Which of the following anions are identified by dil. HCl :
NO−2,NO−3,CO2−3
NO−2,NO−3,SO2−3
S2−,SO2−3,NO−2
CH3COO−,I−,CO2−3
The correct Answer is:C
To determine which anions are identified by dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl), we need to analyze each option provided in the question.
1. Understanding the Reaction with Dilute HCl:
- Dilute HCl can react with certain anions to produce identifiable products. Common anions that react with dilute HCl include carbonate (CO3^2-), sulfite (SO3^2-), and nitrite (NO2^-).
2. Analyzing Each Option:
- Option A: NO2^-, NO3^-, CO3^2-
- NO2^- (Nitrite) reacts with dilute HCl to produce nitrogen dioxide (NO2), which can be identified by its brown color.
- NO3^- (Nitrate) does not react with dilute HCl in a way that produces a noticeable change.
- CO3^2- (Carbonate) reacts with dilute HCl to produce carbon dioxide (CO2), which can be identified by the evolution of gas.
- Conclusion: This option is partially correct (NO2^- and CO3^2-).
- Option B: NO2^-, NO3^-, SO3^2-
- NO2^- is correct as discussed.
- NO3^- does not react with dilute HCl.
- SO3^2- (Sulfite) reacts with dilute HCl to produce sulfur dioxide (SO2), which can be identified by its pungent smell and the evolution of gas.
- Conclusion: This option is partially correct (NO2^- and SO3^2-).
- Option C: CO2^-, SO3^2-, NO2^-
- CO2^- is not a valid anion; it seems to be a typographical error (possibly meant to be CO3^2-).
- SO3^2- is correct as discussed.
- NO2^- is correct as discussed.
- Conclusion: This option is partially correct (assuming CO2^- is a typo for CO3^2-).
- Option D: CS3^-, COO^-, I^-, CO3^2-
- CS3^- (Thioformate) is not typically identified with dilute HCl.
- COO^- (Carboxylate) does not react in a way that produces a noticeable change with dilute HCl.
- I^- (Iodide) does not react with dilute HCl to produce a noticeable change.
- CO3^2- is correct as discussed.
- Conclusion: This option is incorrect.
3. Final Conclusion:
- After analyzing all options, the correct anions that can be identified by dilute HCl are NO2^- and CO3^2- from Option A, and SO3^2- from Option B. However, the most comprehensive option that includes the correct anions is Option B.
Final Answer:
The correct option is B: NO2^-, NO3^-, SO3^2- (considering NO3^- does not contribute but the other two do).
- Dilute HCl can react with certain anions to produce identifiable products. Common anions that react with dilute HCl include carbonate (CO3^2-), sulfite (SO3^2-), and nitrite (NO2^-).
- Option A: NO2^-, NO3^-, CO3^2-
- NO2^- (Nitrite) reacts with dilute HCl to produce nitrogen dioxide (NO2), which can be identified by its brown color.
- NO3^- (Nitrate) does not react with dilute HCl in a way that produces a noticeable change.
- CO3^2- (Carbonate) reacts with dilute HCl to produce carbon dioxide (CO2), which can be identified by the evolution of gas.
- Conclusion: This option is partially correct (NO2^- and CO3^2-).
- NO2^- is correct as discussed.
- NO3^- does not react with dilute HCl.
- SO3^2- (Sulfite) reacts with dilute HCl to produce sulfur dioxide (SO2), which can be identified by its pungent smell and the evolution of gas.
- Conclusion: This option is partially correct (NO2^- and SO3^2-).
- CO2^- is not a valid anion; it seems to be a typographical error (possibly meant to be CO3^2-).
- SO3^2- is correct as discussed.
- NO2^- is correct as discussed.
- Conclusion: This option is partially correct (assuming CO2^- is a typo for CO3^2-).
- CS3^- (Thioformate) is not typically identified with dilute HCl.
- COO^- (Carboxylate) does not react in a way that produces a noticeable change with dilute HCl.
- I^- (Iodide) does not react with dilute HCl to produce a noticeable change.
- CO3^2- is correct as discussed.
- Conclusion: This option is incorrect.
- After analyzing all options, the correct anions that can be identified by dilute HCl are NO2^- and CO3^2- from Option A, and SO3^2- from Option B. However, the most comprehensive option that includes the correct anions is Option B.
The correct option is B: NO2^-, NO3^-, SO3^2- (considering NO3^- does not contribute but the other two do).
टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)BOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)EXERCISE - Exercise-2
44 Videos
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)BOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)EXERCISE - Exercise-3
10 Videos
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)BOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)EXERCISE - Matching List Type
1 Video
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSISBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - QUALITATIVE ANALYSISEXERCISE - INORGANIC CHMISTRY(Qualitative analysis)
35 Videos
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS PART 1BOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS PART 1EXERCISE - A.L.P
37 Videos
समान प्रश्न
ज्ञान जांच
Which of the following anions is most stabilised?
A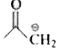 B
B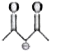 C
C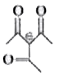 DAll have same stability
DAll have same stabilityWhich of the following anions are more stable than benzyl anion ?
A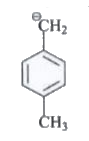 B
B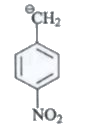 C
C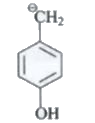 D
D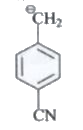
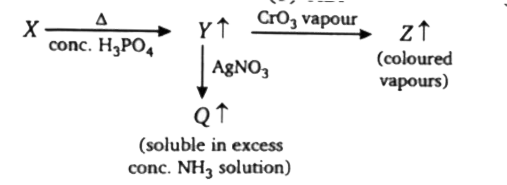
Which of the following anion cannot be in X?
View Solution
Which of the following anion cannot be in X?
View SolutionWhich of the following anions is the weakest base ?
View SolutionThe amines are basic in nature, hence they form salts with hydrochloric acid. Which of the following will be insoluble in dil. HCl?
View SolutionWhich of the following anion(s) is/are interfering radicate ?
View SolutionWhich of the following is an anionic detergent ?
View Solution

