Two identical concave mirrors M1 & M2 with principal axes perpendicular to each other and pole P1 of mirro M1 at origin is as shown. Let f be the focal length and C be the common centre of curvature for both mirrors. A point object O is at (−5f,0) and is moving with a velocity →C=v0ˆi m/s.
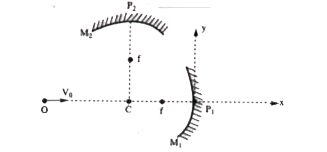
Consider rays incident on mirror M2 the co-ordinates of the final imasge formed is
at (-x,0) and moving along x-axis
at (-y,0) and moving along x-axis
at (+x,0) and moving along x-axis
at (-y,0) and moving along y-axis
The correct Answer is:B
Step by step video solution for Two identical concave mirrors M_(1) & M_(2) with principal axes perpendicular to each other and pole P_(1) of mirro M_(1) at origin is as shown. Let f be the focal length and C be the common centre of curvature for both mirrors. A point object O is at (-5f,0) and is moving with a velocity vecC=v_(0)hati m/s. Consider rays incident on mirror M_(2) the co-ordinates of the final imasge formed is by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE II LEVEL -II (ADVANCED) MATRIX MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS)
Explore 1 Video
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE II LEVEL -II (ADVANCED) INTEGER TYPE QUESTIONS)
Explore 5 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE II LEVEL -II (ADVANCED) STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS)
Explore 2 Videos
- ELEMENTS OF VECTORSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:ELEMENTS OF VECTORSExercise:QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWERS
Explore 10 Videos
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:PRACTICE EXERCISE
Explore 106 Videos
Similar Questions
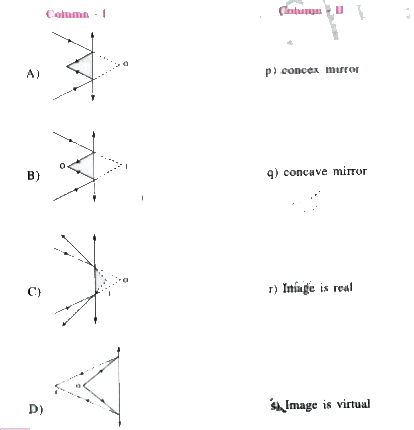
Column I contains the path traced by light rays abnd the positions of object and image, with a reflecting spherical mirror. Choose the possible for type of mirror and the nature of image rom column II to each case in column -I
View SolutionTwo plane mirrors are making an angle of 60∘ to each other. A light ray falls on one of the mirrors. The light ray is incident parallel to angular bisector of mirrors. How many reflection does the light ray undergo?
View SolutionConsider the situation shown in figure. Water (μw=43) is filled in a breaker upto a height of 10 cm. A plane mirror is fixed at a height of 5 cm from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it if an object O at the bottom of the beaker is

View SolutionFind the components of a vector A=2ˆi+3ˆj along the directions of ˆi+ˆjandˆi−ˆj.
View SolutionA force of 50 N acts on a body of mass 10 kg at rest. Its velocity after 5 seconds if the same force acts, is
View SolutionTwo concave mirrors each of radius of curvature 40cm are placed such that their principla axes are parallel to each other and at a distance of 1cm to each other. Both the mirrors are at a distance of 100cm to each other. Consider first reflection at M_(1) and then at M_(2) , find the coordinates of teh image thus formed. Take location of object as the origin
View SolutionAs shown in Figure,. And object O is at the position (-10,2) with respect to the origin P. The concave mirror M1 has radius of curvature 30cm. A plane mirror M2 is kept at a distance of 40cm in front of the concave mirror. Considering first refletion on the concave mirror M1 and second on the plane mirror M2. Find the coordinates of the second image w.r.t. the origin P.

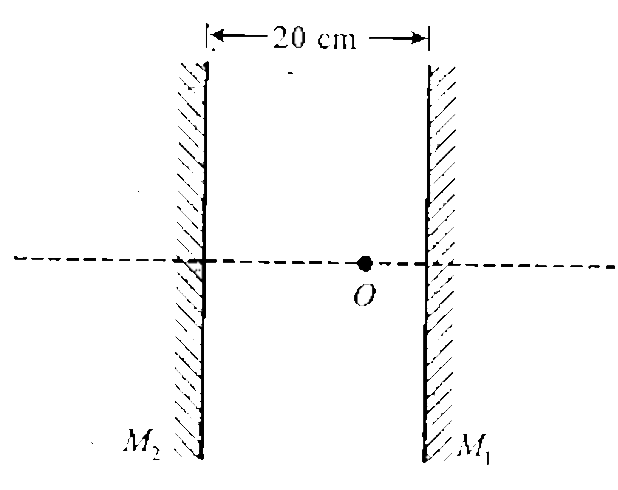
View SolutionTwo plane mirrors M1 and M2 are placed parallel to each other 20 cm apart. A luminous point object 'O' is placed between them at 5 cm from M1 as shown in figure :
View SolutionAn object O is placed in front of a small plane mirror M_(1) and a large convex mirror M_(2) of focal length f . The distance between O and M_(1) is x, and the distance between M_(1) and M_(2) is y. The images of O forned by M_(1) and M_(2) coincide. The magnitude of f is
View SolutionA point object is moving with a speed v before an arrangement of two mirrors as shown in figure. Find the velocity of image in mirror M_(1) with respect to image in mirror M_(2)
View SolutionTwo plane mirror M1andM2 are inclined to each other at 70∘. A ray incident on the mirror M1 at an angle θ fallls on M2 and is then reflected parallel to M1 for
View SolutionThe mirrors are perpendicular to each other as shown in the Fig. A light ray AB is incident on the mirror M_(1) . Then the reflected ray will also suffer a reflection from the mirror M_(2)) . Then the final ray after reflection from M_(2) will be parallel to the incident ray, if -
View SolutionIn the following figure two mirrors M1andM2 are placed in front of each others.
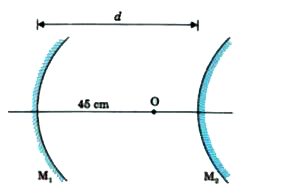
Both the mirrors have same focal length of 30 cm. Mirror M1 is concave but mirror M2 is convex. Distance between the two mirrors is d and their principal axes are coinciding as shown in figure. An object O is placed on principal axis at a distance 45 cm from mirror M1. It is found that final image is formed on object itself. Calculate the value of d.
View SolutionTwo identical concave mirrors M1 & M2 with principal axes perpendicular to each other and pole P1 of mirror M1 at origin is as shown. Let 'f' be the focal length and C be the common centre of curvature for both mirrors. A point object 'O' is at (-5f, 0) and is moving with a velocity →V=V0ˆim/s
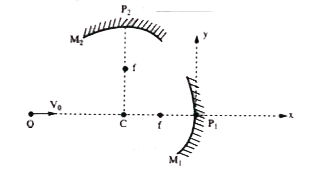
Consider rays incident on mirror M2, the co-ordinates of the final image formed is
View SolutionTwo identical concave mirrors M1 & M2 with principal axes perpendicular to each other and pole P1 of mirror M1 at origin is as shown. Let 'f' be the focal length and C be the common centre of curvature for both mirrors. A point object 'O' is at (-5f, 0) and is moving with a velocity →V=V0ˆim/s
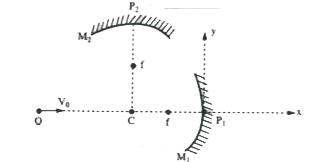
Consider rays incident on mirror M1, the coordinates of the final image is
View SolutionTwo identical concave mirrors M_1 & M_2 with principal axes perpendicular to each other and pole P_1 of mirror M_1 at origin is as shown. Let 'f' be the focal length and C be the common centre of curvature for both mirrors. A point object 'O' is at (-5f, 0) and is moving with a velocity vecV = V_0 hati m//s Consider rays incident on mirror M,, the final image formed is
View Solution
