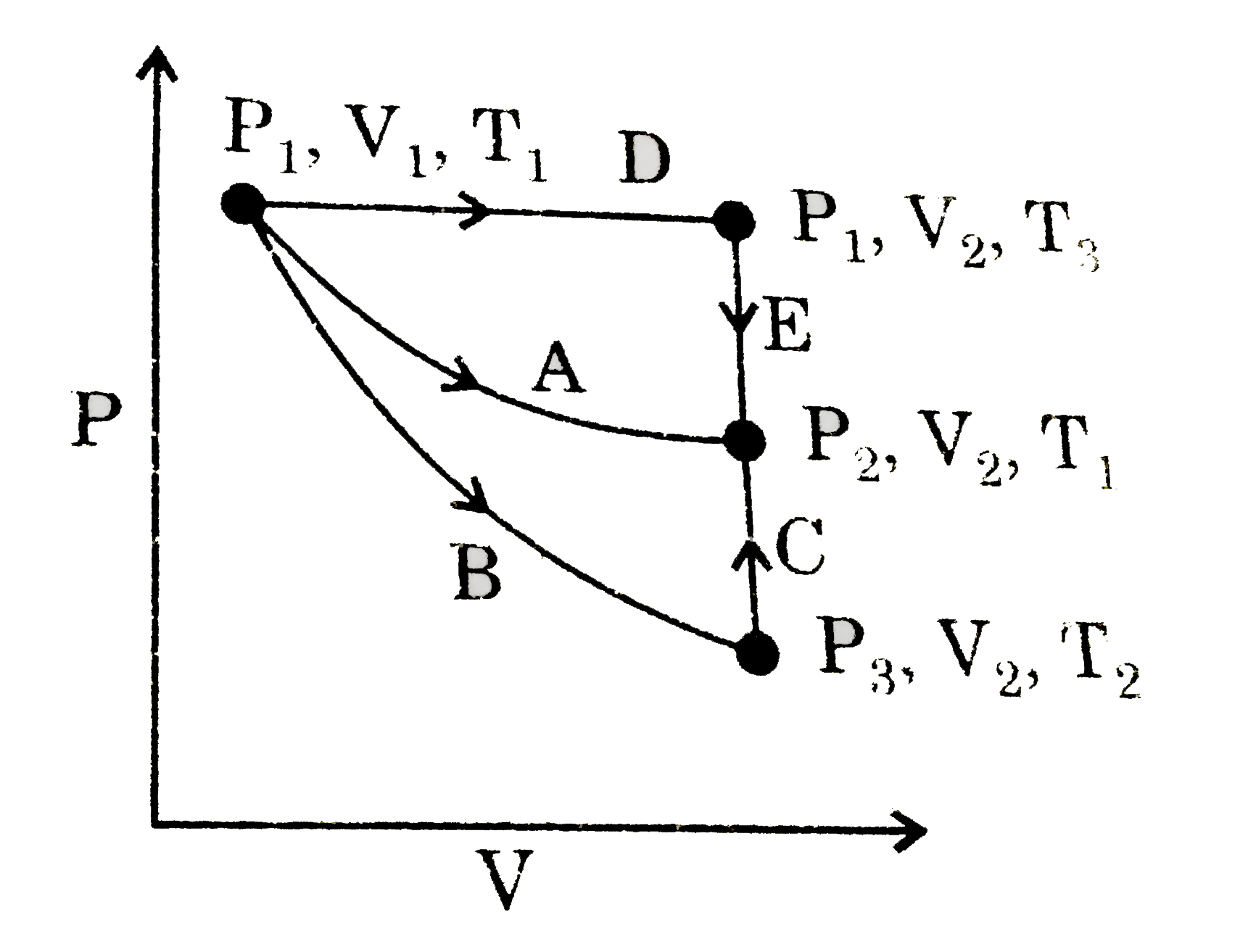
For an ideal gas, an illustration of three different paths A,(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P1,V1,T1 to a final state P2,V2,T1 is shown in the given figure.
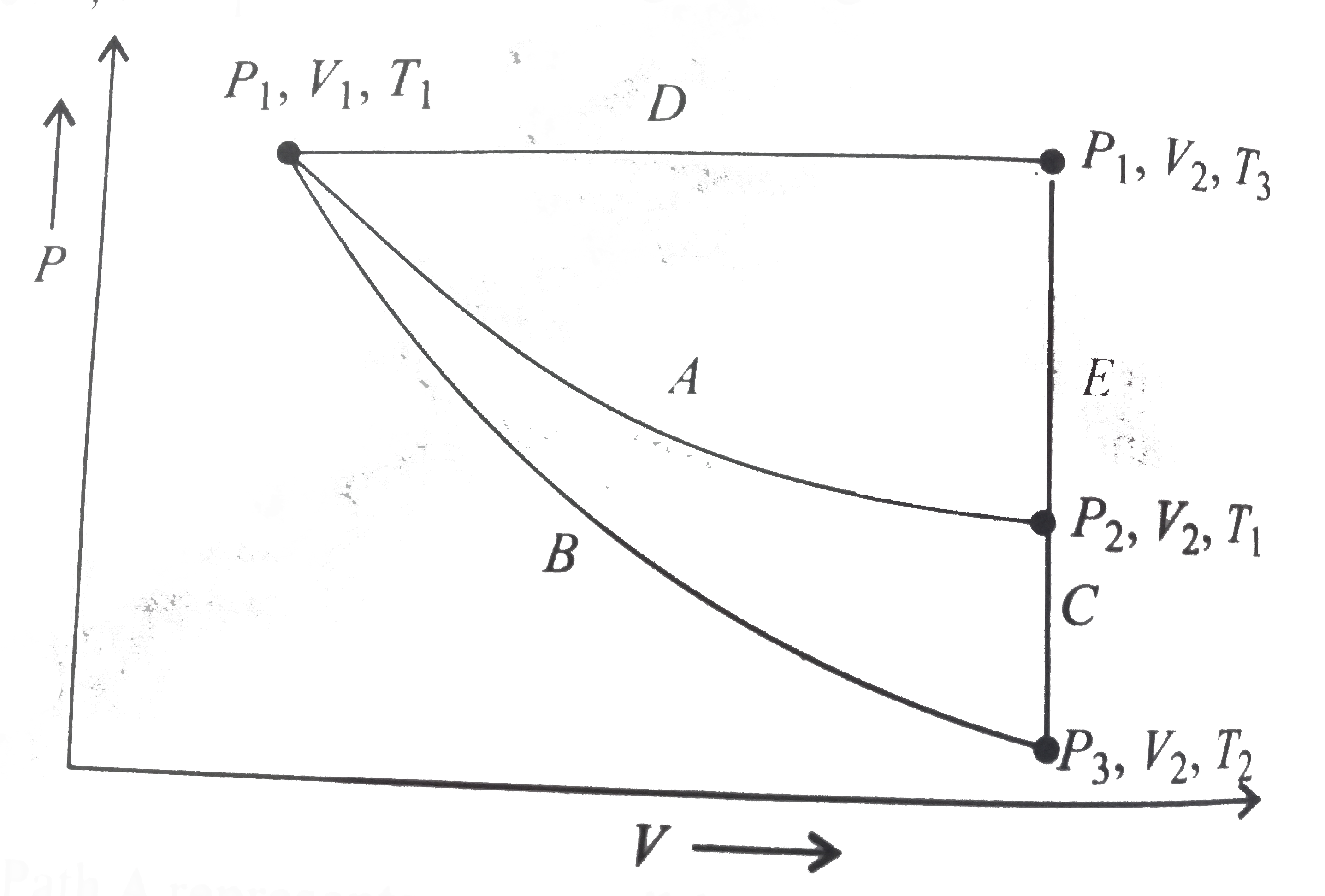
Path Arepresents a reversible isothermal expansion form P1,V1 to P2,V2, Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1→P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C)from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2,T1. Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P1(D) from P1,V1,T1 to P1,V2,T3 followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V2(E) from P1,V2,T3→P2,V2,T1.
What is qrev, for path A?
Stress
Young's modulus
Pressure
all the above
The correct Answer is:D
Step by step video solution for For an ideal gas, an illustration of three different paths A,(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P_(1), V_(1), T_(1) to a final state P_(2), V_(2),T_(1) is shown in the given figure. Path Arepresents a reversible isothermal expansion form P_(1),V_(1) to P_(2),V_(2), Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1)to P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C)from P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) to P_(2),V_(2),T_(1). Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P_(1)(D) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) to P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V_(2)(E) from P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) to P_(2),V_(2),T_(1). What is q_(rev), for path A? by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- UNITS AND MEASUREMENTBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - UNITS AND MEASUREMENTEXERCISE - EXERCISE - II
61 Videos
- UNITS AND MEASUREMENTBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - UNITS AND MEASUREMENTEXERCISE - PRACTICE EXERCISE
45 Videos
- UNITS AND MEASUREMENTBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - UNITS AND MEASUREMENTEXERCISE - PRACTICE EXERCISE
45 Videos
- SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICESBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICESEXERCISE - EXERCISE - III
3 Videos
- UNITS AND MEASUREMENTSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - UNITS AND MEASUREMENTSEXERCISE - EXERCISE -3
66 Videos
Similar Questions
The density of mercury is 13.6gcm−3 in CGS system. Its density in SI system is :
View SolutionThe ratio of S.I unit of the C.G.S unit of gravitational constant 'G' is-
View SolutionThe ratio of S.I unit of the C.G.S unit of gravitational constant 'G' is-
View SolutionThe intrinsic carrier density in germanium crystal at 300 K is 2.5×1013 per cm3. if the electron density in an N-type germanium crystal at 300 K be 0.5×1017 per cm3 the hole density (per cm3) in this N-type crystal at 300 K would be expected around-
View SolutionThe length of a rectangular plate is measured as 10 cm by a vernier scale of least count 0.01 cm and its breadth as 5 cm by the same scale. The percentage error in area is
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P1,V1,T1 to a final state P2,V2,T1 is shown in the given figure.
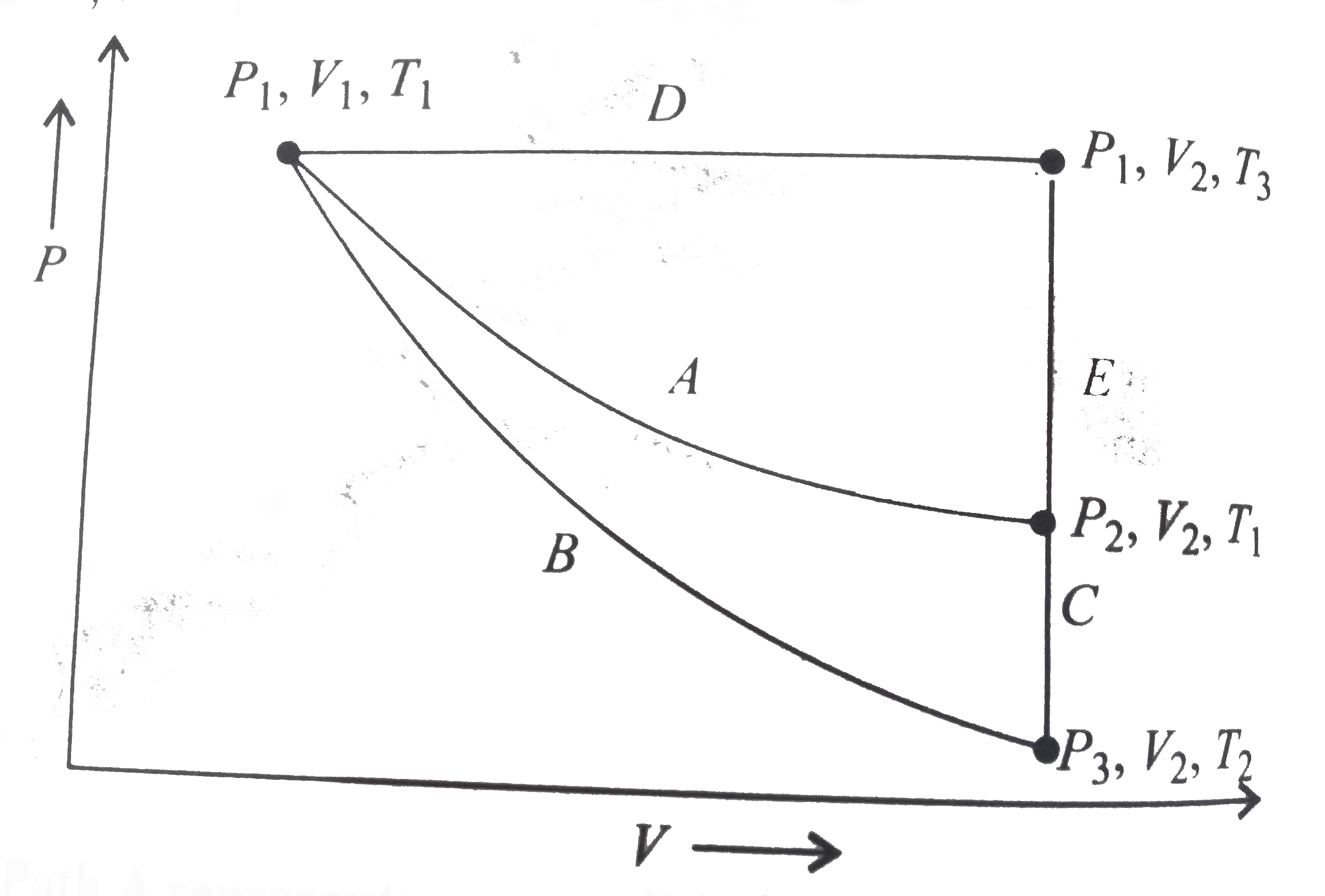
Path Arepresents a reversible isothermal expansion form P1,V1 to P2,V2, Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1→P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C)from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2,T1. Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P1(D) from P1,V1,T1 to P1,V2,T3 followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V2(E) from P1,V2,T3→P2,V2,T1.
What is qrev, for path (A)?
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P_(1), V_(1), T_(1) to a final state P_(2), V_(2),T_(1) is shown in the given figure. Path A represents a reversible isothermal expansion form P_(1),V_(1) to P_(2),V_(2) , Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1)to P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C) from P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) to P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) . Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P_(1)(D) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) to P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V_(2)(E) from P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) to P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) . What is q_(rev) , for path (B +C) ?
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P1,V1,T1 to a final state P2,V2,T1 is shown in the given figure.
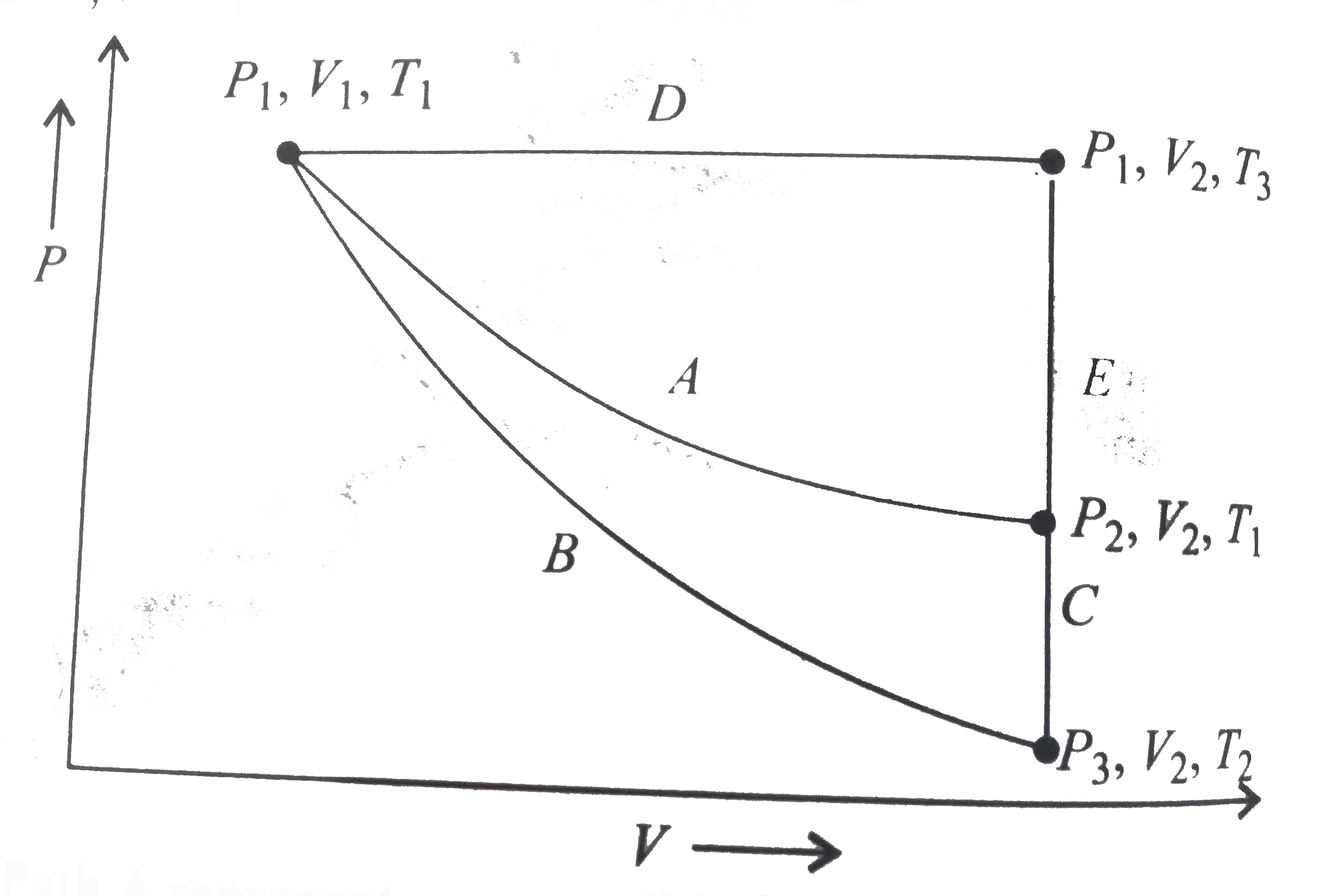
Path Arepresents a reversible isothermal expansion form P1,V1 to P2,V2, Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1→P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C)from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2,T1. Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P1(D) from P1,V1,T1 to P1,V2,T3 followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V2(E) from P1,V2,T3→P2,V2,T1.
What is ΔS for path A?
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P1,V1,T1 to a final state P2,V2,T1 is shown in the given figure.
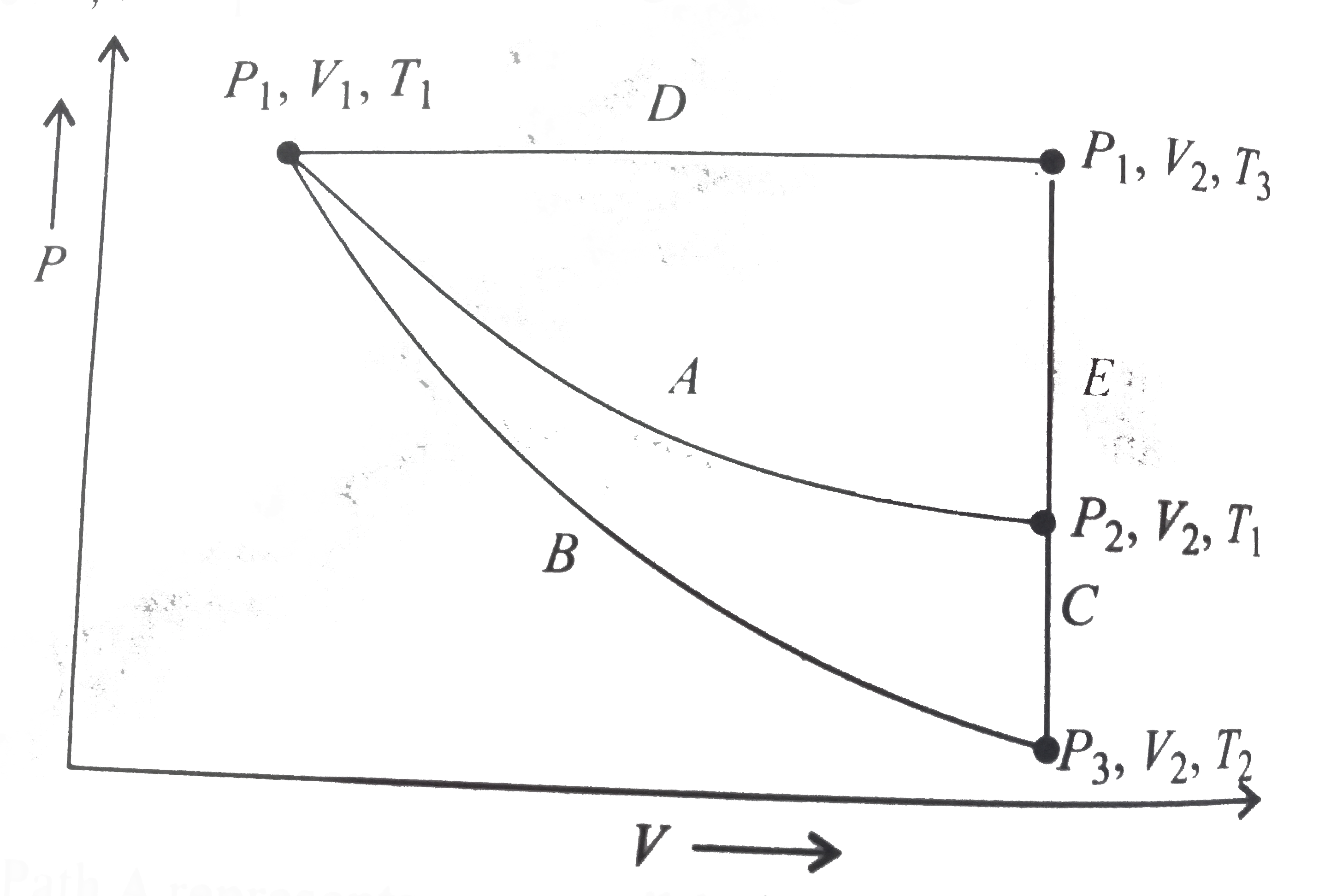
Path Arepresents a reversible isothermal expansion form P1,V1 to P2,V2, Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1→P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C)from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2,T1. Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P1(D) from P1,V1,T1 to P1,V2,T3 followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V2(E) from P1,V2,T3→P2,V2,T1.
What is qrev, for path (D+E)?
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P_(1), V_(1), T_(1) to a final state P_(2), V_(2),T_(1) is shown in the given figure. Path A represents a reversible isothermal expansion form P_(1),V_(1) to P_(2),V_(2) , Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1)to P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C) from P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) to P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) . Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P_(1)(D) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) to P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V_(2)(E) from P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) to P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) . What is DeltaS for path (D +E) ?
View SolutionAn ideal gasa undergoes through folowing cyclic procees. 1-2 : Reversible adialbatic comparession from P_(1)V_(1)T_(1)"to"P_(2)V_(2)T_(2) 2-3 : Reversible isochoric heating from P_(2)V_(2)T_(2)" to " P_(3)V_(3)T_(3) 3-4 Reversible adialbatic expansion from P_(3)V_(3)T_(3)" to " P_(4)V_(4)T_(4) 4-1 Reversible isochoric cooling from P_(4)V_(4)T_(4)" to " P_(1)V_(1)T_(1) Eefficiencyof the cycle is :
View SolutionFor an ideal monoatomic gas, an illustration of three different paths A,(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) to a final state P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) is shown in the given figure . Path A represents a reversible isothermal from P_(1)V_(1)" to "P_(2),V_(2) , path (B+C) represent a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1)" to " P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) followed by reversible heating of the gas at constant volume (C) from P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) " to " P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) . Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P_(1)(D) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) " to "P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V_(2)(E) form P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) " to "P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) What is q_("rev") for path (A)?
View SolutionFor an ideal monoatomic gas, an illustration of three different paths A,(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) to a final state P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) is shown in the given figure . Path A represents a reversible isothermal from P_(1)V_(1)" to "P_(2),V_(2) , path (B+C) represent a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1)" to " P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) followed by reversible heating of the gas at constant volume (C) from P_(3),V_(2),T_(2) " to " P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) . Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P_(1)(D) from P_(1),V_(1),T_(1) " to "P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V_(2)(E) form P_(1),V_(2),T_(3) " to "P_(2),V_(2),T_(1) What is DeltaS for path (A)?
View SolutionFor an ideal monoatomic gas, an illustration of three different paths A,(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P1,V1,T1 to a final state P2,V2,T1 is shown in the given figure .
Path A represents a reversible isothermal from P1V1 to P2,V2, path (B+C) represent a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1 to P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating of the gas at constant volume (C) from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2,T1. Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion at constant pressure P1(D) from P1,V1,T1 to P1,V2,T3 followed by a reversible cooling at constant volume V2(E) form P1,V2,T3 to P2,V2,T1
What is ΔS for (D+E)?
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustration of the different paths, A (B+C) and (D+E) from an intial state P1,V1,T1 to a final state P2,V2,T1 as shown in the given figure.
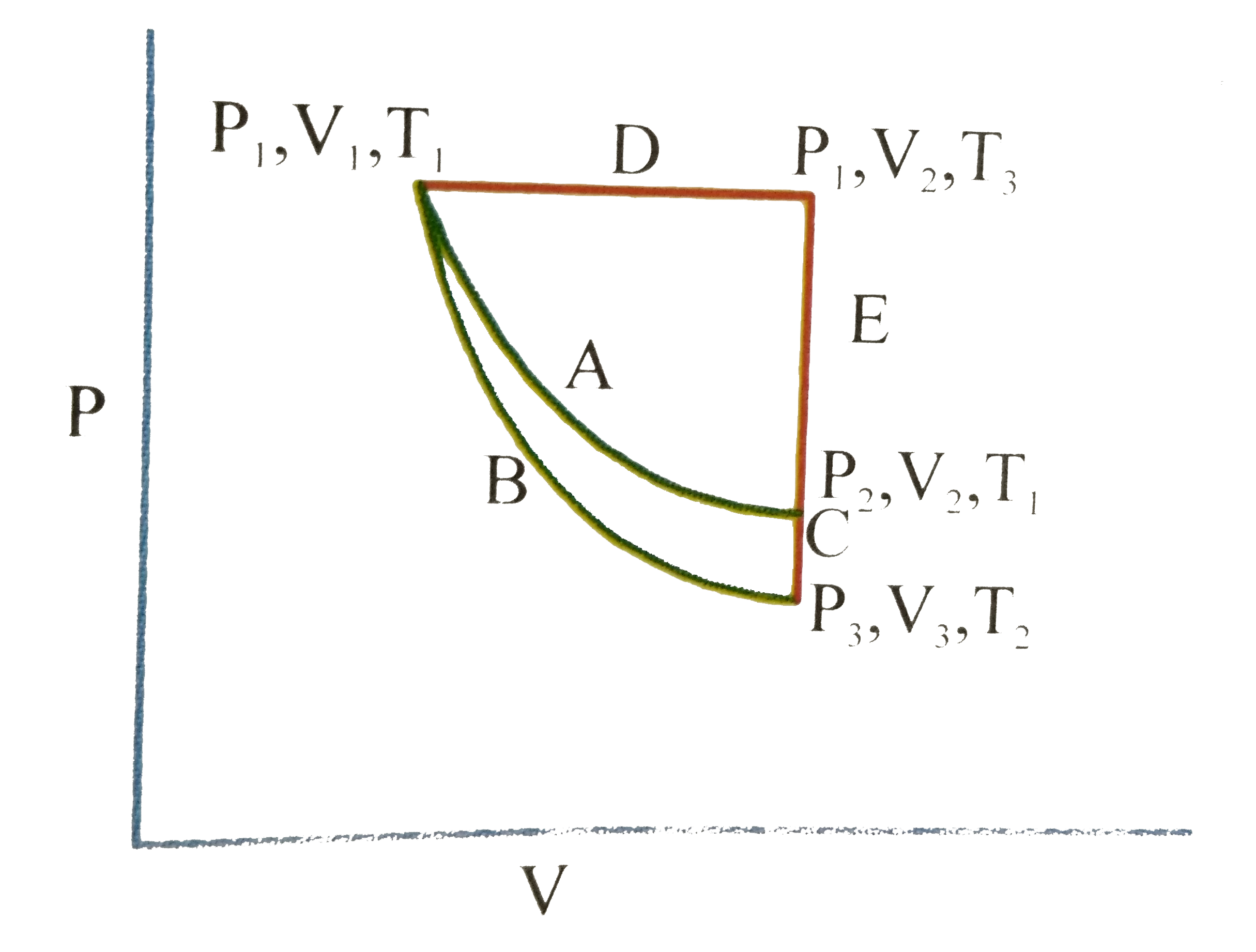
Path (A) represents a reversible isothernal expanison from P1V1 to P2V2. Path (B+C) represents a reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1 to P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating the gas at constant volume (C) from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2T1 to P1,V2,T3 followed by reversible cooling at a constant volume V2 (E) from P1,V2,T3 to P2,V2,T1
What is ΔS for path (D+E) ?
View SolutionEstablish gas equation, (P_(1)V_(1))/(T_(1))=(P_(2)V_(2))/(T_(2)) .
View Solution

