PhSO2CH2−CH2−OMeEtOθ−−−→EtODproduct+PhSO2−D∣CH−CH2OMe(recovered reactant).
The product is :
PhSO2CH=CH2
CH2=CH−OMe
PhSO2CH2−CD2OMe
CD2=CH2
The correct Answer is:A
To solve the problem, we need to analyze the reaction of the compound PhSO₂CH₂CH₂OMe with EtO⁻ in the presence of EtOD. Let's break down the reaction step by step.
Step 1: Identify the Structure
The starting compound can be represented as PhSO₂-CH₂-CH₂-OMe. Here, Ph represents a phenyl group (C₆H₅), SO₂ is a sulfonyl group, and OMe is a methoxy group (–OCH₃).
Step 2: Deprotonation
The base EtO⁻ (ethoxide ion) will act to deprotonate the most acidic hydrogen in the molecule. In this case, the hydrogen on the CH₂ adjacent to the sulfonyl group (PhSO₂) is the most acidic due to the electron-withdrawing effect of the sulfonyl group.
The reaction can be represented as:
PhSO2-CH2-CH2-OMe+EtO−→PhSO2-C−H-CH2-OMe+EtOH
Step 3: Formation of the Carbanion
After deprotonation, we form a carbanion at the carbon adjacent to the sulfonyl group:
PhSO2-C−H-CH2-OMe
Step 4: Resonance Stabilization
The carbanion formed is resonance-stabilized by the sulfonyl group. This stabilization allows the negative charge to delocalize, making the carbanion more stable.
Step 5: Elimination Reaction
The next step involves the elimination of the methoxy group (–OMe) as a leaving group. The carbanion can form a double bond with the adjacent carbon, leading to the formation of an alkene. The reaction can be represented as:
PhSO2-C−H-CH2-OMe→PhSO2-C=CH2+OMe−
Step 6: Final Product
The final product will be:
PhSO2-C=CH2
This product is a vinyl sulfone where the sulfonyl group is attached to a double-bonded carbon.
Summary of the Reaction
The overall reaction can be summarized as:
PhSO2-CH2-CH2-OMe+EtO−→PhSO2-C=CH2+OMe−+EtOH
The starting compound can be represented as PhSO₂-CH₂-CH₂-OMe. Here, Ph represents a phenyl group (C₆H₅), SO₂ is a sulfonyl group, and OMe is a methoxy group (–OCH₃).
The base EtO⁻ (ethoxide ion) will act to deprotonate the most acidic hydrogen in the molecule. In this case, the hydrogen on the CH₂ adjacent to the sulfonyl group (PhSO₂) is the most acidic due to the electron-withdrawing effect of the sulfonyl group.
PhSO2-CH2-CH2-OMe+EtO−→PhSO2-C−H-CH2-OMe+EtOH
After deprotonation, we form a carbanion at the carbon adjacent to the sulfonyl group:
PhSO2-C−H-CH2-OMe
The carbanion formed is resonance-stabilized by the sulfonyl group. This stabilization allows the negative charge to delocalize, making the carbanion more stable.
The next step involves the elimination of the methoxy group (–OMe) as a leaving group. The carbanion can form a double bond with the adjacent carbon, leading to the formation of an alkene. The reaction can be represented as:
PhSO2-C−H-CH2-OMe→PhSO2-C=CH2+OMe−
The final product will be:
PhSO2-C=CH2
This product is a vinyl sulfone where the sulfonyl group is attached to a double-bonded carbon.
The overall reaction can be summarized as:
PhSO2-CH2-CH2-OMe+EtO−→PhSO2-C=CH2+OMe−+EtOH
টপার এই প্রশ্নগুলো সমাধান করেছে
- ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVEXERCISE - APSP PART-2
17 Videos
- ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVEXERCISE - APSP PART-3
22 Videos
- ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVEXERCISE - Exercise-3 Part-2 JEE (MAIN ) ONLINE PROBLEMS
10 Videos
- ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS - IIBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS - IIEXERCISE - APSP Part - 3
22 Videos
- PERIODIC TABLE & PERIODICITYBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - PERIODIC TABLE & PERIODICITYEXERCISE - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(BASIC CONCEPTS)
24 Videos
সম্পর্কিত প্রশ্ন
An alkyl bromide produces a single alkene when it reacts with sodium ethoxide and ethanol. This alkene undergoes hydrogenation and produces 2-methylbutane. What is the alkybromide ?
View SolutionRate of Bimolecular elimination (E2) reaction for the following :

View SolutionThe major product of the reaction is

View Solution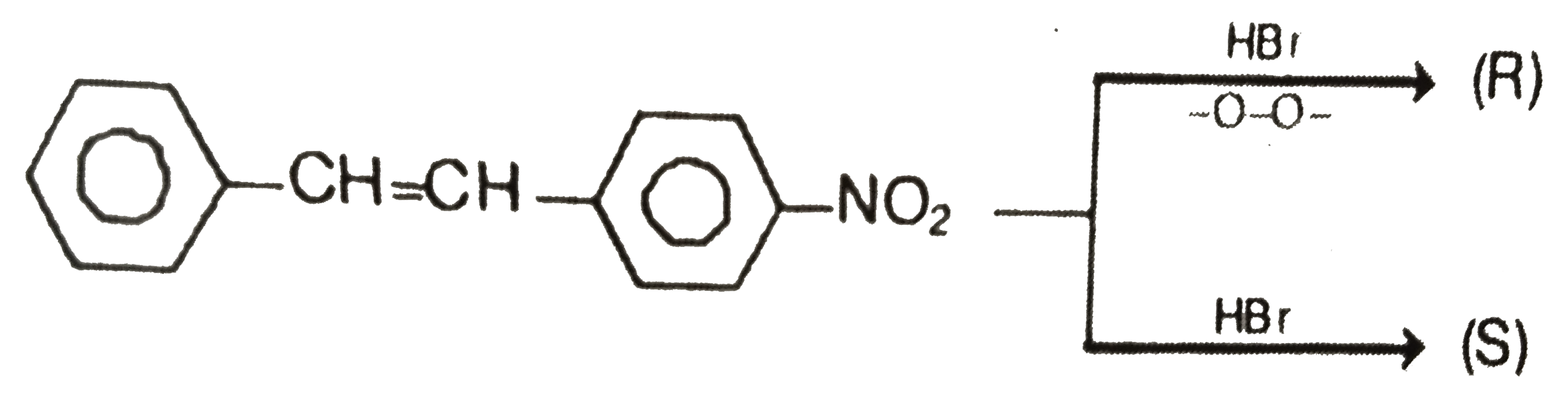
R & S are :
View SolutionAn element with atomic number 107 has recently been discovered. Its block, group number, period and outshell electronic configuration respectively are :
View SolutionCH3−C∣CH3H−Cl∣CH−CH3t−BuO−−−−→Δ Major Product is :
View SolutionMajor product of given reaction is - O_2N-CH_2-undersetunderset(Cl)(|)CH-CH_3overset(overset(Theta)(O)H)underset(Delta)to Major product
View SolutionPhSO2CH2−CH2−OMeEtOθ−−−→EtODproduct+PhSO2−D∣CH−CH2OMe(recovered reactant).
The product is :
View SolutionIn the following reactions , (1)CH_3-oversetoverset(CH_3)|CH-undersetunderset(OH)|CH-CH_3overset(H^+//heat)to underset"(Major product)"A+underset"(Minor Product)"B (2) A underset"in absence of peroxide"overset"HBr, dark"to underset"(Major Product )"C+underset"(Minor Product)"D The major products (A) and (C )are respectively
View SolutionIn the given E2 reaction
CH3−FCH−CH2−CH3+CH3−CH2−⊙O
CH3−CH2OH−−−−−−−−→CH3−CH2−CH(major product)=CH2+−−−−−−−−−→(minor product)CH3−CH=CH−CH3
The transition state has
View SolutionCH_3-underset(OH)underset(|)CH-CH_2-CH_3 overset(Conc. H_2SO_4)to " Product(I) + Product(II)" What is not true regarding the products ?
View SolutionCH_2 = CH- CH= CH_2 overset(HBr( 1 " mole"))to major product
View SolutionCH3C∣BrH=C∣BrH21 equivalent−−−−−−−→ of alc.KOHThe major product is
View SolutionCH3−CH2−CH2−C≡CHBH3−−→THFH2O2−−→OH−Identify the product
View SolutionPh−CH2−C∣DH−CH3Br2/hv−−−−→ Product of the above reaction will be :
View Solution

