A wire, which passes through the hole in a small bead, is bent in the form of quarter of a circle. The wire is fixed vertically on ground as shown in the figure. The bead is released from near the top of the wire and it slides along the wire without friction. As the bead moves from A to B, the force it applies on the wire is
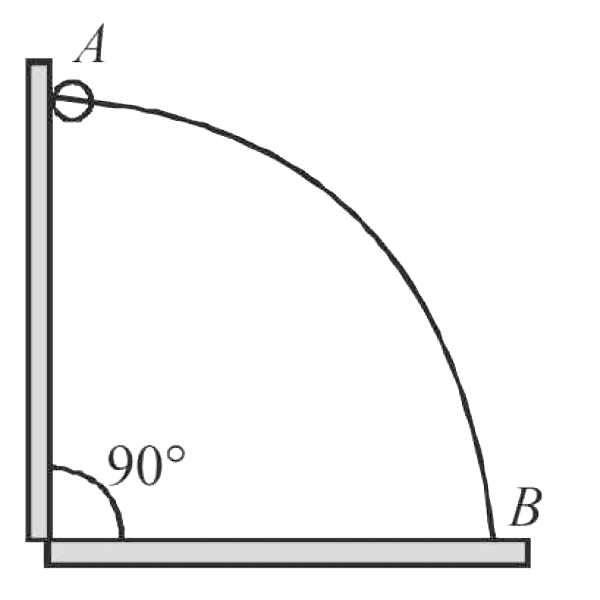 Solution in Gujrati
Solution in Gujrati
Always radially outwards
Always radially inwards
Radially outwards initially and radially inwards later.
Radially inwards initially and radially outwards later
The correct Answer is:D
Step by step video solution for A wire, which passes through the hole in a small bead, is bent in the form of quarter of a circle. The wire is fixed vertically on ground as shown in the figure. The bead is released from near the top of the wire and it slides along the wire without friction. As the bead moves from A to B, the force it applies on the wire is by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
समान प्रश्न
For a particle in uniform circular motion , the acceleration →a at a point p(R,θ) on the circle of radiu R is ( Here θ is measured from the x−aξs )
View SolutionFind dydx for the following :
(i) y=x7/2 (ii) y=x−3
(iii)y=x (iv) y=x5+x3+4x1/2+7
(v) y=5x4+6x3/2+9x (vi) y=ax2+bx+C
(Vii)y=3x^(5)-3x-1/x
View SolutionIn the Bohr's model of hy drogen atom, the electron moves around the nucleus in a circular orbit of radius 5×10−11m. Its time period is 1.5×10−16s. The current associated with the electron motion is:-
View SolutionA wire, which passes through the hole in a small bead, is bent in the form of quarter of a circle. The wire is fixed vertically on ground as shown in the figure. The bead is released from near the top of the wire and it slides along the wire without friction. As the bead moves from A to B, the force it applies on the wire is
View SolutionA piece of wire is bent in the shape of a parabola y = Kx^(2) (y - axis vorical) with a bead of mass m on it . The beat can side on the wire without friction , it stays the wire is now accleated parallel to the bead , where the bead can stay at rest with repect to the wire from the y - axis is
View SolutionA bead of mass m is located on a parabolic wire with its axis vertical and vertex at the origin as shown in figure and whose equastion is x2=4ay. The wire frame is fixed and the bead is released from the point y=4a on the wire frame from rest. The tangential acceleration of the bead when it reaches the position given by y=a is

View Solution
A frictionless wire is fixed between A and B inside a circle of radius R. A small bead slips along the wire. Find the time taken by the bead to slip from A to B.
View SolutionA piece of wire is bent in the shape of a parabola y=kx2 (y-axis vertical) with a bead of mass m on it. The bead can slide on the wire without friction. It stays at the lowest point of the parabola when the wire is at rest. The wire is now accelerated parallel to the x-axis with a constant acceleration a. The distance of the new equilibrium position of the bead, where the bead can stay at rest with respect to the wire, from the y-axis is:
View SolutionA bead of mass m is located on a parabolic wire with its axis vertical and vertex at the origin as shown in figure and whose equations is x2=4ay . The wire frame is fixed and the bead can slide on it without friction . The bead is released from the point y = 4a on the wire frame from rest . The tangential acceleration of the bead when it reaches the position given by y = a is :

View Solutionएक तार जो एक छोटे मोती के मध्य में स्थित छिद्र से गुजरता है, तो एक चतुर्श वृत्त के अनुरूप छोड़ा गया है। तार को भूमि पर उधर्व ताल में स्थित किया गया है जैसा चित्र में दर्शाया गया है। मोती को तार के ऊपरी सिरे से छडा जाता है, जिससे यह तार के अनुदिश बिना किसी घर्षण के सरकता है। जब मोती A से B तक सरकता है, तब इसके द्वारा तार पर लगने वाला बल है:
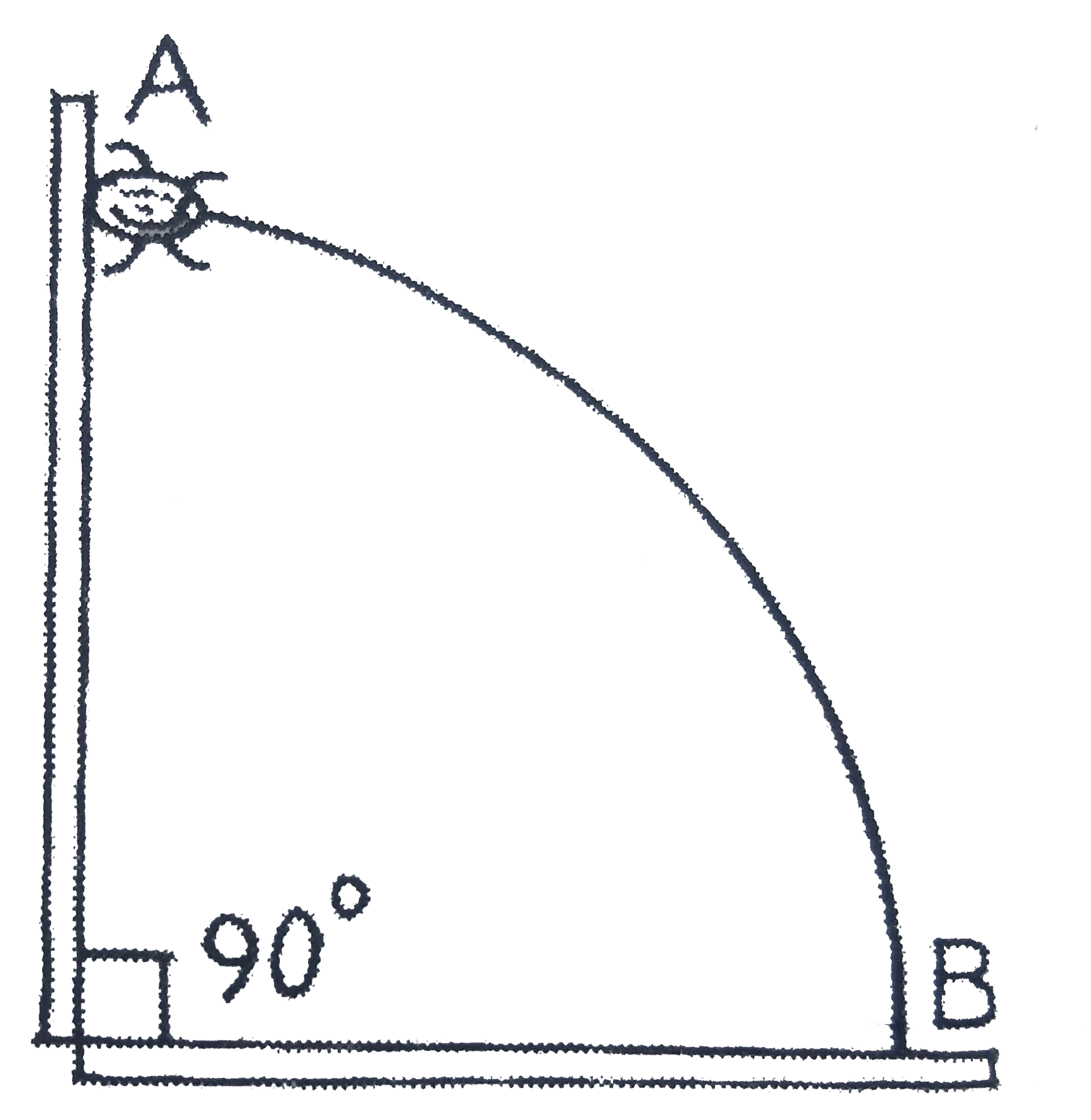
View SolutionA small bead of mass M slides on a smooth wire that is bent in a circle of radius R. It is released at the top of the circular part of the wire (point A in the figure) with a negligibly small velocity. Find the height H where the bead will reverse direction
View SolutionA piece of wire is bent in the shape of a parabola y=kx^(2) (y-axis vertical) with a bead of mass m on it. The bead can slide on the wire without friction. It stays at the lowest point of the parabola when the wire is at rest. The wire is now accelerated parallel to the x-axis with a constant acceleration a. The distance of the new equilibrium position of the bead, where the bead can stay at rest with respect to the wire, from the y-axis is:
View Solutionएक तार जो एक छोटे मोती के मध्य में स्थित छिद्र से गुजरता है, को एक चतुर्थाशा वृत्त के अनुरूप मोड़ा गया है। तार को भूमि पर उर्ध्व तल में स्थित किया गया है, जैसा चित्र में दर्शाया गया है । मोती को तार के ऊपरी सिरे से छोड़ा जाता है, जिससे यह तार के अनुदिश, बिना किसी घर्षण के सरकता है। जब मोती A से B तक सरकता है। तब इसके द्वारा तार पर लगने वाला बल है:
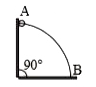
View SolutionA wire, which passes through the hole in a small bead, is bent in the form of quarter of a circle. The wire is fixed vertically on ground as shown in the figure. The bead is released from near the top of the wire and it slides along the wire without friction. As the bead moves from A to B, the force it applies on the wire is

View SolutionA bead of mass m is located on a parabolic wire with its axis vertical and vertex at the origin as shown in figure and whose equastion is x2=4ay. The wire frame is fixed and the bead is released from the point y=4a on the wire frame from rest. The tangential acceleration of the bead when it reaches the position given by y=a is

View SolutionA frictionless wire is fixed between A and B inside a circle of radius R . A small bead slips along the wire. Find the time taken by the bead to slip from A to B .
View Solution

