For one mole of a van der Waals gas when b = 0 and T = 300 K , the PV vs 1/V plot is shown below . The value of the van der Waals constant a (atm litre2mol−2) is

(a) 1.0
(b) 4.5
(c) 1.5
(d) 3.0
The correct Answer is:C
The van der Waals’ equation of state is (p+n2aV2)(V−nb)=nRT
For one mole and when b = 0, the above equation condenses to (p+aV2)V=RT
⇒pV=RT−aV …(i)
Eq. (i) is a straight equation between pV and 1V whose slope is −a . Equating with slope of the straight line given in the graph. −a=20.1−21.63−2=−1.5 a=1.5
Topper's Solved these Questions
- STATES OF MATTERBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:STATES OF MATTERExercise:ILLUSTRATION
Explore 30 Videos
- STATES OF MATTERBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:STATES OF MATTERExercise:SOLVED EXAMPLES
Explore 20 Videos
- STATES OF MATTERBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:STATES OF MATTERExercise:JEE-Main ( ARCHIVE )
Explore 17 Videos
- STATES OF MATTERBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:STATES OF MATTERExercise:IMPECCABLE
Explore 50 Videos
- STOICHIOMETRY - IBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:STOICHIOMETRY - IExercise:JEE Advanced (Archive)
Explore 31 Videos
Similar Questions
Temperature of a gas is 98.6∘F. Convert this into Kelvin.
View SolutionHelium atom is two times heavier than a hydrogen molecule. At 289 K, the average kinetic energy of a helium atom is
View SolutionEqual mass of methane and oxygen are mixed in an empty container at 25∘C. The fraction of the total pressure exerted by oxygen is:
View SolutionPressure remaining the constant, the volume of a given mass of an ideal gas increases for every degree centigrade rise in temperature by definite fraction of its volume at:
View SolutionNaturally occurring boron consists of two isotopes whese atomic weights are 10.01 and 11.01. The atomic weight of natural boron is 10.81. Calculate the percentage of each isotope in natural boron.
View SolutionThe compression factor (compressibility factor) for 1 mol of a van der Waals gas at 0^(@)C and 100 atm pressure is found to be 0.5 . Assuming that the volume of a gas molecule is neligible, calculate the van der Waals constant a .
View SolutionThe compression factor (compressibility factor) for 1 mol of a van der Waals gas at 0^(@)C and 100 atm pressure is found to be 0.5 . Assuming that the volume of a gas molecule is neligible, calculate the van der Waals constant a .
View SolutionFor one mole of a van der Waals gas when b=0 and T=30K the PVvs1/V plot is shown below The value of the van Waals constant a (atm litre2mol−2) is
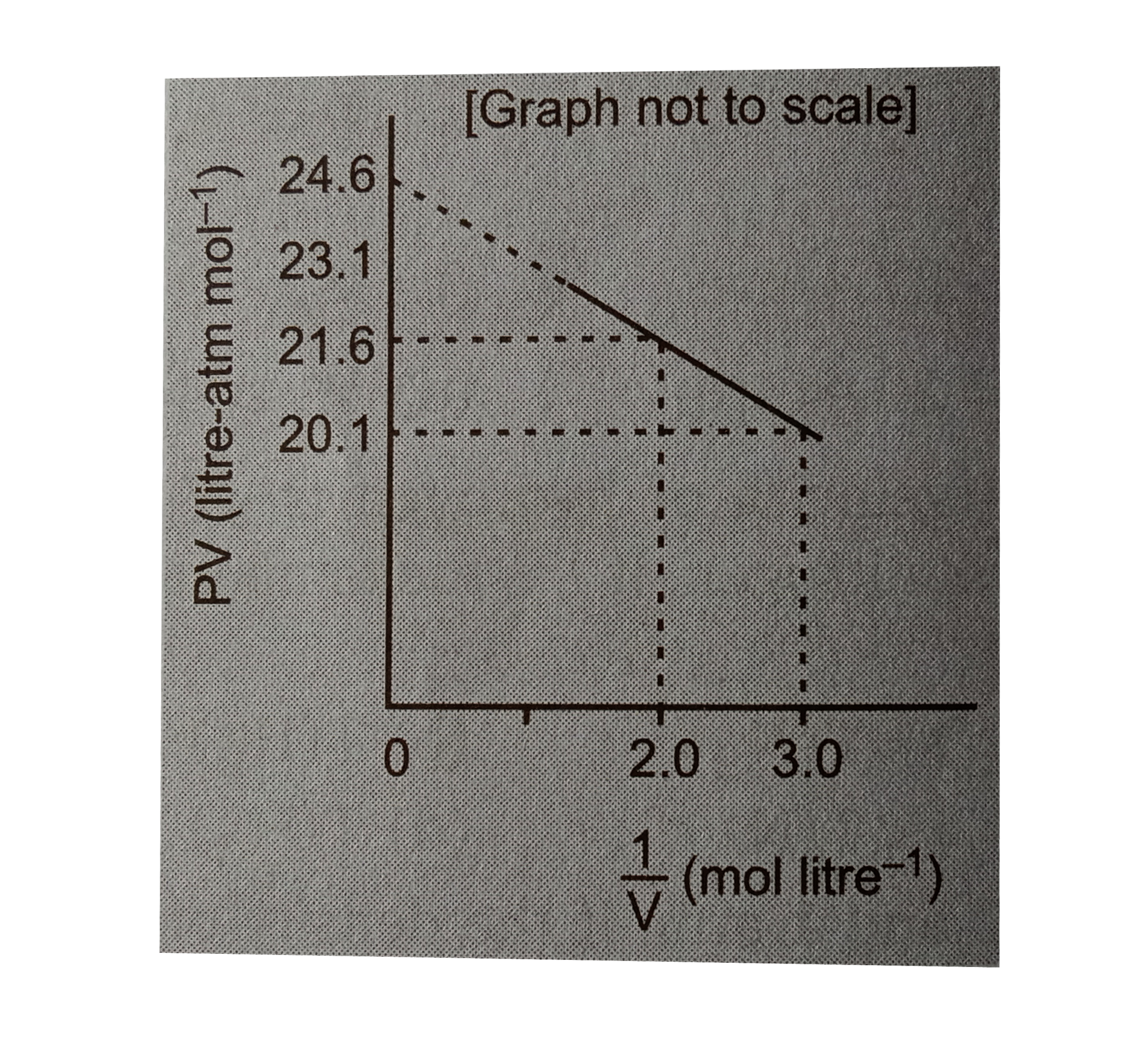 .
.
View SolutionFor one mole of a van der Waals' gas when b=0 and T=300K, the pVvs1/V plot is shown below. The value of the vander Waals' constant a(atm Lmol−2)
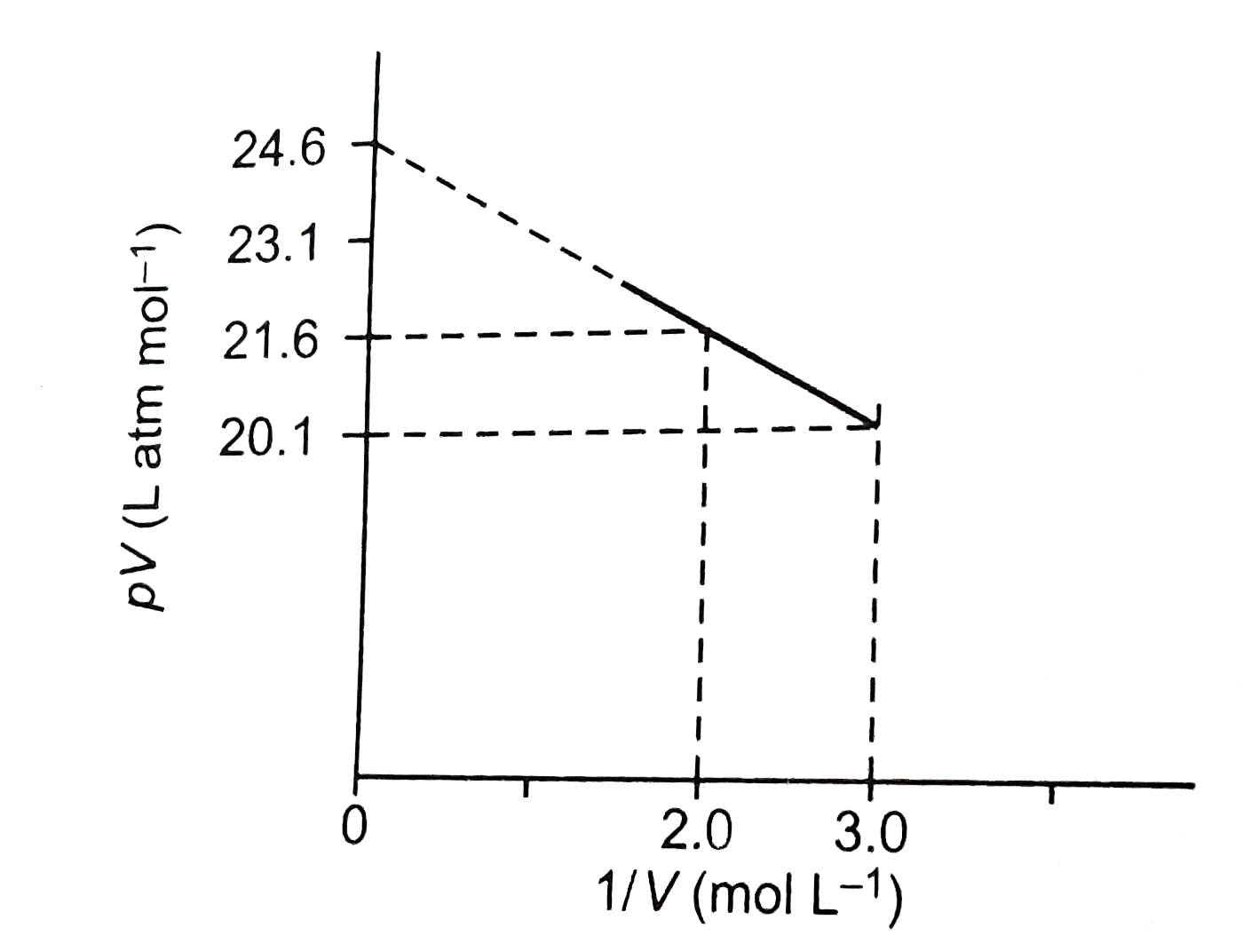
View SolutionFor one mole of a van der Waal's gas when b=0 and T=300K, the PV us 1/V plot is shown ahead. The value of the van der Waal's constant a(atm. litre2mol−2) is:
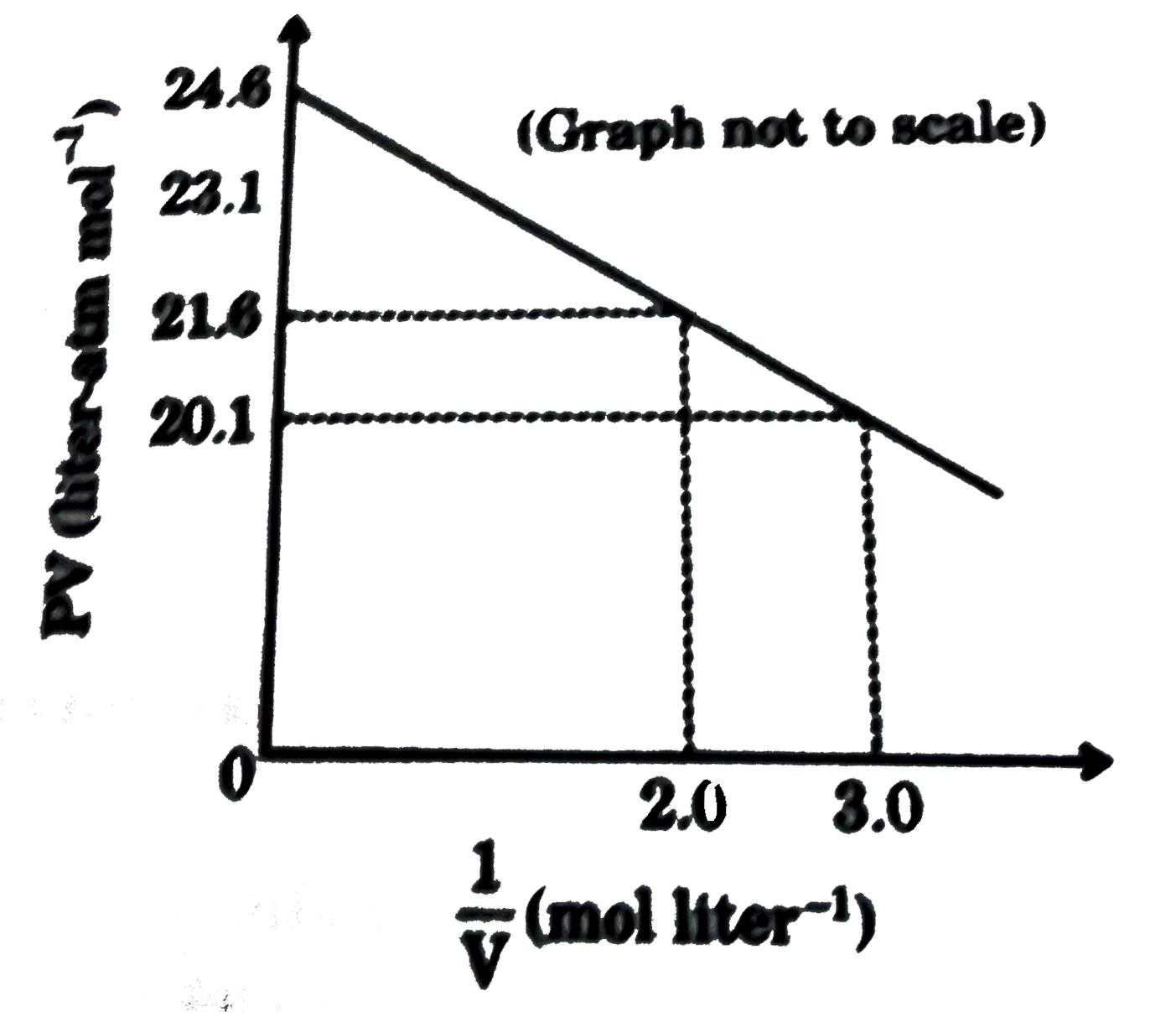
View SolutionThe compression factor (compressibility factor) for one mole of a van der Waals gas at 0^(@)C and 100 atm pressure is found to be 0.5. Assuming that the volume of a gas molecule is negligible, calculate the van der Waals constant a.
View SolutionCalculate the critical constants of a gas whose van der Waals constants are :
a=0.751 L2 atm mol−2 and b=0.0226 L mol−1.
View Solution2 mol of gas is kept in a 4 litre flask. The pressure of the gas at 300 K is 11 atm. If the value of 'b' for the gas is 0.05 L*mol^(-1) , then determine the value of 'a' by using van der waals equation.
View SolutionThe van der Waals equatin for 0.5 mol of a gas is
View SolutionThe unit of van der Waals constant 'a' is
View Solutionजब b=0 और T=300 K है , तब एक मोल वांडरवाल्स (van der Walls') गैस के लिए pV vs 1/V रेखाचित्र नीचे दिखाया गया है।
वांडरवाल्स स्थिरांक a ( वायु. ली2 मोल2 ) का मान है
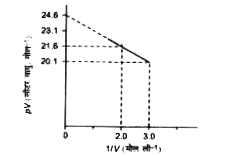
View Solution
