The molar conductance of NaCl varies with the concentration as shown in the following table and all values follows the equation
λCm=λ∞m−b√C where λCm=molar specific conductance
λ∞m=molar specific conductance at infinite dilution
C=molar concentration
Molar Concentration of NaClMolar ConductanceInohm−1cm2mole−14×10−41079×10−49716×10−487
When a certain conductivity cell (C) was filled with 25×10−4(M) NaCl solution.The resistance of the cell was found to be 1000 ohm.At Infinite dilution, conductance of Cl− and SO−24 are 80ohm−1cm2mole−1and160ohm−1cm2mole−1 respectively.
If the cell ( C) is filled with 5×10−3(N)Na2SO4 the obserbed resistance was 400 ohm.What is the molar conductance of Na2SO4.
19.25ohm−1cm2mole−1
96.25ohm−1cm2mole−1
385ohm−1cm2mole−1
192.5ohm−1cm2mole−1
The correct Answer is:D
For Na2SO4 solution
K=(la)×1R=0.1925400=4.81×10−4ohm−1cm−1
λm=K×1000M=4.81×10−4×100052×10−3
λm(Na2SO4)=192.4ohm−1cm2mole−1
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
A red solide is insoluble in water. However it becomes soluble if some KI is added to water. On heating the red solid in a test tube, there is liberation of some violet coloured fumes and droplets of a metal appear on the cooler parts of the test tube. The red solid is :
View SolutionSodium (Na =23) crystallizen in bcc arrangement with the interfacial separation between the atoms at the edge 53.6pm. The density of sodium crystal is:
View SolutionStatement: For a weak electrolyte, the plot of molar conductivity (Lambda_(m)) against sqrt(C )(C is concentration in mol litre^(-1)) is nearly linear. Explanation: The molar conductivity at infinite dilution (Lambda_(m)) for an electrolyte can be considered equal to the sum of the limiting molar conductivities of the individual ions.
View SolutionCalculating The Degree of ionization: The molar conductance of an infinitely dilute solution NH4Cl is 150Scm2mol−1 and the limiting ionic conductacnes of Cl− and OH− ions are 76 and 198Scm2mol−1 respectively. If the molar conductivity of a 0.01M solution of NH4OH is 9.6Scm2mol−1, what will be its degree of ionization
Strategy: At any concentration C, if α is the degree of ionization then it can be approximented to the ratio of molar conductivity Λcm at the concentration C to limiting molar conducting, Λ0m. We are given Λcm but we need to find Λ0m.
View SolutionThe molar conductance is given by the relation (M = concentration in molarity)
View SolutionThe molar conductance of NaCl varies with the concentration as shown in the following table and all values follows the equation.
λcm=λ∞m−b√C where λcm= molar specific conductance λ∞m= molar specific conductance at infinite dilution C=molar concentration
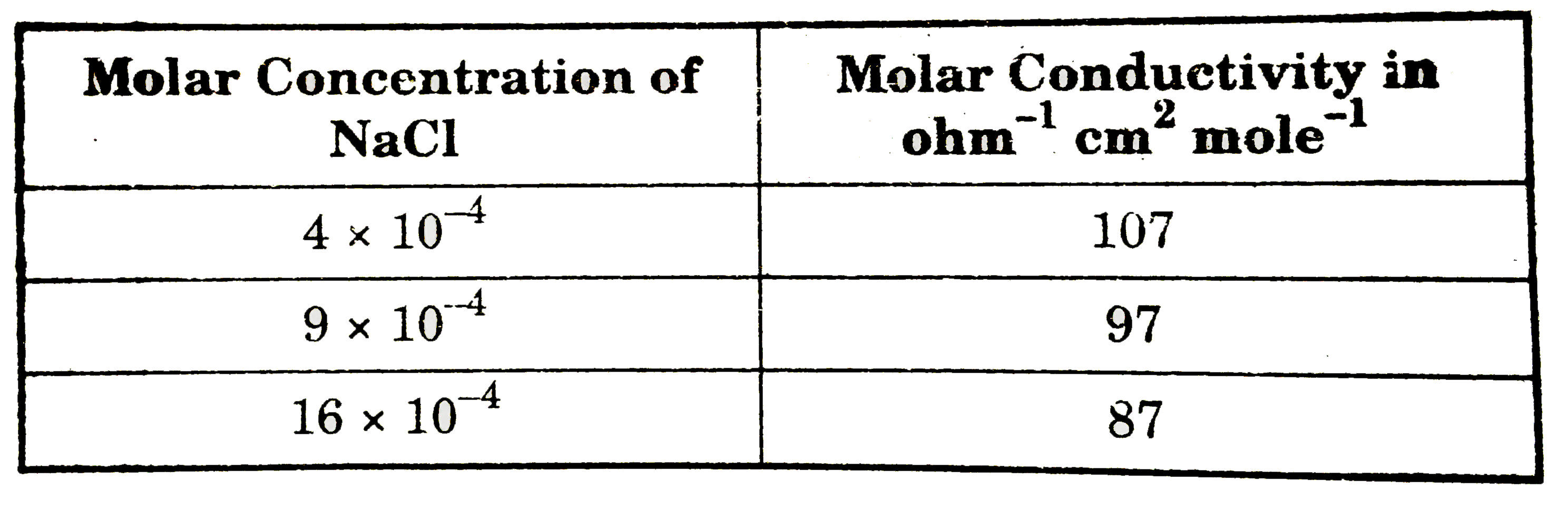
When a certain conductivity cell (C) was filled with 25×10−4(M)NaCl solution, the resistance of the cell was found to be 1000 ohm. At infinite dilution, conductance of Cl− and SO2−4 are 80ohm−1cm2mole−1 and 160ohm−1cm2mole−1 respectively.
What is the molar conductance of NaCl at infinite dilution?
View SolutionThe molar conductance of NaCl varies with the concentration as shown in the following table and all values follows the equation.
λcm=λ∞m−b√C where λcm= molar specific conductance λ∞m= molar specific conductance at infinite dilution C=molar concentration
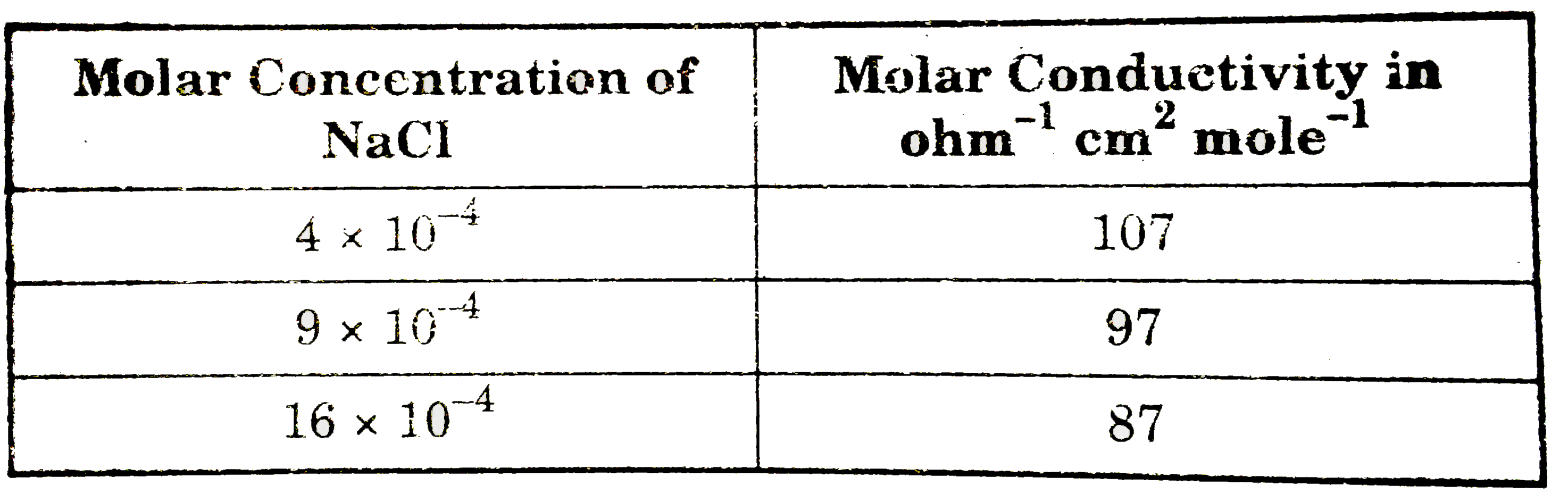
When a certain conductivity cell (C) was filled with 25×10−4(M)NaCl solution, the resistance of the cell was found to be 1000 ohm. At infinite dilution, conductance of Cl− and SO2−4 are 80ohm−1cm2mole−1 and 160ohm−1cm2mole−1 respectively.
What is the cell constant of the conductivity cell (C)?
View SolutionThe molar conductance of NaCl vauies with the concentration as shown in the following table. And all values follows the equation lambda_(m)^(C)=lambda_(m)^(oo)-bsqrtC Where lambda_(m)^(C) = molar specific conductance lambda_(m)^(oo) =molar specific conductance at infinite dilution C = molar concentration {:("Molar concentration","Molar conductance of NaCl in ohm"^(-1)"cm"^(2)"mole"^(-1)),(4xx10^(-4),107),(9xx10^(-4),97),(16xx10^(-4),87):} When a certain conductivity cell (C) was filled with 25xx10^(-4)(M) NaCl solution. The resistance of the cell was found to be 1000 ohm. At Infinite dilution, conductance of CI^(-) and SO_(4)^(-2) are 80 ohm^(-1)cm^(2)"mole"^(-1) and 160 ohm^(-1)cm^(2)"mole"^(-1) respectively. What is the molar conductance of NaCl at infinite dilution?
View SolutionThe molar conductance of NaCl vauies with the concentration as shown in the following table. And all values follows the equation lambda_(m)^(C)=lambda_(m)^(oo)-bsqrtC Where lambda_(m)^(C) = molar specific conductance lambda_(m)^(oo) =molar specific conductance at infinite dilution C = molar concentration {:("Molar concentration","Molar conductance of NaCl in ohm"^(-1)"cm"^(2)"mole"^(-1)),(4xx10^(-4),107),(9xx10^(-4),97),(16xx10^(-4),87):} When a certain conductivity cell (C) was filled with 25xx10^(-4)(M) NaCl solution. The resistance of the cell was found to be 1000 ohm. At Infinite dilution, conductance of CI^(-) and SO_(4)^(-2) are 80 ohm^(-1)cm^(2)"mole"^(-1) and 160 ohm^(-1)cm^(2)"mole"^(-1) respectively. What is the cell constant of the conductivity cell (C) :
View SolutionThe molar conductance of NaCl vauies with the concentration as shown in the following table. And all values follows the equation λCm=λ∞m−b√C Where λCm= molar specific conductance λ∞m=molar specific conductance at infinite dilution C = molar concentration Molar concentrationMolar conductance of NaCl in ohm−1cm2mole−14×10−41079×10−49716×10−487
When a certain conductivity cell (C) was filled with 25×10−4(M) NaCl solution. The resistance of the cell was found to be 1000 ohm. At Infinite dilution, conductance of CI− and SO−24 are 80 ohm−1cm2mole−1 and 160 ohm−1cm2mole−1 respectively.
It the cell (C) is filled with 5×10−3(N)Na2SO4 the obserbed resistance was 400 ohm. What is the molar conductance of Na2SO4.
View SolutionMolar conductivity of an electrolyte is the conductance of all the ions produced by one gram mole of the electrolyte in solution and is denoted as Lambda_(m) . Lambda_(m)=(kxx1000)/(c ) Here k is the specific conductance while c is the molar concentration of the electrolyte. The molar conductance of the strong electrolytes at infinite dilution (Lambda_(m)^(oo)) can be obtained graphically by extrapolation while the same for weak electrolytes cannot be obtained graphically. It can be calculated theoretically with the help of Kohrausch's. Law. Lambda_(m(AxBy))^(oo)=xlambda_(m (A^(y+)))^(oo)+ylambda_(m(B^(x)))^(oo) Which of the following solution of KCl will have the maximum value of specific conductance ?
View SolutionThe molar conductance of NaCl varies with the concentration as shown in the following table and all values follows the equation lambda_m^( C)=lambda_m^(oo)-bsqrtC where lambda_(m)^( C) =molar specific conductance lambda_(m)^(oo) =molar specific conductance at infinite dilution C=molar concentration {:("Molar Concentration of NaCl","Molar Conductance" "In" "ohm"^(-1)cm^(2)"mole"^(-1)),(4xx10^(-4),107),(9xx10^(-4),97),(16xx10^(-4),87):} When a certain conductivity cell (C) was filled with 25xx10^(-4) (M) NaCl solution.The resistance of the cell was found to be 1000 ohm.At Infinite dilution, conductance of Cl^(-) and SO_4^(-2) are 80 ohm^(-1) cm^(2) "mole"^(-1) and 160 ohm^(-1) cm^2 "mole"^(-1) respectively. If the cell ( C) is filled with 5xx10^(-3)(N)Na_(2)SO_(4) the obserbed resistance was 400 ohm.What is the molar conductance of Na_(2)SO_(4) .
View SolutionThe molar conductance of NaCl varies with the concentration as shown in the following table. And all values follows the equation
λCm=λ∞m−b√C Where λCm=Molar specific conductance
λ∞m=Molar specific conductance at infinite direction
C=Molar concentration
Molar Concentration of NaClMolar Conductance inohm−1cm2mole14×10−41079×10−49716×10−487
When a certain conductivity cell (C ) was filled with 25×10−4 (M) NaCl solution.The resistance of the cell was found to be 1000 ohm.At infinite dilution, conductance of Cl− and SO−24 are 800 ohm−1cm2mole−1and160ohm−1cm2mole−1 respectively.
What is the cell constant of the conductivity cell ( C) ?
View SolutionThe molar conductance of NaCl varies with the concentration as shown in the following table. And all values follows the equation lambda_m^C=lambda_m^oo-bsqrtC Where lambda_m^C =Molar specific conductance lambda_m^oo =Molar specific conductance at infinite direction C=Molar concentration {:("Molar Concentration of NaCl","Molar Conductance inohm"^(-1)cm^(2)"mole"^(1)),(4xx10^(-4),107),(9xx10^(-4),97),(16xx10^(-4),87):} When a certain conductivity cell (C ) was filled with 25xx10^(-4) (M) NaCl solution.The resistance of the cell was found to be 1000 ohm.At infinite dilution, conductance of Cl^(-) and SO_(4)^(-2) are 800 "ohm"^(-1) cm^(2)"mole"^(-1) and 160 "ohm"^(-1) cm^(2)"mole"^(-1) respectively. If the cell ( C) is filled with 5xx10^(-3) (N)Na_2SO_4 the observed resistance was 400 ohm. What is the molar conductance of Na_2SO_4 ?
View SolutionAt a particular temperature, the ratio of molar conductance to specific conductance of 0.01 M NaCl is :
View SolutionThe molar conductance of NzCl varies with the concentration as shown in the following table and all values follows the equation lamda_(m)^(C)=lamda_(m)^(infty)-bsqrt(C) where lamda_(m)^(C)= molar specific conductance lamda_(m)^(infty)= molar specific conductance at infinite dilution C= molar concentration When a cenrtain conductivity cell (C) was filled with 25xx10^(-4)(M) NaCl solution. The resistance of the cell was found to be 1000 ohm At infinite dilution, Conductance of Cl^(-) and SO_(4)^(-2) are 80ohm^(-1)cm^(2)"mole"^(-1) and 160ohm^(-1)cm^(2)"mole"^(-1) respectively. Q. If the cell (C) is filled with 5xx10^(-3)(N)Na_(2)SO_(4) the observed resistance was 400 ohm. what is the molar conductance of Na_(2)SO_(4)
View Solution

