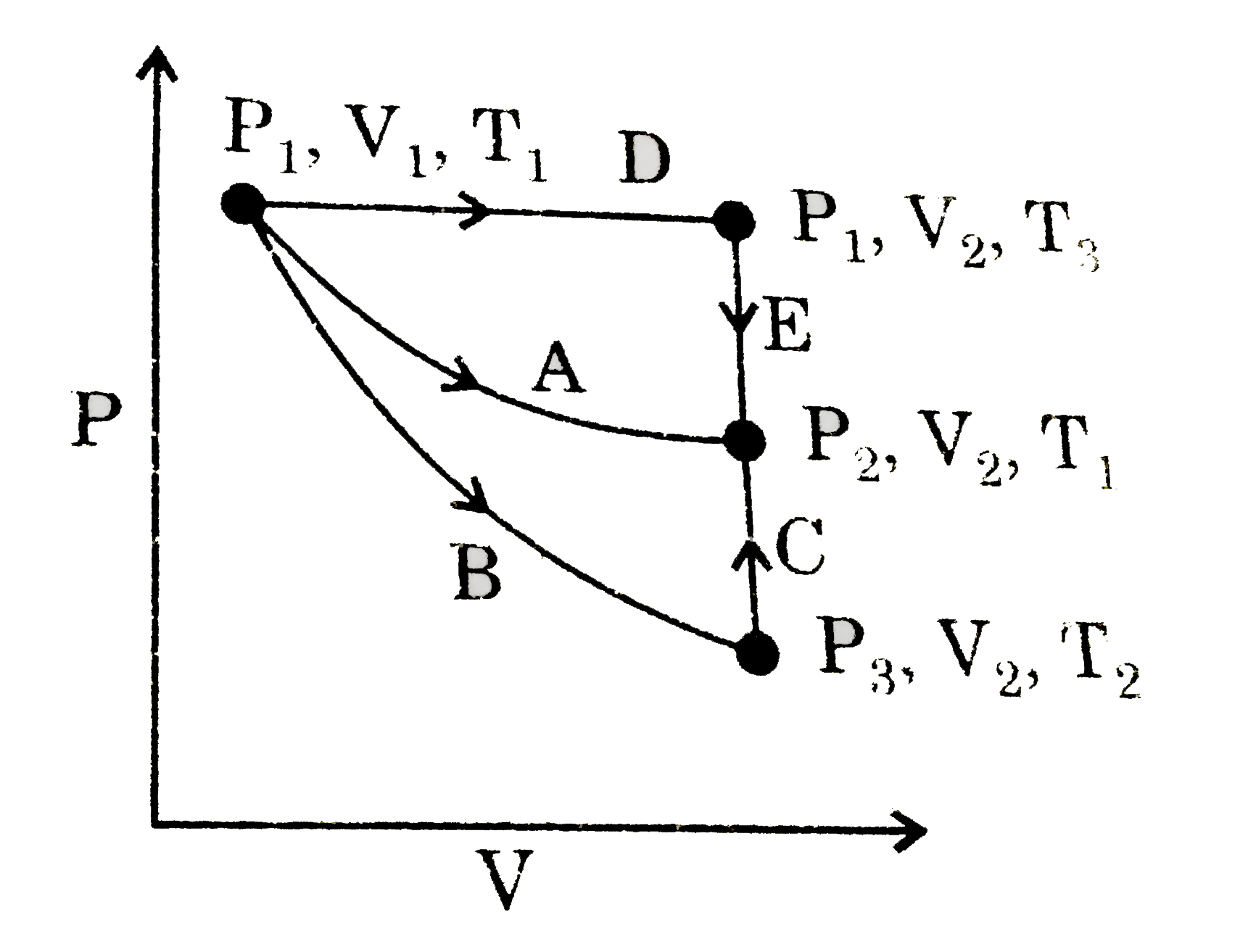
Path A represents a reversible isothermal from P1V1 to P2,V2, path (B+C) represent a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1 to P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating of the gas at constant volume (C) from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2,T1. Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P1(D) from P1,V1,T1 to P1,V2,T3 followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V2(E) form P1,V2,T3 to P2,V2,T1
What is ΔS for (D+E)?
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustration of the different paths, A (B+C) and (D+E) from an intial state P1,V1,T1 to a final state P2,V2,T1 as shown in the given figure.
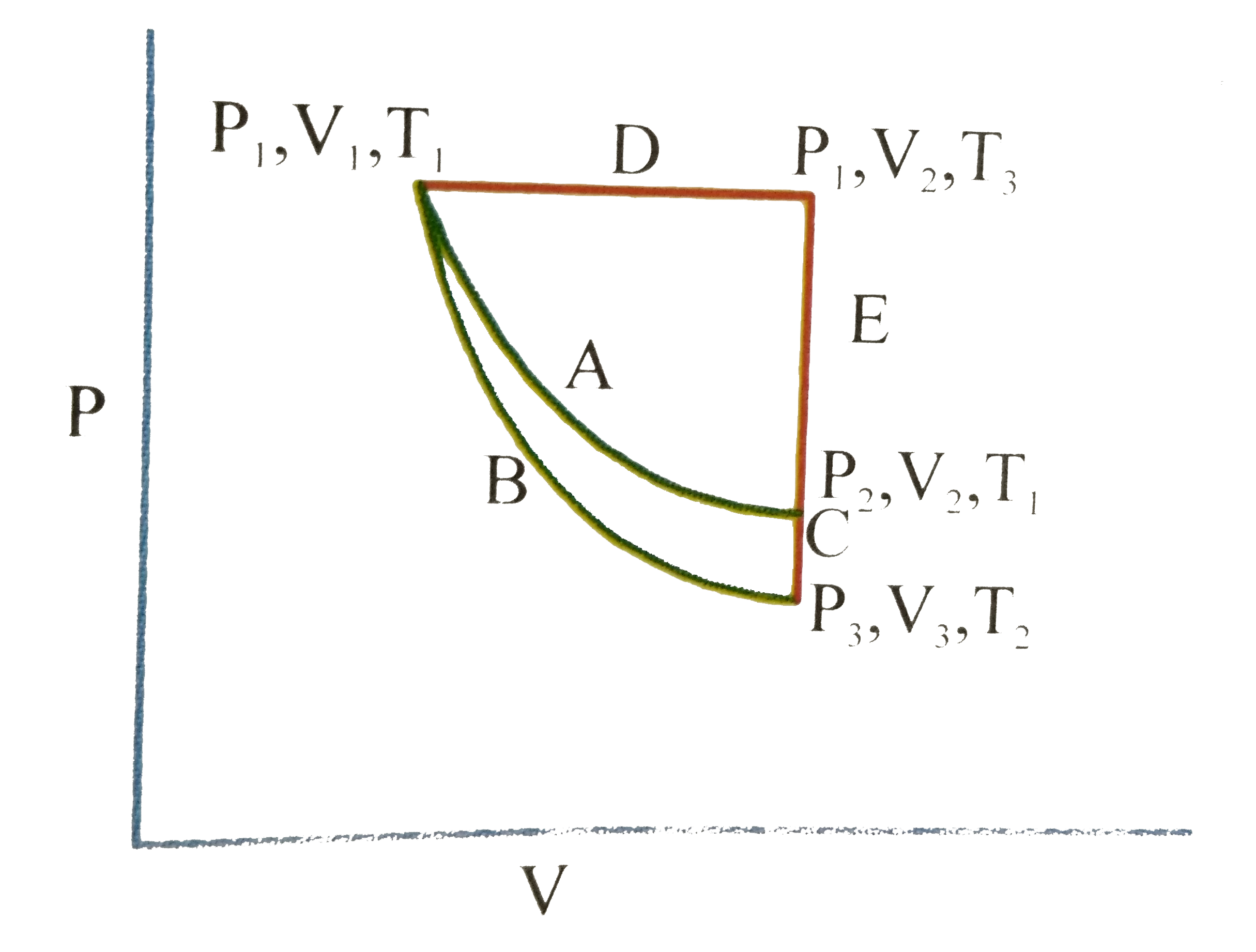
Path (A) represents a reversible isothernal expanison from P1V1 to P2V2. Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1 to P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C) from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2T1 to P1,V2,T3 followed by reversible cooling at a constant volume V2 (E) from P1,V2,T3 to P2,V2,T1
What is ΔS for path (D+E) ?
View SolutionEstablish gas equation, (P_(1)V_(1))/(T_(1))=(P_(2)V_(2))/(T_(2)) .
View SolutionA sample of gas changes from p1,V1 and p2. V2andT2 by one path and then back to p1,V1andT1. ΔU for the process is :
View Solution

