ICOCl2←−−−AnilineC2H5MgI−−−−−→II. Products I and II are :
Diphenylurea , ehtane
Diphenylurea ,C6H5MgI
Dipphenlamine , ethane
Diphenylamine , benzene
The correct Answer is:A
To solve the question, we need to identify the products formed when aniline reacts with phosgene (COCl₂) and when it reacts with the Grignard reagent (C₂H₅MgI).
Step 1: Reaction of Aniline with Phosgene (COCl₂)
1. Identify the reactants: We have aniline (C₆H₅NH₂) and phosgene (COCl₂).
2. Mechanism of reaction:
- The carbonyl carbon in phosgene is electrophilic due to the presence of the electronegative oxygen.
- The nitrogen atom in aniline, which has a lone pair of electrons, attacks the electrophilic carbon of phosgene.
- This leads to the formation of an intermediate where the chlorine atom is displaced.
3. Formation of the product:
- The intermediate can further react with another molecule of aniline, leading to the formation of a compound known as 1,3-diphenylurea.
- The final product can be represented as:
C6H5N(C=O)N(C6H5)(1,3-diphenylurea)
Step 2: Reaction of Aniline with Grignard Reagent (C₂H₅MgI)
1. Identify the reactants: Aniline (C₆H₅NH₂) and the Grignard reagent (C₂H₅MgI).
2. Mechanism of reaction:
- The carbon in the Grignard reagent (C₂H₅MgI) acts as a nucleophile and can react with the acidic hydrogen of the amine group in aniline.
- The Grignard reagent will abstract the hydrogen from the amine, forming ethane (C₂H₆) and a new compound where the nitrogen is bonded to the magnesium halide (MgI).
3. Formation of the product:
- The reaction leads to the formation of a compound represented as:
C6H5N(MgI)+C2H6(with ethane as a byproduct)
Summary of Products
- Product I (from aniline + phosgene): 1,3-diphenylurea
- Product II (from aniline + C₂H₅MgI): Ethane (C₂H₆)
Final Answer
- Product I: 1,3-diphenylurea
- Product II: Ethane (C₂H₆)
---
2. Mechanism of reaction:
- The carbonyl carbon in phosgene is electrophilic due to the presence of the electronegative oxygen.
- The nitrogen atom in aniline, which has a lone pair of electrons, attacks the electrophilic carbon of phosgene.
- This leads to the formation of an intermediate where the chlorine atom is displaced.
3. Formation of the product:
- The intermediate can further react with another molecule of aniline, leading to the formation of a compound known as 1,3-diphenylurea.
- The final product can be represented as:
C6H5N(C=O)N(C6H5)(1,3-diphenylurea)
2. Mechanism of reaction:
- The carbon in the Grignard reagent (C₂H₅MgI) acts as a nucleophile and can react with the acidic hydrogen of the amine group in aniline.
- The Grignard reagent will abstract the hydrogen from the amine, forming ethane (C₂H₆) and a new compound where the nitrogen is bonded to the magnesium halide (MgI).
3. Formation of the product:
- The reaction leads to the formation of a compound represented as:
C6H5N(MgI)+C2H6(with ethane as a byproduct)
- Product II (from aniline + C₂H₅MgI): Ethane (C₂H₆)
- Product II: Ethane (C₂H₆)
Topper's Solved these Questions
- AMINESBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - AMINESEXERCISE - ILLUSTRATION
23 Videos
- AMINESBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - AMINESEXERCISE - SOLVED EXAMPLES
20 Videos
- AMINESBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - AMINESEXERCISE - EFFICIENT
49 Videos
- ALDEHYDES,KETONES & CARBOXYLIC ACIDS BOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - ALDEHYDES,KETONES & CARBOXYLIC ACIDS EXERCISE - IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE-M
10 Videos
- ATOMIC STRUCTUREBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - ATOMIC STRUCTUREEXERCISE - JEE Advanced (Archive )
64 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Reaction I Ph−O∣∣C−NH2⊕OD,Br2−−−−→A
Reaction II Ph−O∣∣C−ND2⊕OD,Br2−−−−→B
Products A and B are :APh−NH2andPh−ND2BPh−ND2andPh−NH2CBoth Ph−NH2DBoth Ph−ND2Compound having −O∣∣C−CH3 group reacts rapidly with halogen in presence of a base to form haloform. The reaction is known as haloform.
R−O∣∣C−CH3X2+ϴOH−−−−→R−O∣∣C−ϴO+CHX3
Mechanism
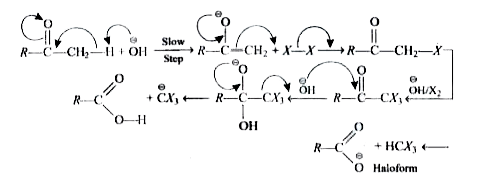
Consider the following reactions:
Reaction I →Ph−O∣∣C−CH3Cl2,ϴOH−−−−→Ph−O∣∣C−ϴO+CHCl3
Reaction II →Ph−O∣∣C−CD3−Cl2,ϴOH−−−−→Ph−O∣∣C−ϴO+CDCl3
Which of the following is correct comparison of the rate of reaction I and II?ArI>rIIBrI>rIICrI=rIIDCannot be determinedCH3−O∣∣C−O−HNaH14CO3−−−−−→(A)(gas)(i)PhMgBr−−−−−−−→(ii)H3O⊕(B)
CH3−O∣∣S∣∣O−O−HNaH14CO3−−−−−→(C)gas(i)PhMgBr−−−−−−−→(ii)H3O⊕(D)
Product (B) and (D) in the above reaction are :APh−O∣∣C−O−H,Ph−O∣∣S∣∣O−O−HBPh−O∣∣C14−O−H,Ph−O∣∣S−O−HCPh−O∣∣C14−O−H,Ph−O∣∣C14−O−HDPh−O∣∣C−OH,Ph−O∣∣S−O−H
PhCOOMe(A)(i)NH2OH−−−−−−−−−→(ii)ӨOH(iii)EtOH(B)
Product (B) is :
View SolutionC2H5IAgNO2−−−→X. Here X(major product) is :
View SolutionIdentify the compounds A, B and C :
(i) C6H5COOHPCl5−−→AH2−Pd/BaSO4−−−−−−−−−→BKCN alc−−−−→distilC
(ii) H−C≡C−HH2O−−−−−−−−−−−−−→ dil H2SO4+HgSO4AH2−−→NiB140∘C−−−−−−→concH2SO4C
View SolutionNumber of monocloro structural isomers of :
(i)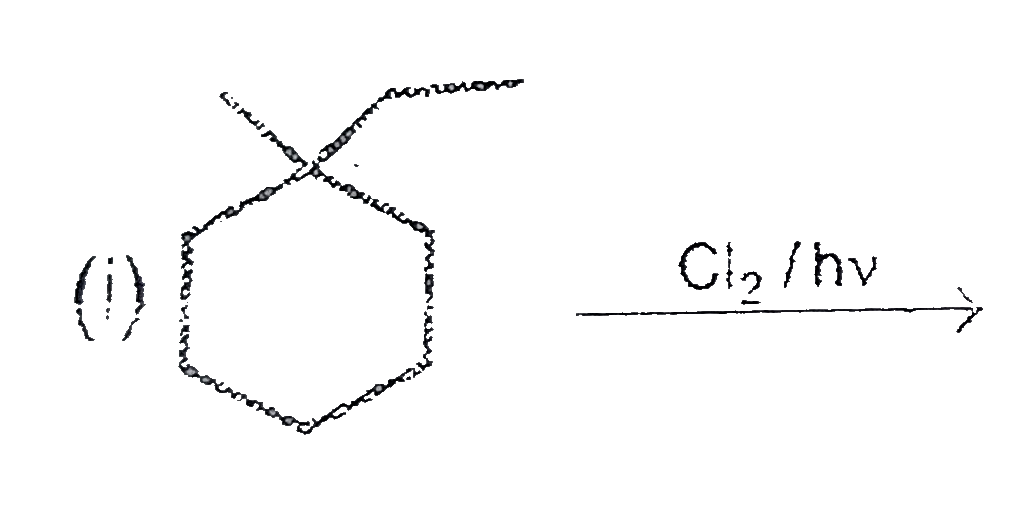 , Cl2/hv−−−→ " " (ii)
, Cl2/hv−−−→ " " (ii) 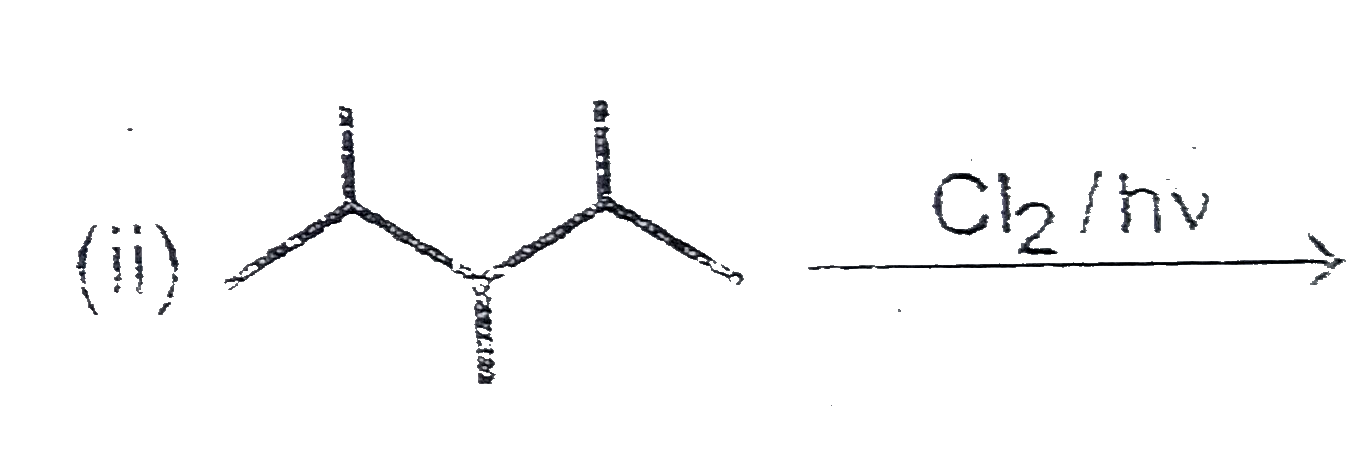 , Cl2/hv−−−→
, Cl2/hv−−−→
View SolutionEtCOCl(A)(i)H2N.OH−−−−−−−→(ii)ӨOH(B)EtOH−−−→(C)
Which of the following statements are correct about the given reaction ?
View Solution

