The order of stability of the alkenes
R2C=CR2'IR2C=CHRII,R2C=CH2'III<IVbr>(RCH=CHR,)andRCH=CH2V
is -
I>II>III>IV>V
I=II>III>IV>V
II>II>IV>III>V
V>IV>III>I>II
The correct Answer is:A
To determine the order of stability of the given alkenes based on the number of alpha hydrogens and hyperconjugation, we will analyze each alkene step by step.
1. Identify the Structures of the Alkenes:
- Alkene I: R2C=CR′2
- Alkene II: R2C=CHR
- Alkene III: R2C=CH2
- Alkene IV: RCH=CHR
- Alkene V: RCH=CH2
2. Assume R as Methyl (CH₃):
To simplify the calculation, we will assume that R is a methyl group (CH₃) for each alkene.
3. Count Alpha Hydrogens:
- Alkene I: R2C=CR′2 (Assuming R = CH₃)
- Structure: (CH3)2C=CH2
- Alpha Hydrogens: 12 (from both CH3 groups)
- Alkene II: R2C=CHR
- Structure: (CH3)2C=CH3
- Alpha Hydrogens: 9 (from two CH3 groups and one CH group)
- Alkene III: R2C=CH2
- Structure: (CH3)2C=CH2
- Alpha Hydrogens: 6 (from two CH3 groups)
- Alkene IV: RCH=CHR
- Structure: CH3CH=CH3
- Alpha Hydrogens: 6 (from two CH3 groups)
- Alkene V: RCH=CH2
- Structure: CH3CH=CH2
- Alpha Hydrogens: 3 (from one CH3 group)
4. Order of Stability:
Based on the number of alpha hydrogens:
- Alkene I: 12 alpha hydrogens (most stable)
- Alkene II: 9 alpha hydrogens
- Alkene III: 6 alpha hydrogens
- Alkene IV: 6 alpha hydrogens
- Alkene V: 3 alpha hydrogens (least stable)
5. Final Order:
The order of stability from most stable to least stable is:
- I > II > III = IV > V
Conclusion:
Thus, the order of stability of the alkenes is:
I > II > III = IV > V
- Alkene I: R2C=CR′2
- Alkene II: R2C=CHR
- Alkene III: R2C=CH2
- Alkene IV: RCH=CHR
- Alkene V: RCH=CH2
To simplify the calculation, we will assume that R is a methyl group (CH₃) for each alkene.
- Alkene I: R2C=CR′2 (Assuming R = CH₃)
- Structure: (CH3)2C=CH2
- Alpha Hydrogens: 12 (from both CH3 groups)
- Alkene II: R2C=CHR
- Structure: (CH3)2C=CH3
- Alpha Hydrogens: 9 (from two CH3 groups and one CH group)
- Alkene III: R2C=CH2
- Structure: (CH3)2C=CH2
- Alpha Hydrogens: 6 (from two CH3 groups)
- Alkene IV: RCH=CHR
- Structure: CH3CH=CH3
- Alpha Hydrogens: 6 (from two CH3 groups)
- Alkene V: RCH=CH2
- Structure: CH3CH=CH2
- Alpha Hydrogens: 3 (from one CH3 group)
Based on the number of alpha hydrogens:
- Alkene I: 12 alpha hydrogens (most stable)
- Alkene II: 9 alpha hydrogens
- Alkene III: 6 alpha hydrogens
- Alkene IV: 6 alpha hydrogens
- Alkene V: 3 alpha hydrogens (least stable)
The order of stability from most stable to least stable is:
- I > II > III = IV > V
Thus, the order of stability of the alkenes is:
I > II > III = IV > V
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ALKENE, ALKANE & ALKYNE BOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - ALKENE, ALKANE & ALKYNE EXERCISE - EXERCISE-2
103 Videos
- ALKENE, ALKANE & ALKYNE BOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - ALKENE, ALKANE & ALKYNE EXERCISE - EXERCISE-3
99 Videos
- ALKENE, ALKANE & ALKYNE BOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - ALKENE, ALKANE & ALKYNE EXERCISE - EXCERSISE-3
28 Videos
- AIIMS 2019BOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - AIIMS 2019EXERCISE - CHEMISTRY
40 Videos
- ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDEBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDEEXERCISE - EXERCISE-05 (B)
35 Videos
Similar Questions
Which of the following reactions will result in the formation of a chiral centre in the product?
View SolutionStatement-I : Of two isomeric alkennes shown,
_E01_041_Q01.png) II is more stable than I.
II is more stable than I.
Because
Statement-II : The alkene (II) has sp^(2)-hybridlzed carbons.
View Solution_E01_735_Q01.png) True or False
True or False
View SolutionSelect the correct statements
View SolutionMonochlorination of toluene in sunlight followed by hydrolysis with aq. NaOH yields
View SolutionCH3−C∣ClH−C∣IH−CH3
CH3−C∣CH3H−(CH2)4−C∣CH3H−C∣BrH−CH2CH3
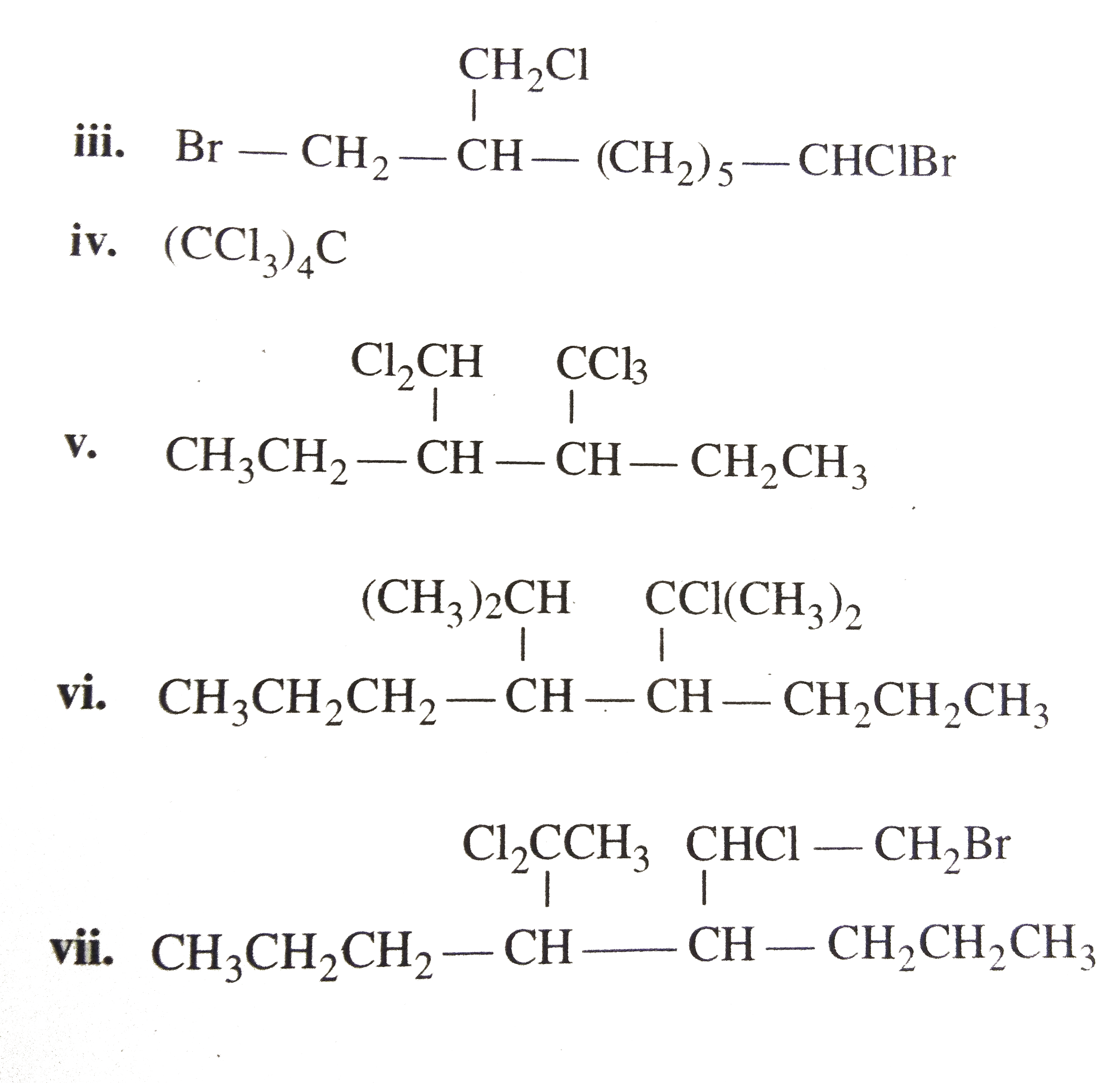
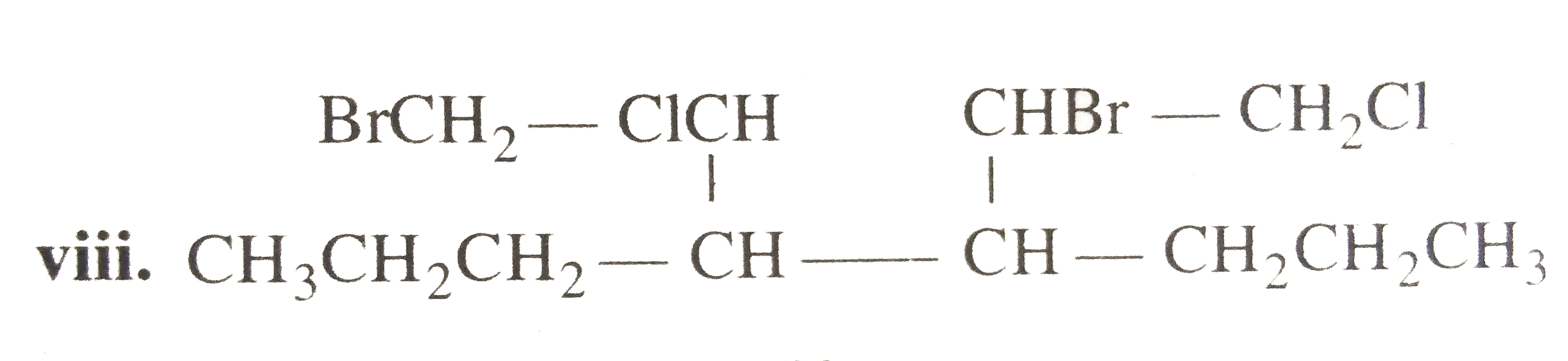
View SolutionRelative stabilities of various alkenes represented as R2C=CR2,R2C=CHR,RCH=CHR (trans), RCH=CHR(cis) are in the increasing order
View SolutionArrange the following free radicals in order of stability underset(I)underset()((CH_(3))_(3)overset(cdot)C)" "underset(II)underset()((CH_(3))_(2)overset(cdot)CH)" "underset(III)underset()(CH_(3)overset(cdot)CH_(2))" "underset(IV)underset()(overset(cdot)CH_(3))
View SolutionArrange the following carbonium ions in order of decreasing stability : underset(I)underset()((CH_(3))_(3)overset(+)C)" "underset(II)underset()((CH_(3))_(2)overset(+)CH)" "underset(III)underset()(CH_(3)overset(+)CH_(2))" "underset(IV)underset()(overset(+)H_(3)C)
View SolutionArrange the following compounds in increasing order of reactivity towards the addition of HBr RCH = CHR, CH_(2)=CH2, R2C = CHR, R2 = CR_(2)
View SolutionThe basic strength of
CH≡CI,CH2=CHII,CH3CH−2III
will be in order
View SolutionStability of pi -bond in following alkenes in the increasing order is : underset("(I)")CH_(3)-CH=CH-CH_(3)" "underset("(II)")(CH_(3)-underset(CH_(3))underset(|)C=underset(CH_(3))underset(|)C-CH_(3))" "underset("(III)")(CH_(3)-underset(CH_(3))underset(|)C=CH_(2))" "underset("(IV)")(CH_(3)-underset(CH_(3))underset(|)C=CH-CH_(3))
View SolutionConsidering the following alkene: The correct decreasing order of stability is: {:(underset("(I)")underset("But-l-ene")(CH_(3)CH_(2)=CH_(2))", "underset("(II)")underset("2,3-Dimethylbut-2-ene")((CH_(3))_(2)C=C(CH_(3))_(2)",")),(underset("(III)")underset("2-Methylbut-2-ene")((CH_(3))_(2)C=CHCH_(3))", "underset("(IV)")underset("2-Methylpropene")((CH_(3))_(2)C=CH_(2))):}
View Solution:CH_(2)-underset(underset(..)(O: ))underset(||)(C )-CH_(3) and H_(2)C=underset(underset(..)( :O: ))underset("|")("C")-CH_(3) are :
View SolutionArrange the following compounds in increasing order of reactivity towards the addition of HBr
RCH=CHR,CH2∣∣CH2,R2C=CHR,R2C=CR2
View SolutionName the following compounds according to IUPAC system. (i) CH_(3) - CH_(2) - underset (CH_(2)Cl) underset(|)(CH) - overset (CH_(2)OH) overset(|) (CH) - underset (CH_(3)) underset (|) (CH) - CH_(3) CH_(3)- underset (CH_(3)) underset(|) (CH) -CH_(2) - underset(OH) underset(|) (CH) - overset (CH_(2)OH) overset(|) (CH) - CH_(2) (iii) (iv) H_(2)C = CH - underset (OH)underset (|) (CH) - CH_(2) - CH_(2) - CH_(3) (v) CH_(3) - underset (CH_(3)) underset ( |) C = underset (Br)underset(|) C - CH_(2)OH
View Solution

