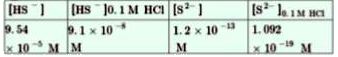
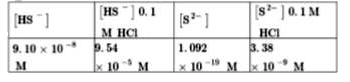
The first ionization constant of H2S is 9.1×10−8. Calculate the concentration of HS− ion in its 0.1 M solution. How will this concentration be affected, if the solution is 0.1 M in HCl also? If the second dissociation constant of H2S is 1.2×10−13 , then calculate the concentration of S2− under both conditions. Select these four answers from the choices given below.

None of these
The correct Answer is:A
(i) H2S+H2O)(+)⇔H3O++HS−
Ka1=[H3O+][HS−][H2S]
[H3O+]=[HS−]=√Ka1⋅C
=√9.1×10−8×0.1=9.54×10−5M
(ii) In the presence of 0.1 M HCl, [H3O+]=0.1M
Ka1=[H2O+][HS−][H2S]
9.1×10−8=[0.1][HS−][0.1]
[HS−]=9.1×10−8M.
Hence, the concentration of [HS−] is decreased in the presence of 0.1 M HCl due to the common-ion effect.
(iii) For the second dissociation constant,
HS−+H2O⇔H3O++S2− [In the absence of HCI]
[HS−]=[H3O+]
Ka2=[H3O+][S2−][HS−]
[S−2]=Ka2=1.2×10−13
(iv) In the presence of 0.1 M HCI,
Ka2=[H2O+][S2−][HS−]=1.2×10−13=[0.1][S2−][9.1×10−8]
[S2−]=1.092×10−19M.
टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
- EQUILIBRIUM TEST (CHEMICAL)-1BOOK - NTA MOCK TESTSCHAPTER - EQUILIBRIUM TEST (CHEMICAL)-1EXERCISE - SINGLE CHOICE
30 Videos
- ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY TESTBOOK - NTA MOCK TESTSCHAPTER - ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY TESTEXERCISE - CHEMISTRY
30 Videos
- GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TEST-1BOOK - NTA MOCK TESTSCHAPTER - GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TEST-1EXERCISE - MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
30 Videos
समान प्रश्न
Bromine monochloride ( BrCl ) decomposes into bromine and chlorine according to reaction 2BrCl(g)=Br2(g)+Cl2(g),Kc=32 at 500 K. If initially, pure BrCl is taken at concentration 3.3×10−3mol L−1, what is its molar concentration in the mixture at equilibrium state?
View SolutionEutrophication causes reduction in
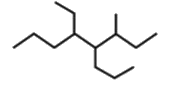
View SolutionThe correct IUPAC name of the following hydrocarbon is
View SolutionThe first ionization constant of H2S is 9.1×10−8. Calculate the concentration of HSΘ ion in its 0.1M solution. How will this concentration be affected if the solution is 0.1M in HCl also? If the second dissociation constant if H2S is 1.2×10−13, calculate the concentration of S2− under both conditions.
View SolutionThe dissociation constant of H2S and HS− are respectively 10−7 and 10−13 . The pH of 0.1 M aqueous solution of H2S will be
View SolutionAn aqueous solution contains 0.10 M H_(2)S " is "1.0 xx 10^(-7)" and that of " S^(2-) "ion from " HS^(-) "ions is " 1.2 xx 10^(-3) ," then the concentration of " S^(2-) " ions in aqueous solution is "
View SolutionThe first ionization constant of H_(2)S is 9.1xx10^(-8) . Calculate the concentration of HS^(-) ions in its 0.1 M solution and how will this concentration be affected if the solution is is 0.1 M in HCl also ? If the second dissociation constant of H_(2)S is 1.2xx10^(-13) , calculate the concentration of S^(2-) under both conditions.
View SolutionH2S का प्रथम आयनन सिथरांक 9.1×10−8 हैं। इसके 0.1 M विलयन में HS− आयनों की सांद्रता की गड़ना कीजिये तथा बताइये की यदि इसमें 0.1 M HCl भी उपस्थित हो तो सांद्रता किस प्रकार प्रभावित होगी? यदि H2S का द्वितीय वियोजन सिथरांक 1.2×10−13 हो तो सल्फाइड S2− आयनों की दोनों सिथितयों की गड़ना कीजिये।
View SolutionH2S का प्रथम आयनन स्थिरांक 9.1×10−8 है। इसके 0.1M विलयन में HS− आयनों की सान्द्रता की गणना कीजिए तथा बताइये की यदि इसमें 0.1MHCI भी उपस्थित हो तो सान्द्रता किस प्रकार प्रभावित होगी ? यदि H2S का द्वितीय वियोजन स्थिरांक 1.2×10−13 हो तो सल्फाइड S2− आयनों की दोनों स्थितियों में सान्द्रता की गणना कीजिए।
View SolutionH2S का प्रथम आयनन स्थिरांक 9.1×10−8 हैं । 0.1 हो , तो विलयन में HS− आयनो की सांद्रता की गणना कीजिए तथा बताइए की यदि इसमें 0.1 M HCI भी उपस्थित हो , तो सांद्रता किस प्रकार प्रभावित होगी , यदि H2S द्वितीय वियोजन स्थिरांक 1.2×10−13 हो तो सल्फाइड S2− आयनों की दोनों स्थितियों में सांद्रता की गणना कीजिए ।
View SolutionThe first ionisation constant of H2S is 9.1×10−8. Calculate the concentration of HS− ion in its 0.1(M) solution. How this concentration be affected if the solution is 0.1(M) in HCl also? If the second dissociation constant of H2S is 1.2×10−13, calculate the concentration of S2− under both conditions.
View SolutionAn aqueous solution contains 0.10MH2S and 0.20MHCl . If the equilibrium constants for the formation of HS− from H2S is 1.0×10−7 and that of S2− from HS− ions is 1.2×10−13 then the concentration of S2− ions in aqueous solution is -
View Solutionएक जलीय विलयन में 0.10M H2S तथा 0.20 MHCl है। यदि H2S से HS− बनाने के लिये साम्य स्थिरांक 1.0×10−7 तथा HS− से S2− बनाने के लिये 1.2×10−13 हो तो, S2− आयनों की जलीय विलयन में सान्द्रता होगी
View SolutionAn aqueous solution contains 0.10 M H2S and 0.20 M HCl. If the equilibrium constants for the formation of HS^(-) from H_(2)S" is " 1.0 xx 10^(-7) " and that of " S^(2-) " from " 4S^(-) " ions is " 1.2 xx 10^(-13) , then find the concentration of S^(-2) ions in aqueous solution
View SolutionThe first ionization constant of H2S is 9.1×10−8. Calculate the concentration of HS− ion in its 0.1M solution. How will this concentration be affected if the solution is 0.1M in HCl also ? If the second dissociation constant of H2S is 1.2×10−13 , calculate the concentration of S2− under both conditions.
View SolutionThe first ionization constant of H2S is 9.1×10−8. Calculate the concentration of HSΘ ion in its 0.1M solution. How will this concentration be affected if the solution is 0.1M in HCl also? If the second dissociation constant if H2S is 1.2×10−13, calculate the concentration of S2− under both conditions.
View Solution

