A organic compound A has molecular formula C11H14O.A on treatment with H2N−OH yields two stereoisomer B and C having moleuclar formula C11H15NO. B and C on treatment with concentrated H2SO4 yield D and E. D and E are respective isomer of B and C. D on alkaline hydrolysis produces optically active amine F(C4H11N) . E on alkaline hydrolysis produces aniline as one product.
Compounds D and F are :
Functional isomer
Enantiomer
Geometrical isomer
Metamers
The correct Answer is:D
Step by step video, text & image solution for A organic compound A has molecular formula C_(11)H_(14)O.A on treatment with H_(2)N-OH yields two stereoisomer B and C having moleuclar formula C_(11)H_(15)NO. B and C on treatment with concentrated H_(2)SO_(4) yield D and E. D and E are respective isomer of B and C. D on alkaline hydrolysis produces optically active amine F(C_(4)H_(11)N) . E on alkaline hydrolysis produces aniline as one product. Compounds D and F are : by Chemistry experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- CARBONYL COMPOUNDSBOOK - HIMANSHU PANDEYCHAPTER - CARBONYL COMPOUNDSEXERCISE - Linked Comprehension Type (Q.26 To Q.33)
8 Videos
- CARBONYL COMPOUNDSBOOK - HIMANSHU PANDEYCHAPTER - CARBONYL COMPOUNDSEXERCISE - Match The Column
11 Videos
- CARBONYL COMPOUNDSBOOK - HIMANSHU PANDEYCHAPTER - CARBONYL COMPOUNDSEXERCISE - More Than One Correct (Q.26 To Q.50)
25 Videos
- CABOXYLIC ACIDS AND ITS DERIVATIVESBOOK - HIMANSHU PANDEYCHAPTER - CABOXYLIC ACIDS AND ITS DERIVATIVESEXERCISE - Subjective Type Problems
8 Videos
- CHEMISTRY IN DAILY LIFEBOOK - HIMANSHU PANDEYCHAPTER - CHEMISTRY IN DAILY LIFEEXERCISE - Integer Answer Type Problems
7 Videos
Similar Questions
An organic compound (A) C8H10O was subjected to a series of test in laboratory. It was found that this compound :
(i) Rotates the plane polarized light
(ii) Evolves H2 gas with Na.
(iii)Reacts with I2 and NaOH to produce yellow ppt.
(iv) Does not react with Br2/CCl4
(v) Reats wtih not KMnO4 to form (B)C7H6O2, which can also be synthesized by benzene and carbonyl chloride followed by hydrolysis.
(vi) Loses optical activity as a result of reduction with Res P+HI to form 'C'
(vii) Reacts with Lucas reagent in about 5 minutes.
Compounds B and C are respectively :
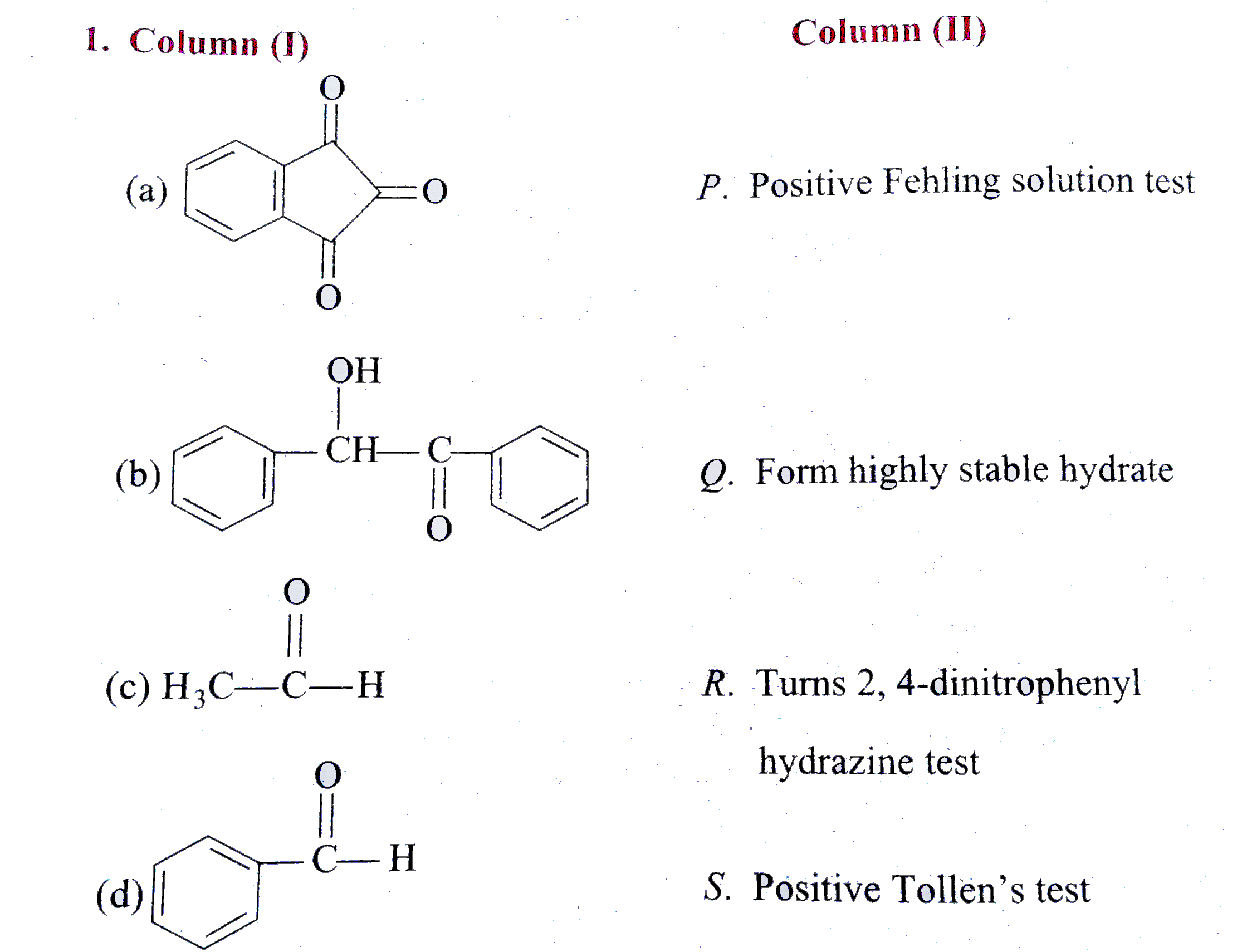
View SolutionMatch the following columns
View SolutionComplete the following reaction

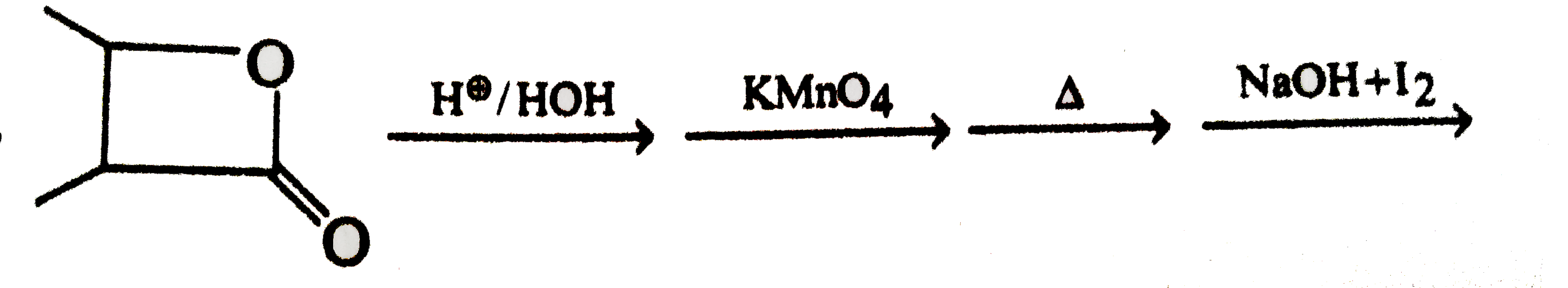
View SolutionFind out products of following reactions.
View SolutionAmongst the following the maximum number of antacids is _____.
Ranitidine, cimetidine, omerprazole, chloramphenicol, chlorpheniramine.
View SolutionAn optically inactive compound (A) having molecular formula C_(4)H_(11)H on treatment with HNO_(2) gave an alconot (B) which on heating with conc. H_(2)SO_(4) at 440 k gave an alkene ( C) . ( C) on treatment with HBr gave an optically active compound (D ) having molecular formula C_(4)H_(9)Br Identify (A) ,(B) ,(C) and (D).
View SolutionCompound (A) with molecular formula C_(2)H_(4)O reduces Tollen's reagent. (A) on treatment with HCN gives compound (B). Compound (B) on hydrolysis with an acid gives compound ( C) with molecular formula C_(3)H_(6)O which is an optically active compound. Compound (A) on reduction with N_(2)H_(4)//C_(2)H_(5)ONa gives a hydrocarbon (D) of molecular formula C_(2)H_(6) . Identify (A), (B), ( C) and (D) and explain the reactions.
View SolutionAn organic compound A(C_(6)H_(10)) on reduction first gives B(C_(6)H_(12)) and finally C(C_(6)H_(14)) . Compound A on ozonolysis followed by hydrolysis gives two aldehydes D(C_(2)H_(4)O) and E(C_(2)H_(2)O_(2)) . Oxidation of B with acidified KMnO_(4) gives the acid F(C_(4)H_(8)O_(2)) . determine the structures of the compounds A to F with reasoning.
View SolutionAn organic compound ‘A’ has molecular formula C9H13NO and it can be resolve into enantiomers. Adoes not decolourise bromine water solution. A on refluxing with dilute H2SO4, yields another revolvable compound B(C9H14O3) which give effervescence with NaHCO3. B on treatment with NaBH4 yields C(C9H16O3) on heating with concentrated H2SO4 yields ester D (C6H14O2).
Compound A on reduction with LiAlH4 followed by treatment of H2SO4 yields following compound :
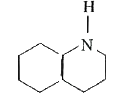
Find out structure of compound 'A''
View Solution4 A neutral, resolvable organic compound A has molecular formula (C8H16O2). A on treatment with LiAlH4 gives isomeric B and C(C4H10O) of which only B is optically active. B on treatment with acidified dichromate solution gives D(C4H8O), which on refluxing with dilute NaOH followed by acidification of product gave E(C8H14O). E on heating with N2H4 in alkaline medium affords F(C8H16) which on treatment with B.H/H,O,/HO produced a resolvable G (C8H18O). G on treatment with acidified dichromate solution produced H(C8H16O), which on treatment with MCPBA produces A.
Compound (A) is
View Solution4 A neutral, resolvable organic compound A has molecular formula (C_(8)H_(16)O_(2)) . A on treatment with LiAlH_(4) gives isomeric B and C(C_(4)H_(10)O) of which only B is optically active. B on treatment with acidified dichromate solution gives D (C_(4)H_(8)O) , which on refluxing with dilute NaOH followed by acidification of product gave E (C_(8)H_(14)O) . E on heating with N_(2)H_(4) in alkaline medium affords F(C_(8)H_(16)) which on treatment with B.H/H,O,/HO produced a resolvable G (C_(8)H_(18)O) . G on treatment with acidified dichromate solution produced H (C_(8)H_(16)O) , which on treatment with MCPBA produces A. Compound (B) is
View Solution4 A neutral, resolvable organic compound A has molecular formula (C_(8)H_(16)O_(2)) . A on treatment with LiAlH_(4) gives isomeric B and C(C_(4)H_(10)O) of which only B is optically active. B on treatment with acidified dichromate solution gives D (C_(4)H_(8)O) , which on refluxing with dilute NaOH followed by acidification of product gave E (C_(8)H_(14)O) . E on heating with N_(2)H_(4) in alkaline medium affords F(C_(8)H_(16)) which on treatment with B.H/H,O,/HO produced a resolvable G (C_(8)H_(18)O) . G on treatment with acidified dichromate solution produced H (C_(8)H_(16)O) , which on treatment with MCPBA produces A. Compound (E)
View Solution4 A neutral, resolvable organic compound A has molecular formula (C8H16O2). A on treatment with LiAlH4 gives isomeric B and C(C4H10O) of which only B is optically active. B on treatment with acidified dichromate solution gives D(C4H8O), which on refluxing with dilute NaOH followed by acidification of product gave E(C8H14O). E on heating with N2H4 in alkaline medium affords F(C8H16) which on treatment with B.H/H,O,/HO produced a resolvable G (C8H18O). G on treatment with acidified dichromate solution produced H(C8H16O), which on treatment with MCPBA produces A.
Compound (H) is
View SolutionCompound A of formula C_(8)H_(14)O reacts with LiAIH_(4) to yield two isomeric products B and C, both in equal yield. Heating either B or C with conc. H_(2)SO_(4) produces D with for mula C_(8)H_(14) . Ozonolysis of D produces a keto aldehyde after Zn//H_(2)O treatment. Oxidation of this keto aldehyde with aq. Cr (VI) produces The structure of D is
View SolutionCompound A of formula C_(8)H_(14)O reacts with LiAIH_(4) to yield two isomeric products B and C, both in equal yield. Heating either B or C with conc. H_(2)SO_(4) produces D with for mula C_(8)H_(14) . Ozonolysis of D produces a keto aldehyde after Zn//H_(2)O treatment. Oxidation of this keto aldehyde with aq. Cr (VI) produces The structures of B and C are
View SolutionCompound A of formula C_(8)H_(14)O reacts with LiAIH_(4) to yield two isomeric products B and C, both in equal yield. Heating either B or C with conc. H_(2)SO_(4) produces D with for mula C_(8)H_(14) . Ozonolysis of D produces a keto aldehyde after Zn//H_(2)O treatment. Oxidation of this keto aldehyde with aq. Cr (VI) produces The compounds B and C are
View Solution

