The van der Waal's constant 'b' for N2 and H2 has the values 0.04 lit mol−1 and 0.025 lit mol−1.The density of solid N2 is 1 g cm−3.Assuming the molecules in the solids to be close packed with the same percentage void, the density of solid H2 would be (in cm−3)
0.114
0.682
1.466
0.071
The correct Answer is:A
To find the density of solid H2 given the van der Waals constants for N2 and H2, and the density of solid N2, we can follow these steps:
1. Identify the Given Values:
- Van der Waals constant for N2 (b): bN2=0.04litre mol−1
- Van der Waals constant for H2 (b): bH2=0.025litre mol−1
- Density of solid N2: DN2=1g cm−3
- Molar mass of N2: MN2=28g mol−1
- Molar mass of H2: MH2=2g mol−1
2. Use the Relationship Between Density, Molar Mass, and Van der Waals Constant:
The relationship can be expressed as:
bN2bH2=MN2/DN2MH2/DH2
3. Rearranging the Equation:
Rearranging gives:
DH2=DN2×bH2bN2×MH2MN2
4. Substituting the Values:
Now substitute the known values into the equation:
DH2=1g cm−3×0.0250.04×228
5. Calculating the Ratios:
Calculate the ratio of the van der Waals constants:
0.0250.04=0.625
Calculate the ratio of the molar masses:
228=114≈0.0714
6. Final Calculation:
Now, multiply these ratios:
DH2=1×0.625×0.0714≈0.0447g cm−3
7. Final Result:
Therefore, the density of solid H2 is approximately:
DH2≈0.114g cm−3
- Van der Waals constant for N2 (b): bN2=0.04litre mol−1
- Van der Waals constant for H2 (b): bH2=0.025litre mol−1
- Density of solid N2: DN2=1g cm−3
- Molar mass of N2: MN2=28g mol−1
- Molar mass of H2: MH2=2g mol−1
The relationship can be expressed as:
bN2bH2=MN2/DN2MH2/DH2
Rearranging gives:
DH2=DN2×bH2bN2×MH2MN2
Now substitute the known values into the equation:
DH2=1g cm−3×0.0250.04×228
Calculate the ratio of the van der Waals constants:
0.0250.04=0.625
Calculate the ratio of the molar masses:
228=114≈0.0714
Now, multiply these ratios:
DH2=1×0.625×0.0714≈0.0447g cm−3
Therefore, the density of solid H2 is approximately:
DH2≈0.114g cm−3
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
A red solide is insoluble in water. However it becomes soluble if some KI is added to water. On heating the red solid in a test tube, there is liberation of some violet coloured fumes and droplets of a metal appear on the cooler parts of the test tube. The red solid is :
View SolutionSodium (Na =23) crystallizen in bcc arrangement with the interfacial separation between the atoms at the edge 53.6pm. The density of sodium crystal is:
View SolutionFor a van der Waal's gas with a = 0.2463 atm lit^(2) mol^(-1) and b=0.01 lit mol^(-1) subjected to adiabatic free exapansion at an initial temperature of 650 K will show which of the following characterstics?
View SolutionThe density of apure substance 'A' whose atoms are in cubic close pack arragement is 1g/cc. If the all the tetrahedral voids are occu[pioed by 'B' atom , What is the density of resulting solid in g/cc.[ "Atomic mass" =(A)=30g/mol and atomic mass (B)=50g/mol]
View SolutionThe van der Waal's constant 'b' for water vapour is 0.03 litre mol−1. The radius of water vapour molecule is :
View SolutionThe critical volume of a gas is 0.072 lit. "mol"^(-1) .The radius of the molecule will be, in cm
View SolutionThe van der Waal's constant 'b' for N_2 and H_2 has the values 0.04 lit "mol"^(-1) and 0.025 lit "mol"^(-1) .The density of solid N_2 is 1 g cm^(-3) .Assuming the molecules in the solids to be close packed with the same percentage void, the density of solid H_2 would be (in cm^(-3) )
View SolutionConsider the following reaction in a 1 L closed vessel.
N2+3H2⇔NH3
If all the species: N2,H2 and NH3 are in 1 mol in the beginning of the reaction and equilibrium is attained after unreacted N2 is 0.7 mol. What is the value of equilibrium constant?
View Solution400gm द्रव्यमान वाले ठोस का आयतन 250cm3 है।
(a) ठोस का घनत्व ज्ञात करें । (b) ठोस का आपेक्षिक घनत्व ज्ञात करें। यदि पानी का घनत्व 1gcm−3 है।
View SolutionWhat is the density (in "g lit"^(-1)) of CO_2 , at 400 K and exerting a pressure of 0.0821 atm (R = 0.0821 "lit atm mol"^(-1) k^(-1))
View SolutionThe density of apure substance 'A' whose atoms are in cubic close pack arragement is 1 g//c c . If the all the tetrahedral voids are occu[pioed by 'B' atom , What is the density of resulting solid in g//c c .[ "Atomic mass" = (A)= 30 g//"mol" and atomic mass (B)= 50 g//"mol" ]
View SolutionIf density if mercury is 13.6gm//cm^3 then find the mass of 1 lit merury?
View SolutionThe decomposition of ammonia on platinum surface is a zero order reaction. What are the rates of production of N2 and h2 if rates constant is 2.5×10−4mollit−1sec−1
View Solutionvan der Waals constant 'b' for a real gas is 0.02788 lit mole−1. Calculate the radius of the molecule of the gas.
View Solution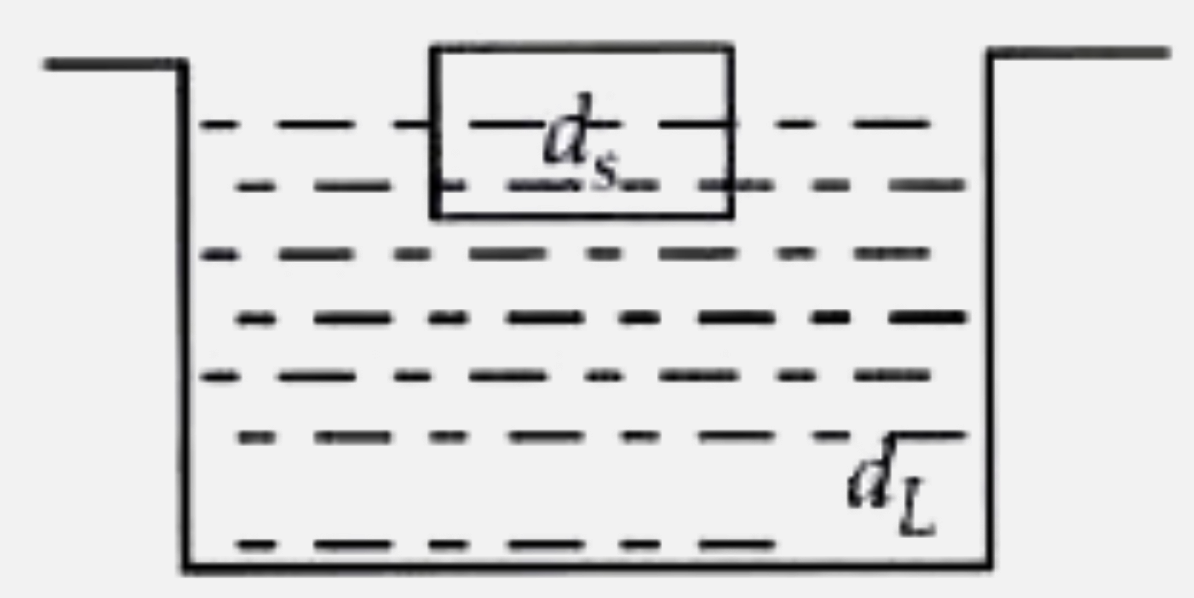
The figure above shows a solid of density dS floating in a liquid of density dL.
The same solid floats in water with 3th5 of its volume immersed in it. Calculate the density of the solid. (density of water = 1 g cm−3 )
View SolutionTwo solids A and B of density 2.5 g cm^(-3) and 0.80g cm^(-3) are placed in a liquid L of density 1.2 g cm^(-3) Which solid is likely to float and why?
View Solution
