Molality of pure liquid benzene (C6H6) is its density d = 2 gram/ml
is-
2m
0.78m
12.8m
50m
To find the molality of pure liquid benzene (C₆H₆) with a density of 2 grams/mL, we can follow these steps:
Step 1: Understand the Definition of Molality
Molality (m) is defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. In this case, since we are considering pure benzene, we will treat it as the solute.
Step 2: Calculate the Moles of Benzene
First, we need to find the number of moles of benzene. The molecular weight of benzene (C₆H₆) can be calculated as follows:
- Carbon (C) has an atomic mass of approximately 12 g/mol. Since there are 6 carbon atoms:
12g/mol×6=72g/mol
- Hydrogen (H) has an atomic mass of approximately 1 g/mol. Since there are 6 hydrogen atoms:
1g/mol×6=6g/mol
- Therefore, the molecular weight of benzene is:
72+6=78g/mol
Now, using the density of benzene, we can find the mass of benzene in a specific volume. Since the density is 2 g/mL, in 1 mL of benzene, the mass is 2 grams.
To find the number of moles:
Moles of benzene=massmolar mass=2g78g/mol≈0.02564mol
Step 3: Convert the Mass of Benzene to Kilograms
Since molality is defined per kilogram of solvent, we need to convert the mass of benzene from grams to kilograms:
Mass of benzene in kg=2g1000=0.002kg
Step 4: Calculate Molality
Now we can calculate molality using the formula:
Molality (m)=moles of solutemass of solvent in kg=0.02564mol0.002kg≈12.82mol/kg
Final Answer
Thus, the molality of pure liquid benzene is approximately 12.82 mol/kg.
---
Molality (m) is defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. In this case, since we are considering pure benzene, we will treat it as the solute.
First, we need to find the number of moles of benzene. The molecular weight of benzene (C₆H₆) can be calculated as follows:
- Carbon (C) has an atomic mass of approximately 12 g/mol. Since there are 6 carbon atoms:
12g/mol×6=72g/mol
- Hydrogen (H) has an atomic mass of approximately 1 g/mol. Since there are 6 hydrogen atoms:
1g/mol×6=6g/mol
- Therefore, the molecular weight of benzene is:
72+6=78g/mol
Moles of benzene=massmolar mass=2g78g/mol≈0.02564mol
Since molality is defined per kilogram of solvent, we need to convert the mass of benzene from grams to kilograms:
Mass of benzene in kg=2g1000=0.002kg
Now we can calculate molality using the formula:
Molality (m)=moles of solutemass of solvent in kg=0.02564mol0.002kg≈12.82mol/kg
Thus, the molality of pure liquid benzene is approximately 12.82 mol/kg.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- RACEBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - RACEEXERCISE - Multiple correct
19 Videos
- RACEBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - RACEEXERCISE - Subjective
13 Videos
- Periodic Table BOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - Periodic Table EXERCISE - All Questions
40 Videos
- REACTION MECHANISM (PART-I)BOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - REACTION MECHANISM (PART-I)EXERCISE - MCQ
21 Videos
Similar Questions
The number of oxygen atoms present in 24.5 gm of H3PO4 is equal to (P = 31)
View SolutionFind the volume (in ml) of monoatomic gas that contain 0.005NA atoms at 0∘C & 760 torr.
View SolutionWhich of the following is not correctly matched
View SolutionArrange the following in decreasing order of their stability :- (I)CH3−⊕CH2 (II)CH3−⊕CH∣CH3
(III)CH3−CH3∣C⊕−CH3 (IV)CH2−⊕CH2∣F
View SolutionMole fraction of I2 in C6H6 is 0.2. Calculate molality of I2 in C6H6. (MwofC6H6=78gmol−1)
View Solution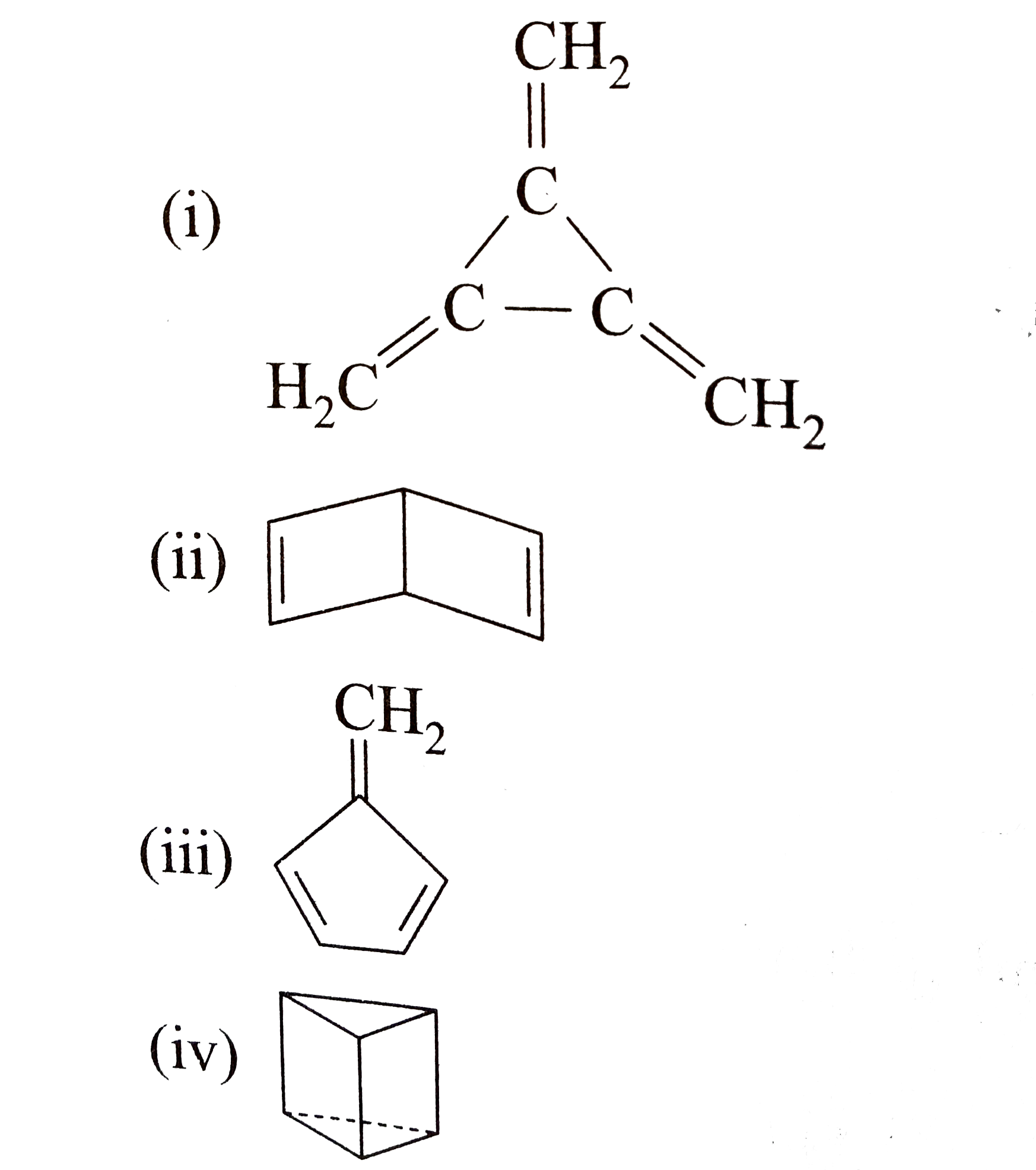
Which of the followng C6H6 structures give only one C6H5Br isomer?
View SolutionC6H6+Br2→C6H5Br+HBr
In an experiment, to prepare bromobenzene according to the equation, a student reacted 20.0g of C6H6 with 0.310 mol of bromine. If 28.0 g of C6H5Br was obtained, what was the percentage yield?
View SolutionMolality of pure liquid ethanol (C_(2)H_(5)OH) if its density d=1.2g//ml is :
View SolutionMolality of pure liquid benzene (C6H6) if its density d=1.2g/ml is :
View SolutionMolality of pure water if its density is 0.936gm/ml :
View SolutionThe mole fraction of a given sample of I_(2) " in " C_(6)H_(6) " is " 0.2 . The molality of I_(2) " in " C_(6) H_(6) is:
View SolutionThe correct order of reactivity of the compounds
(I) C6H5H2(Br), (II) C6H5CH(C6H5)Br, (III) C6H5CH(CH3)Br, (IV) C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5)Br in the increasing order of reactivity in SN2 reactions is
View SolutionHow will you distinguish between C2H5BrandC6H5Br?
View SolutionC2H5Br और C6H5Br में विभेद करने का एक रासयनिक परीक्षण दीजिए-
View SolutionWhich of the following C_(6)H_(6) structures will not give only one C_(6)H_(5)Br isomer
View SolutionThe gram molecule of benzene is equal to __________ g C6H6
View Solution

