Of the following statements:
(a) C6H5N=CH−C6H5 is a Schiff's base
(b) A dye is obtained by the reaction of aniline and C6H5N=NCl
(c) C6H5CH2NH2 on treatment with [NaNO2+HCl] gives diazonium salt
(d) p-Toluidine in treatment with [HNO2+HCl] gives diazonium salt
Only (a) and (b) are correct
Only (a) and (c) are correct
Only (c) and (d) are correct
(a),(b) and (d) are correct
The correct Answer is:D
To solve the question regarding the statements about amines and their reactions, we will analyze each statement step by step.
1. Definition of Schiff's Base: A Schiff's base is an imine formed by the condensation of an amine with an aldehyde or ketone. It has the general structure R2C=NR'.
2. Analysis of the Given Compound: The compound C6H5N=CH−C6H5 can be rewritten as Ph−N=CH−Ph, where Ph represents the phenyl group (C6H5).
3. Conclusion: Since it has the structure of an imine, it is indeed a Schiff's base.
Result: Statement (a) is correct.
---
Statement (b): A dye is obtained by the reaction of aniline and C6H5N=NCl.
1. Understanding the Reaction: Aniline (C6H5NH2) can react with benzene diazonium chloride (C6H5N2Cl) in a coupling reaction.
2. Mechanism: In this reaction, the diazonium salt acts as an electrophile and substitutes at the para position of aniline, forming an azo dye.
3. Conclusion: The product of this reaction is indeed a dye, specifically an azo dye.
Result: Statement (b) is correct.
---
Statement (c): C6H5CH2NH2 on treatment with (NaNO2+HCl) gives diazonium salt.
1. Analyzing the Compound: The compound C6H5CH2NH2 is benzylamine.
2. Reaction with NaNO2 and HCl: When benzylamine is treated with sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and hydrochloric acid (HCl), it forms an unstable diazonium salt (C6H5CH2N2Cl).
3. Stability of the Diazonium Salt: Benzyl diazonium chloride is unstable and decomposes to form benzyl alcohol and nitrogen gas upon warming.
4. Conclusion: Therefore, while a diazonium salt is formed, it is not stable.
Result: Statement (c) is incorrect.
---
Statement (d): p-Toluidine in treatment with (HNO2+HCl) gives diazonium salt.
1. Understanding p-Toluidine: p-Toluidine (C6H4(CH3)NH2) is an aromatic amine.
2. Reaction with HNO2 and HCl: When p-toluidine is treated with nitrous acid (generated from NaNO2 and HCl), it forms the corresponding diazonium salt (p-toluidine diazonium chloride).
3. Conclusion: This reaction is valid and leads to the formation of a stable diazonium salt.
Result: Statement (d) is correct.
---
Final Conclusion:
- Statements (a), (b), and (d) are correct.
- Statement (c) is incorrect.
Thus, the correct answer is that statements A, B, and D are correct.
2. Analysis of the Given Compound: The compound C6H5N=CH−C6H5 can be rewritten as Ph−N=CH−Ph, where Ph represents the phenyl group (C6H5).
3. Conclusion: Since it has the structure of an imine, it is indeed a Schiff's base.
2. Mechanism: In this reaction, the diazonium salt acts as an electrophile and substitutes at the para position of aniline, forming an azo dye.
3. Conclusion: The product of this reaction is indeed a dye, specifically an azo dye.
2. Reaction with NaNO2 and HCl: When benzylamine is treated with sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and hydrochloric acid (HCl), it forms an unstable diazonium salt (C6H5CH2N2Cl).
3. Stability of the Diazonium Salt: Benzyl diazonium chloride is unstable and decomposes to form benzyl alcohol and nitrogen gas upon warming.
4. Conclusion: Therefore, while a diazonium salt is formed, it is not stable.
2. Reaction with HNO2 and HCl: When p-toluidine is treated with nitrous acid (generated from NaNO2 and HCl), it forms the corresponding diazonium salt (p-toluidine diazonium chloride).
3. Conclusion: This reaction is valid and leads to the formation of a stable diazonium salt.
- Statements (a), (b), and (d) are correct.
- Statement (c) is incorrect.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- AMINESBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:AMINESExercise:ILLUSTRATION
Explore 23 Videos
- AMINESBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:AMINESExercise:SOLVED EXAMPLES
Explore 20 Videos
- AMINESBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:AMINESExercise:EFFICIENT
Explore 49 Videos
- ALDEHYDES,KETONES & CARBOXYLIC ACIDS Book:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:ALDEHYDES,KETONES & CARBOXYLIC ACIDS Exercise:IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE-M
Explore 10 Videos
- ATOMIC STRUCTUREBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:ATOMIC STRUCTUREExercise:JEE Advanced (Archive )
Explore 64 Videos
Similar Questions
Give the structure of (A) (explanations are not required). A(C3H9N) reacts with bezenesulphonyl chloride to give a solid insoluble in alkali'.
View SolutionConvert
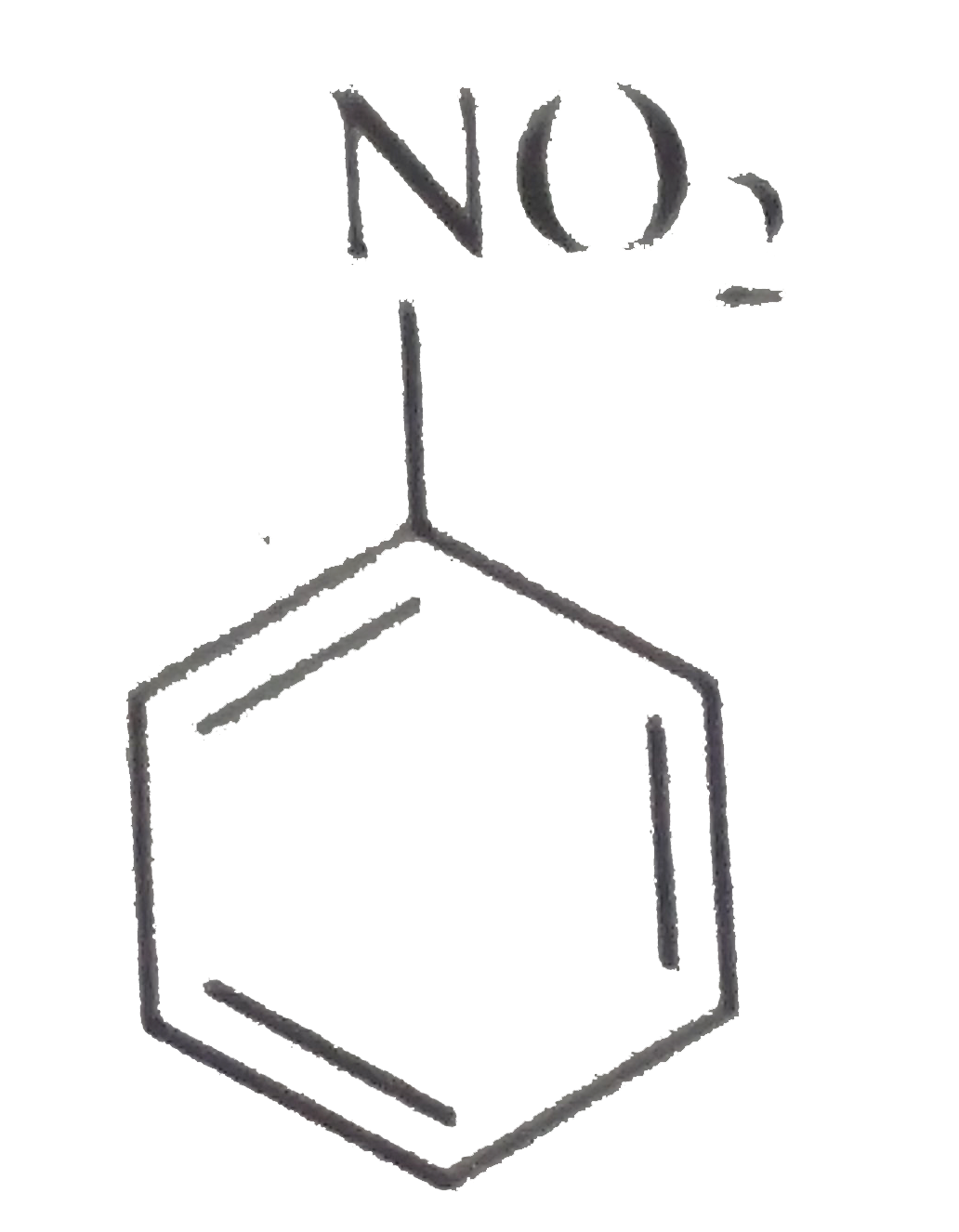
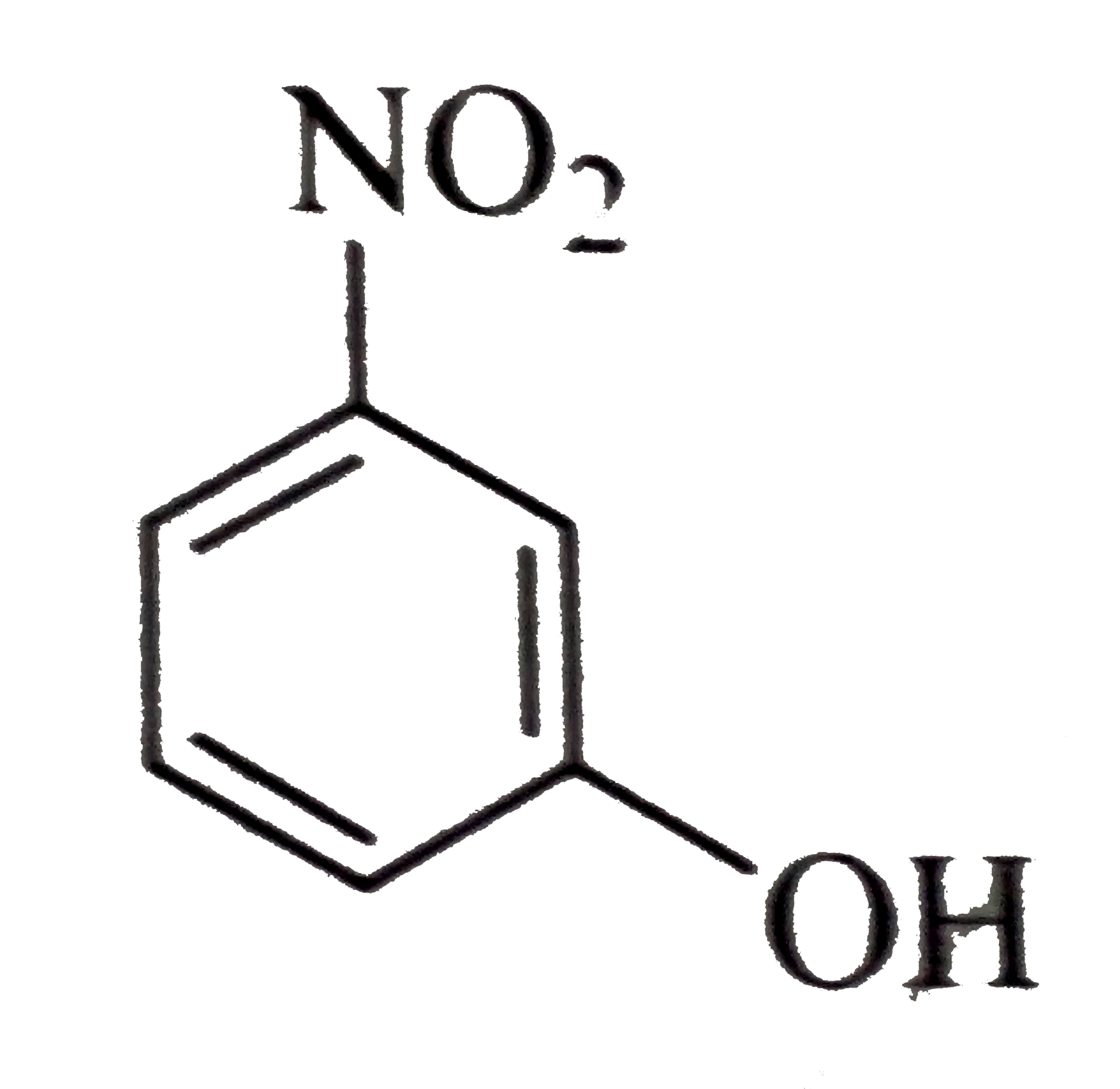 in not more than four steps. Also mention the temperature and reaction conditions.
in not more than four steps. Also mention the temperature and reaction conditions.
View SolutionA compound give violet flame rest and gives a white ppt with AgNO3 .The compound is
View SolutionLiAlH4 is used as :
View SolutionRutherford’s alpha-particle scattering experiment was responsible for the discovery of
View SolutionName the following reaction. C_(6)H_(5)-C-=N overset(SnCl_(2)+HCl)rarr C_(6)H_(5)-CH=N^(o+)H_(2)]Cl^(Θ) overset(H_(2)O)rarr C_(6)H_(5)CHO+NH_(3)
View SolutionIn the reaction
C6H5CHO+C6H5NH2→C6H5N→CHC6H5+H2O.
The compound C6H5N=CHC6H5 is known as
View SolutionArrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength:
(i) C2H5NH2,C6H5NH2,NH3,C6H5CH2NH2and(C2H5)2NH
(ii) C2H5NH2,(C2H5)2NH,(C2H5)3N,C6H5NH2
(iii) CH3NH2,(CH3)2NH,(CH3)3N,C6H5CH2NH2.
View SolutionArrange the following: (i) In decreasing order of the pK_(b) values: C_(2)H_(5)NH_(2),C_(6)H_(5)NHCH_(3),(C_(2)H_(5))_(2)NHandC_(6)H_(5)NH_(2) (ii) In increasing order of basic strength: C_(6)H_(5)NH_(2),C_(6)H_(5)N(CH_(3))_(2),(C_(2)H_(5))_(2)NH andCH_(3)NH_(2) (iii) In increasing order of basic strength: (a) Aniline, p-nitroaniline and p-toluidine (b) C_(6)H_(5)NH_(2),C_(6)H_(5)NHCH_(3),C_(6)H_(5)CH_(2)NH_(2) (iv) In decreasing order of basic strength in gas phase: C_(2)H_(5)NH_(2),(C_(2)H_(5))_(2)NH,(C_(2)H_(5))_(3)NandNH_(3) (v) In increasing order of boiling point: C_(2)H_(5)OH,(CH_(3))_(2)NH,C_(2)H_(5)NH_(2) (vi) In increasing order of solubility in water: C_(6)H_(5)NH_(2),(C_(2)H_(5))_(2)NH,C_(2)H_(5)NH_(2^.)
View SolutionThe decreasing order of basicity of nitrogen in the following compounds is : (a) CH_(3)-CH_(2)-NH_(2),C_(6)H_(5)-NH_(2),H_(2)C=CH-NH_(2) (b) (C_(6)H_(5))_(3)N,(C_(6)H_(5))_(2)NH,C_(6)H_(5)NH_(2) (c) H_(2)C=NH,HCN,CH_(3)NH_(2) (d) C_(6)H_(5)NH_(2),C_(6)H_(11)NH_(2),C_(6)H_(5)CONH_(2) (e) C_(5)H_(5)N,C_(4)H_(4)NH,C_(6)H_(5)NH_(2),CH_(3)CONH_(2) (f) C_(6)H_(5)N(CH_(3))_(2),C_(6)H_(3)(CH_(3))_(2)N(CH_(3))_(2),C_(6)H_(5)NH_(2) (g) H_(2)N-C_(6)H_(4)-OCH_(3),C_(6)H_(5)NH_(2), H_(2)N-C_(6)H_(4)-NO_(2),H_(2)N-C_(6)H_(4)-CH_(2) , H_(2)N-C_(6)H_(4)-Cl (h) {:(C_(6)H_(5)-underset("NH")underset("|| ")"C "-NH_(2)", "O_(2)N-C_(6)H_(4)-underset("NH")underset("|| ")"C "-NH_(2)),(Cl-C_(6)H_(4)-underset("NH")underset("|| ")"C "-NH_(2)", "H_(2)N-C_(6)H_(4)-underset("NH")underset("|| ")"C "-NH_(2)):}
View SolutionC6H5NH2+C6H5COCl→C6H5NHCOC6H6+HCl. This reaction is called
View Solutionनिम्नलिखित को क्रम में लिखिए-
(i) pKb मान के घटते क्रम में -
C2H5NH2,C6H5NHCH3,(C2H5)2NH एवं C6H5NH2
(ii) क्षारकीय प्राबल्य के घटते क्रम में-
C6H5NH2,C6H5(CH3)2,(C2H5)2NH एवं C6H5NH2
(iii) क्षारकीय प्राबल्य के बढ़ते क्रम में- (क) ऐनिलीन , पैरा – नाइट्रोऐनिलीन ,एवं पैरा-टॉलूईन
(ख) C6H5NH2,C6H5NHCH3,C6H5CH2NH2
(iv) गैस अवस्था में घटते हुए क्षारकीय प्राबल्य के क्रम में-
C6H5NH2,(C2H5)2NH,(C2H5)3N एवं NH3
(v) क्वथनांक के बढ़ते क्रम में-
C6H5ON,(CH3)2NH,C2H5NH2
(vi) जल में विलेयता के बढ़ते क्रम में-
C6H5OH,(CH3)2NH,C2H5NH2
View Solutionनिम्नलिखित पदार्थों को बेसिक तीव्रता के घटते क्रम में व्यवस्थित करो-
(i) p टॉलुडीन, N,N− डाइमेथिल−p− टॉलुडीन, p− नाइट्रोऐनिलीन, ऐनिलीन।
(ii) मेथिल ऐमीन, डाइमेथिल ऐमीन, ऐनिलीन, N− मेथिल ऐनिलीन।
(iii) C6H5NH2,C2H5NH2,C2H6,C6H5OH
(iv) p−H2N−C6H4−NH2,
m−H2N−C6H4−NH2 व C6H5NH2
View Solutionनिम्नलिखित को क्रम में लिखिएः
(i) pKb मान घटते क्रम में:
C2H5NH2,C6H5NHCH3,(C2H5)2NH एवं C6H5NH2
(ii) क्षारकीय प्राबल्य के घटते क्रम से:
C6NH5NH2,C6H5N(CH3)2,(C2H5)2NH एवं CH3NH2
(iii) क्षारकीय प्राबल्य के बढ़ते क्रम में:
a. ऐनिलीन, पैरा-नाइइट्रोऐनिलीन एवं पैरा-टॉलूडीन
b. C6H5NH2,C6H5NHCHH3,C6H5C2NH2
(iv) गैस अवस्था में घटते हुए क्षारकीय प्राबलय के क्रम में: C2H5NH2,(C2H5)2NH,(C2H5)3N एवं NH3
(v) क्वथनांक के बढ़ते क्रम में
C2H5OH,(CH3)2,NH,C2H5NH2
(vi) जल में विलेयता के बढ़ते क्रम में:
C6H5NH2,(C2H4)2NH,C2H5NH2
View SolutionIn the reaction : C6H5CHO+C6H5NH2→C6H5N=HCC6H5+H2O, the compound C6H5N=HCC6H5 is known as
View Solutionनिम्नलिखित को क्रम में लिखिए -
(i) pKb मान के घटते क्रम में -
C2H5NH2,C6H5NHCH3,(C2H5)2NHएवं C6H5NH2
(ii) क्षारकीय प्राबल्य के घटते क्रम में -
C6H5NH2,C6H5N(CH3)2,(C2H5)2NH एवं CH3NH2
(iii) क्षारकीय प्राबल्य के बढ़ते क्रम में -
(a) ऐनिलीन , पैरा - नाइट्रोऐनिलीन एवं पैरा-टोलूडीन
(b) C6H5NH2,C6H5NHCH3,C6H5CH2NH2
(iv) गैस अवस्था में घटते हुए क्षारकीय प्राबल्य के क्रम में -
C2H5OH,(C2H5)2NH,(C2H5)3N एवं NH3
(v) क्वथनांक के बढ़ते क्रम में -
C2H5OH,(CH3)2NH,C2H5NH2
(vi) जल में विलेयता के बढ़ते क्रम में -
C6H5NH2,(C2H5)2NH,C2H5NH2.
View Solution
