Which of the following is correctly ordered :
−Oh>−NH2 (+M effect)
−SO3H>−NO2 (-M effect)
−F>−CN (-l effect)
−CN>−F (-l effect)
The correct Answer is:D
To determine which of the given options is correctly ordered based on the effects of substituents in organic chemistry, we need to analyze the mesomeric (plus M) and inductive (minus I) effects of the groups involved. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the reasoning:
Step 1: Analyze Option A (OH vs NH2)
- Concept: The plus M effect refers to the ability of a substituent to donate electron density through resonance.
- Analysis:
- Hydroxyl group (OH) and amino group (NH2) both have lone pairs that can participate in resonance.
- However, oxygen (in OH) is more electronegative than nitrogen (in NH2).
- Therefore, NH2 has a greater plus M effect than OH because it can donate its lone pair more effectively due to its lower electronegativity.
- Conclusion: Option A is incorrect.
Step 2: Analyze Option B (SO3H vs NO2)
- Concept: The minus M effect refers to the ability of a substituent to withdraw electron density through resonance.
- Analysis:
- Both SO3H and NO2 groups withdraw electrons.
- However, NO2 is more electronegative than SO3H.
- Thus, NO2 has a stronger minus M effect compared to SO3H.
- Conclusion: Option B is incorrect.
Step 3: Analyze Option C (F vs CN)
- Concept: The minus I effect refers to the inductive effect where a substituent pulls electron density through sigma bonds.
- Analysis:
- Fluorine (F) is highly electronegative and exerts a strong minus I effect.
- However, the carbon-nitrogen triple bond (C≡N) has a significant amount of s-character (due to sp hybridization), which increases the electronegativity of the carbon atom involved.
- Therefore, CN exerts a greater minus I effect than F.
- Conclusion: Option C is incorrect.
Step 4: Analyze Option D (CN vs F)
- Analysis:
- As established, CN has a higher electronegativity due to its sp hybridization, leading to a stronger minus I effect compared to F.
- Conclusion: Option D is correct.
Final Answer:
The correctly ordered option is D (CN > F).
- Concept: The plus M effect refers to the ability of a substituent to donate electron density through resonance.
- Analysis:
- Hydroxyl group (OH) and amino group (NH2) both have lone pairs that can participate in resonance.
- However, oxygen (in OH) is more electronegative than nitrogen (in NH2).
- Therefore, NH2 has a greater plus M effect than OH because it can donate its lone pair more effectively due to its lower electronegativity.
- Conclusion: Option A is incorrect.
- Concept: The minus M effect refers to the ability of a substituent to withdraw electron density through resonance.
- Analysis:
- Both SO3H and NO2 groups withdraw electrons.
- However, NO2 is more electronegative than SO3H.
- Thus, NO2 has a stronger minus M effect compared to SO3H.
- Conclusion: Option B is incorrect.
- Concept: The minus I effect refers to the inductive effect where a substituent pulls electron density through sigma bonds.
- Analysis:
- Fluorine (F) is highly electronegative and exerts a strong minus I effect.
- However, the carbon-nitrogen triple bond (C≡N) has a significant amount of s-character (due to sp hybridization), which increases the electronegativity of the carbon atom involved.
- Therefore, CN exerts a greater minus I effect than F.
- Conclusion: Option C is incorrect.
- Analysis:
- As established, CN has a higher electronegativity due to its sp hybridization, leading to a stronger minus I effect compared to F.
- Conclusion: Option D is correct.
The correctly ordered option is D (CN > F).
Topper's Solved these Questions
- GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-IBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-IExercise:PART-III : PRACTICE TEST-3
Explore 1 Video
- GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-IBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-IExercise:PART-III : PRACTICE TEST-4
Explore 1 Video
- GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-IBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-IExercise:PART-2(NSEC)
Explore 24 Videos
- GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY IIBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY IIExercise:Part-III: Section-5: Matching List Type
Explore 1 Video
- HYDROGEN AND ITS COMPOUNDSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:HYDROGEN AND ITS COMPOUNDSExercise:INORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Hydrogen & its compunds Y environment chemistry)
Explore 33 Videos
Similar Questions
Which of the following compound(s) is/are aromatic compounds ?
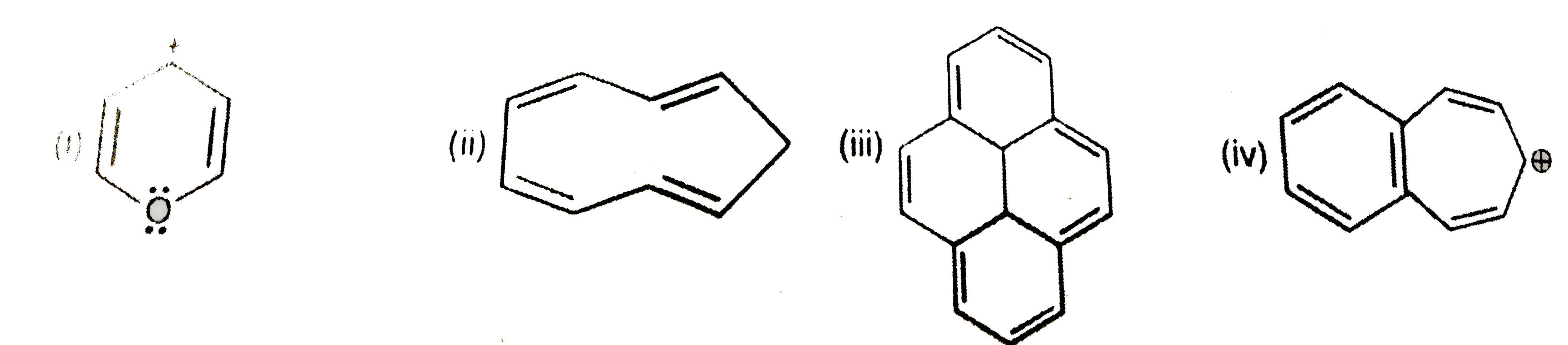
View SolutionWhich of the following resonating structures of 1-methoxy-1,3-butadiene is least stable ?
View SolutionWhich of the following is true about the cycloheptatrienyl free radical ?
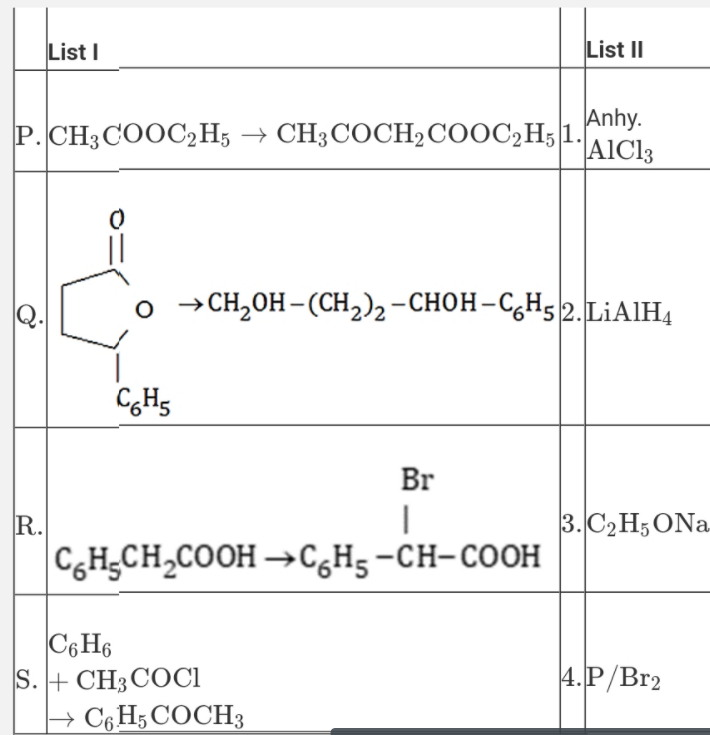
View SolutionMatch List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists
View SolutionHydrogen molecule differs from chlorine molecule in the following respect :
View SolutionWhich of the following orders of ionic radii is correctly represented?
View SolutionWhich of the following is correctly ordered :
View SolutionWhich of the following orders correctly depicts the decreasing order of stability of carbanion?
View SolutionWhich of the following orders of ionic radii is correctly represented ?
View SolutionWhich of the following correctly represents the order of atomic radii
View SolutionWhich of the following orders of ionic radii is correctly represented ?
View SolutionWhich of the following orders of ionic radii is correctly represented ?
View SolutionWhich of the following correctly represents the order of atomic radii
View Solutionनिम्न में से किसके द्वारा आयनिक त्रिज्या का क्रम सही रूप से प्रदर्शित है
View SolutionWhich of the following orders correctly depicts the decreasing order of stability of carbanion?
View Solution
