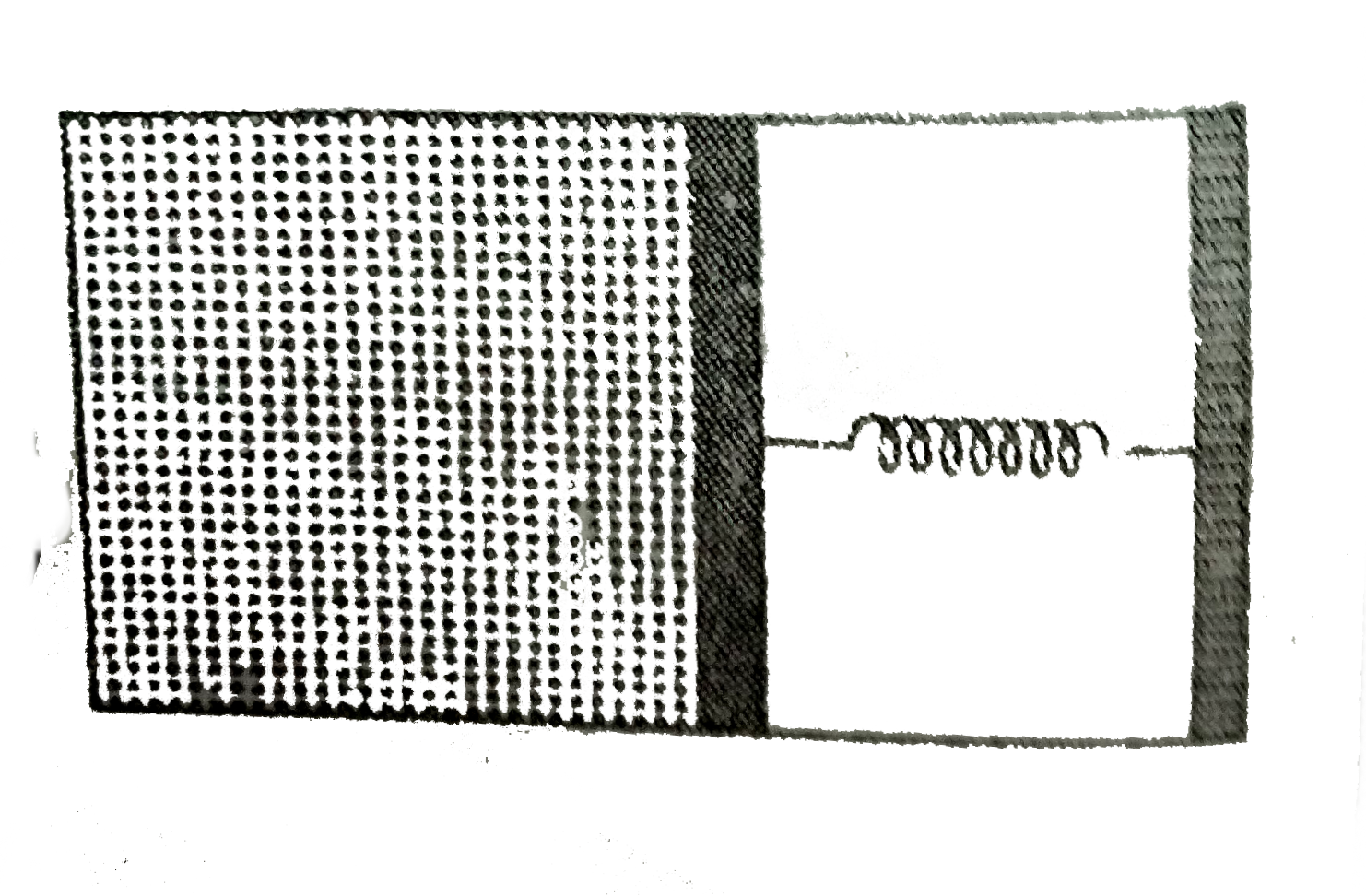
An ideal monatomic gas is confined in a horizontal cylinder by a spring loaded piston (as shown in the figure). Initially the gas is at temperature T1, pressure P1 and volume V1 and the spring is in its relaxed state. The gas is then heated very slowly to temperature T2, pressure P2 and volume V2. During this process the piston moves out by a distance x. lgnoring the friction between the piston and the cylinder, the correct statement (s) is (are)
If V2=2V1 and T2=3T then the energy stored in the spring is
If V2=2V1 and T2=3T1 then the change in internal energy is
If V2=3V1 and T2=4T1 then the work done by the gas is 73P1V1
If V2=3V1 and T2=4T, then the heat supplied to the gas is 176P1V1
The correct Answer is:A, B, C
We will assume that the gas on the side of container having spring is connected to atmosphere. Hence, its pressure remains constant at P1.
In final position of Piston, force balance gives :Kx+P1A=P2A
Where A = cross sectional area of piston
So, Kx=(P2−P1)A ...(1)
Also, P1V1T1=P2V2T2
If V2=2V1,T2=3T1, Then pP2=32P1
Also, V2−V1=Ax ...(ii)
(i) and (ii) give : Kx=(P2−P1)(V2−V1)x
∴ 12Kx2=12(P2−P1)((V2−V1)) ....(iii)
=12(P12)(V1)=P1V14 Hence, (A) is correct.
ΔU=f2(P2V2−P1V1) =32[32×2P1V2−P1V1]=3P1V1
Hence, (B) is correct as well.
Net work done on piston by all forces is zero. So, Wgas=12Kx2−P1(V2−V1)=0
∴ Wgas=P1V13+2P2V1 Wgas=73P1V1
So, (C) also turns out to be correct.
Q=ΔU+W
ΔU=32(P2V2−P1V1)=32(43P1⋅3V1−P1V1) ⇒ ΔU=92P1V1
∴ Q=92P1V1+73P1V1 ⇒ Q=416P1V1
Topper's Solved these Questions
- GASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICSBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:GASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICSExercise:JEE MAIN (ARCHIVE )
Explore 81 Videos
- ENERGY & MOMENTUMBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:ENERGY & MOMENTUMExercise:JEE ADVANCE (ARCHIVE) - TRUE/FALSE TYPE
Explore 1 Video
- GRAVITATIONBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:GRAVITATIONExercise:JEE Advance (Archive) TRUE/FALSE
Explore 1 Video
Similar Questions
Explain why a Carnot engine cannot have 100% efficiency?
View SolutionTwo particles of mass 1 kg and 3 kg move towards each other under their mutual force of attraction. No other force acts on them. When the relative velocity of approach of the two particles is 2m/s, their centre of mass has a velocity of 0.5 m/s. When the relative velocity of approach becomes 3m/s, the velocity of the centre of mass is 0.75 m/s.
View SolutionIs it possible to put an artificial satellite in an orbit in such a way that it always remain visible directly over New Delhi ?
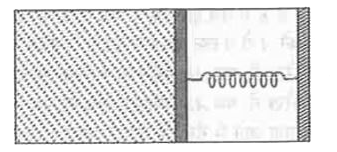
View SolutionAn ideal monoatomic gas is confined in a horizontal cylinder by a spring loaded piston (as shown in the figure). Initially the gas is at temperature T_1 , pressure P_1 and volume V_1 and the spring is in its relaxed state. The gas is tehn heated very slowly to temperature T_2 ,pressure P_2 and volume V_2 . During this process the piston moves out by a distance x. Ignoring the friction between the piston and the cylinder, the correct statement (s) is (are)
View SolutionAn adiabatic cylinder of cross section A is fitted with a mass less conducting piston of thickness d and thermal conductivity K. Initially, a monatomic gas at temperature T_(0) and pressure P_(0) occupies a volume V_(0) in the cylinder. The atmospheric pressure is P_(0) and the atmospheric temperature is T_(1) (gt T_(0)) . Find (a) the temperature of the gas as a function of time (b) the height raised by the piston as a function of time. Neglect friction and heat capacities of the container and the piston.
View SolutionAn ideal gas in thermally insulated vessel at internal (pressure)=P_(1), (volume)=V_(1) and absolute temperature = T_(1) expands irreversiby against zero external, pressure , as shown in the diagram, The final internal pressure, volume and absolute temperature of the gas are p_(2), V_(2) and T_(2) , respectively . For this expansion
View SolutionA cylinder of cross-section area. A has two pistons of negligible mass separated by distances l loaded with spring of negligible mass. An ideal gas at temperature T1 is in the cylinder where the springs are relaxed. When the gas is heated by some means its temperature becomes T2 and the springs get compressed by l2 each . if P0 is atmospheric pressure and spring constant k=2P0Al, then find the ratio of T2 and T1 .
_S01_124_Q01.png)
View SolutionAn ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure =P1, volume =V1 and absolute temperature =T1 expands irreversibly against zero external pressure, as shown in the diagram. The final internal pressure, volume and absolute temperature of the gas are P2,V2 and T2 respectively. For this expansion.
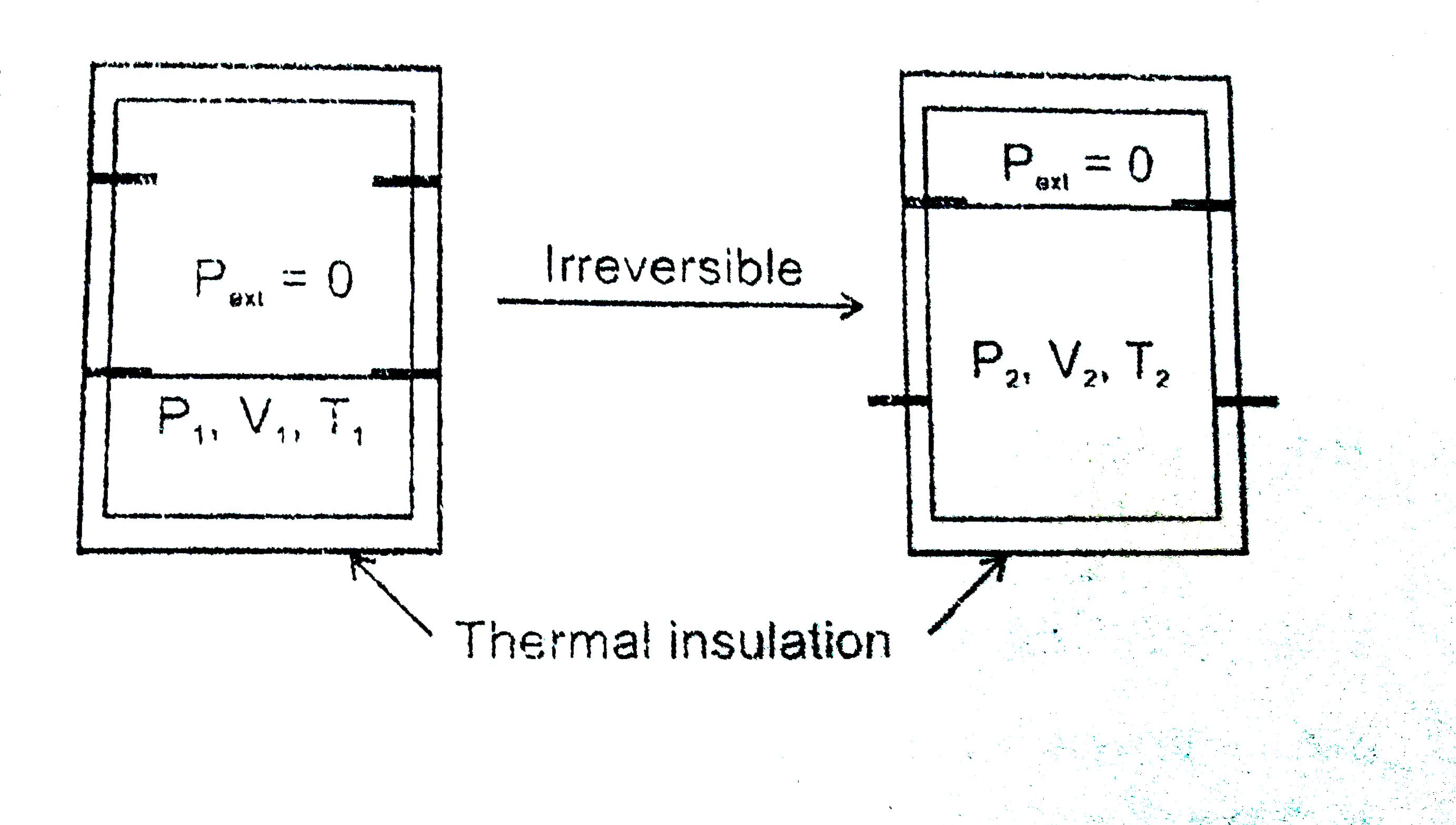
View SolutionIf a gas of a volume V1 at pressure p1 is compressed adiabatically to volume V2 and pressure p2, calculate the work done by the gas.
View SolutionThe initial pressure, temperature & volume of 1 mol of a gas are P1,T1andV1 respectively. The state of the gas is changed by the following two ways. Will the internal energy change be the same in both cases?
(1) P1V1T2Reversible−−−−−→ProcessP2V2T2
(2) P1V1T1Irreversible−−−−−−→processP2V2T2.
View Solutionएकपरमाणुक आदर्श गैस एक क्षैतिज बर्तन (Horizontal cylinder) में स्प्रिंग युक्त पिस्टन द्वारा बन्द है (दर्शाए चित्रानुसार) | प्रारम्भ में गैस का तापमान T1 दाब p1 तथा आयतन V1 है तथा स्प्रिंग विश्रांत अवस्था में है | अब गैस को बहुत धीरे - धीरे तापमान T2 तक गर्म करने पर दाब p2 तथा आयतन V2 हो जाता है | इस प्रक्रिया में पिस्टन x दुरी तय करता है | पिस्टन एवं बर्तन के मध्य घर्षण को नगण्य मानते हुए, सही कथन है (हैं)
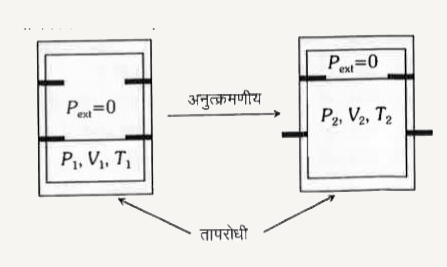
View Solutionऊष्मारोधी बर्तन में एक आदर्श गैस आन्तरिक दाब = P1 आयतन =V1 तथा परमताप = T1 पर शून्य बाह्य दाब के विरूद्ध नीचे दशाये चित्रानुसार अनुत्क्रमणीय प्रसारित होती है। गैस का आखिरी आन्तरिक दाब, आयतन एवं परमताप क्रमशः P2V2 तथा T2 है। इस विस्तारण के लिए
View SolutionAn ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure = P4, volume =V1 and absolute temperature =T1 expands irreversibly against zero external pressure, as shown in the diagram. The final internal pressure, volume and absolute temperature of the gas are P2,V2andT2, respectively. For this expansion.
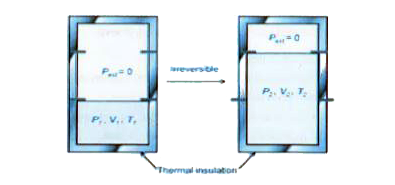
View SolutionAt 25∘C temperature and 760 mm Hg pressure volume of gas is 600 mL, Then calculate pressure when volume of this gas becomes 640 mL at 10∘C temperature. (p1V1T1=p2V2T2)
View SolutionA cylinder of cross-section area. A has two pistons of negligible mass separated by distances l loaded with spring of negligible mass. An ideal gas at temperature T1 is in the cylinder where the springs are relaxed. When the gas is heated by some means its temperature becomes T2 and the springs get compressed by l2 each . if P0 is atmospheric pressure and spring constant k=2P0Al, then find the ratio of T2 and T1 .
_S01_124_Q01.png)
View SolutionAn ideal monoatomic gas is confined in a horizontal cylinder by a spring loaded piston (as shown in the figure). Initially the gas is at temperature T1, pressure P1 and volume V1and the spring is in its relaxed state. The gas is then heated very slowly to temperature T2,pressure P2and volume V2. During this process the piston moves out by a distance x. Ignoring the friction between the piston and the cylinder, the correct statement (s) is (are)

View Solution
