Redox is a reaction in which both oxidation and reduction will take place simultaneously . It is obvious that if one substance gives electron there must be another substance to accept these electrons . In some reactions, same substance is reduced as well as oxidised, these reactions are termed as disproportionation reactions.
For calculating equivalent mass in redox reaction change in oxidtaion number is realted to n-factor which is reciprocal of molar ratio.
The equivalent weight of Cu2S in the following reaction is
Cu2S+O2→Cu+2+SO3
M.wt1
M.wt10
M.wt8
M.wt11
The correct Answer is:B
To calculate the equivalent weight of Cu2S in the given redox reaction, we will follow these steps:
Step 1: Write the balanced redox reaction
The reaction given is:
Cu2S+O2→Cu2++SO3
Step 2: Determine the oxidation states of the elements
- In Cu2S:
- Let the oxidation state of Cu be x.
- The oxidation state of S is -2.
- The overall charge is 0:
2x−2=0
2x=2
x=+1
- Therefore, the oxidation state of Cu in Cu2S is +1.
- In SO3:
- Let the oxidation state of S be y.
- The oxidation state of O is -2.
- The overall charge is 0:
y+3(−2)=0
y−6=0
y=+6
- Therefore, the oxidation state of S in SO3 is +6.
- In O2:
- The oxidation state is 0 (elemental state).
Step 3: Calculate the change in oxidation states
- For Cu:
- Changes from +1 in Cu2S to +2 in Cu2+.
- Change = +2−(+1)=+1.
- Since there are 2 Cu atoms, the total change for Cu is 2×1=2.
- For S:
- Changes from -2 in Cu2S to +6 in SO3.
- Change = +6−(−2)=+8.
Step 4: Calculate the total change in electrons
- Total change in electrons = Change in Cu + Change in S
Total change=2+8=10
Step 5: Determine the n-factor
- The n-factor is the total change in electrons involved in the reaction, which we found to be 10.
Step 6: Calculate the molar mass of Cu2S
- Molar mass of Cu2S:
- Cu: 63.5 g/mol (2 Cu = 127 g/mol)
- S: 32 g/mol
- Total = 127+32=159 g/mol
Step 7: Calculate the equivalent weight
- The equivalent weight is given by the formula:
Equivalent weight=Molar massn-factor
Equivalent weight of Cu2S=159 g/mol10=15.9 g/equiv
Final Answer
The equivalent weight of Cu2S is 15.9 g/equiv.
---
The reaction given is:
Cu2S+O2→Cu2++SO3
- In Cu2S:
- Let the oxidation state of Cu be x.
- The oxidation state of S is -2.
- The overall charge is 0:
2x−2=0
2x=2
x=+1
- Therefore, the oxidation state of Cu in Cu2S is +1.
- Let the oxidation state of S be y.
- The oxidation state of O is -2.
- The overall charge is 0:
y+3(−2)=0
y−6=0
y=+6
- Therefore, the oxidation state of S in SO3 is +6.
- The oxidation state is 0 (elemental state).
- For Cu:
- Changes from +1 in Cu2S to +2 in Cu2+.
- Change = +2−(+1)=+1.
- Since there are 2 Cu atoms, the total change for Cu is 2×1=2.
- Changes from -2 in Cu2S to +6 in SO3.
- Change = +6−(−2)=+8.
- Total change in electrons = Change in Cu + Change in S
Total change=2+8=10
- The n-factor is the total change in electrons involved in the reaction, which we found to be 10.
- Molar mass of Cu2S:
- Cu: 63.5 g/mol (2 Cu = 127 g/mol)
- S: 32 g/mol
- Total = 127+32=159 g/mol
- The equivalent weight is given by the formula:
Equivalent weight=Molar massn-factor
Equivalent weight of Cu2S=159 g/mol10=15.9 g/equiv
The equivalent weight of Cu2S is 15.9 g/equiv.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- REDOX REACTIONSBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHCHAPTER - REDOX REACTIONSEXERCISE - Assignment (Section E) (Assertion-Reason Type Questions)
8 Videos
- REDOX REACTIONSBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHCHAPTER - REDOX REACTIONSEXERCISE - Assignment (Section F) (Matrix-Match Type Questions)
4 Videos
- REDOX REACTIONSBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHCHAPTER - REDOX REACTIONSEXERCISE - Assignment (Section C) (Objective type Questions (More than one option is correct))
18 Videos
- PRINCIPLES OF QUALITATIVE ANALYSISBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHCHAPTER - PRINCIPLES OF QUALITATIVE ANALYSISEXERCISE - Assignment (SECTION H)
9 Videos
- SOLUTIONSBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHCHAPTER - SOLUTIONSEXERCISE - ASSIGMENT (SECTION-J) AAKASH CHALLENGERS QUESTIONS
10 Videos
Similar Questions
STATEMENT-1 KMnO4acidic medium−−−−−−−→Mn2+, n factor of KMnO4 is 5 and
STATEMENT-2 Equivalent mass of KMnO4 in acidic medium is M5 (M=molecular mass of KMnO4)
View SolutionMatch Column-I with Column-II
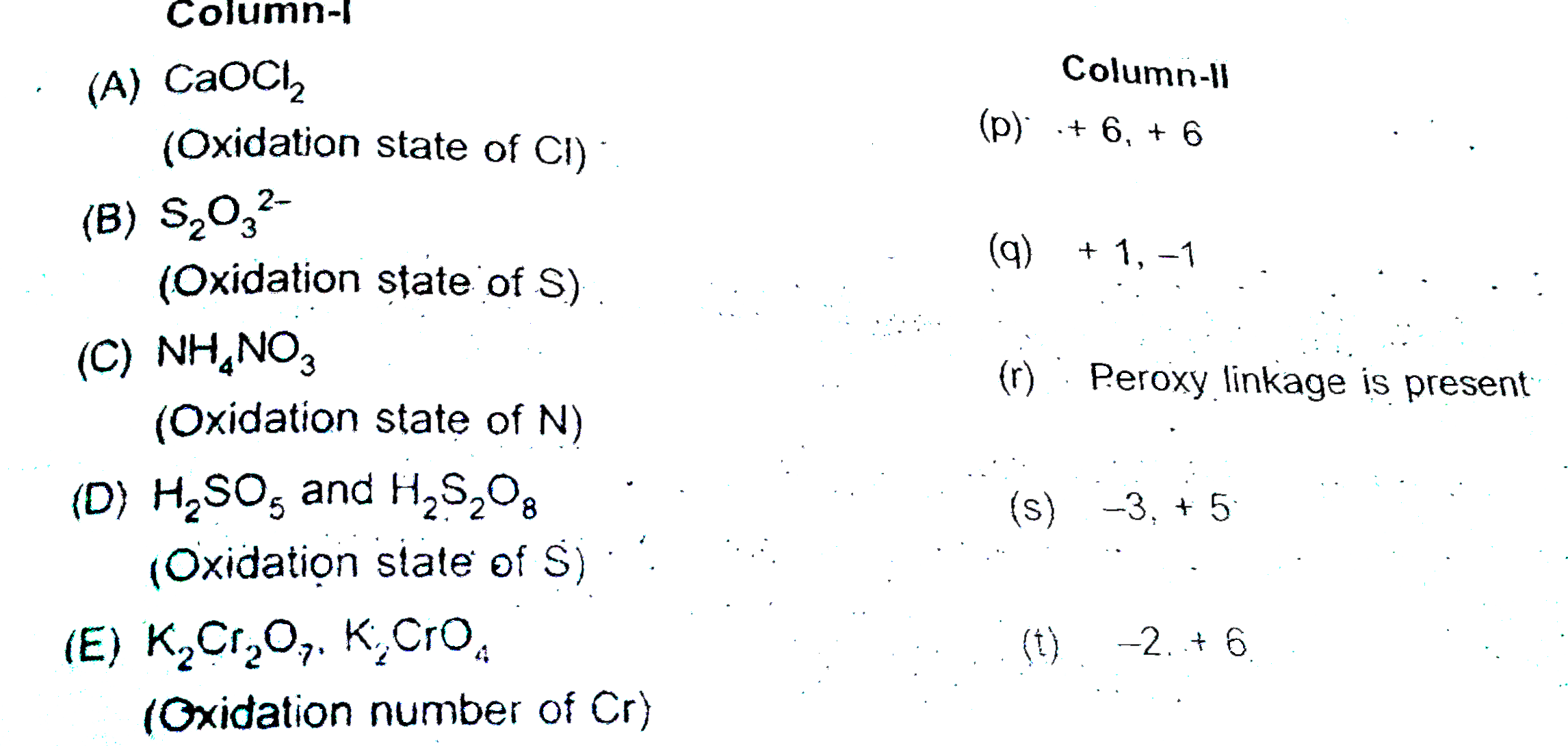
View SolutionRegarding the compound CrO5 which of the following statement is/are correct ?
View SolutionWhen a white powder (A) is strongly heated, it gives of a colourless, odourless gas (B) which turns lime water milky (C) and if the passage of this gas is continued the milkiness disappears and gives a solution (D). The solid residue (E) is yellow when hot, but turns white on cooling. Idnetify (A) to (E) with help of the equations.
View SolutionAn aqueous solution of H2SO4 has density 1.84 g/ml. Solution contains 98% H2SO4 by mass.Calculate
(i) Molarity of solution
(ii) Molar volume of solution
(iii) Relative lowering of vapour pressure w.r.t. water, assuming H2SO4 as non-electrolyte at this high concentration.
View SolutionOxidation is de-electronation whereas reduction is electronation. Oxidants are the substances which oxidise others and reduced themselves. On the other hand reductants are the substances which reduce others and oxidised themselves. The oxidation number of an element in a compound decides its nature to act as oxidant or reductant. Oxidation-reduction occur simultaneously and the overal chemical change is called redox reaction. Redox reactions are of three types : (i) Intermolecular erdox reactions, (ii) Auto-redox or disproportionation reaction, and (iii) Intramolecular redox reactions. Six mole of Cl_(2) undergoes a loss and gain of 10 mole of electrons to form two oxidation state of cl . The balance redox change is :
View SolutionOxidation is de-electronation whereas reduction is electronation. Oxidants are the substances which oxidise others and reduced themselves. On the other hand reductants are the substances which reduce others and oxidised themselves. The oxidation number of an element in a compound decides its nature to act as oxidant or reductant. Oxidation-reduction occur simultaneously and the overal chemical change is called redox reaction. Redox reactions are of three types : (i) Intermolecular erdox reactions, (ii) Auto-redox or disproportionation reaction, and (iii) Intramolecular redox reactions. Select the oxidant in the reaction, F_(2) + 1//2O_(2) rarr F_(2)O
View SolutionOxidation is de-electronation whereas reduction is electronation. Oxidants are the substances which oxidise others and reduced themselves. On the other hand reductants are the substances which reduce others and oxidised themselves. The oxidation number of an element in a compound decides its nature to act as oxidant or reductant. Oxidation-reduction occur simultaneously and the overal chemical change is called redox reaction. Redox reactions are of three types : (i) Intermolecular erdox reactions, (ii) Auto-redox or disproportionation reaction, and (iii) Intramolecular redox reactions. The missing terms in the reaction : Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-) + 14H^(+) + ? rarr 2Cr^(3+) + 7H_(2)O
View SolutionOxidation is de-electronation whereas reduction is electronation. Oxidants are the substances which oxidise others and reduced themselves. On the other hand reductants are the substances which reduce others and oxidised themselves. The oxidation number of an element in a compound decides its nature to act as oxidant or reductant. Oxidation-reduction occur simultaneously and the overal chemical change is called redox reaction. Redox reactions are of three types :
(i) Intermolecular erdox reactions, (ii) Auto-redox or disproportionation reaction, and (iii) Intramolecular redox reactions.
Total number of electrons transferred during the change :
3Fe+4H2O→Fe3O4+4H2
View SolutionOxidation is de-electronation whereas reduction is electronation. Oxidants are the substances which oxidise others and reduced themselves. On the other hand reductants are the substances which reduce others and oxidised themselves. The oxidation number of an element in a compound decides its nature to act as oxidant or reductant. Oxidation-reduction occur simultaneously and the overal chemical change is called redox reaction. Redox reactions are of three types :
(i) Intermolecular erdox reactions, (ii) Auto-redox or disproportionation reaction, and (iii) Intramolecular redox reactions.
Ox. no. of Fe in FeSO4.NO is :
View SolutionOxidation and reduction process involves the transaction of electrons. Loss of electrons is oxidation and the gain of electrons is reduction. It is thus obvious that in a redox reaction, the oxidant is reduced by accepting the electrons and the reductant is oxidised by losing electrons. The reactions in which a species disproportionates into two oxidation states (lower and higher) are called disproportionation reactions. In electrochemical cells, redox reaction is involved, i.e., oxidation takes place at anode and reduction at cathode.
In the reaction:
I2+2S2O2−3→2I−+S4O2−6
View SolutionOxidation and reduction process involves the transaction of electrons. Loss of electrons is oxidation and the gain of electrons is reduction. It is thus obvious that in a redox reaction, the oxidant is reduced by accepting the electrons and the reductant is oxidised by losing electrons. The reactions in which a species disproportionates into two oxidation states (lower and higher) are called disproportionation reactions. In electrochemical cells, redox reaction is involved, i.e., oxidation takes place at anode and reduction at cathode. Which of the following reactions is/are correctly indicated?
View SolutionRedox is a reaction in which both oxidation and reduction will take place simultaneously . It is obvious that if one substance gives electron there must be another substance to accept these electrons . In some reactions, same substance is reduced as well as oxidised, these reactions are termed as disproportionation reactions.
For calculating equivalent mass in redox reaction change in oxidtaion number is realted to n-factor which is reciprocal of molar ratio.
This reaction is an example of
Br2+OH−→BrO−3+H2O+Br−
View SolutionRedox is a reaction in which both oxidation and reduction will take place simultaneously . It is obvious that if one substance gives electron there must be another substance to accept these electrons . In some reactions, same substance is reduced as well as oxidised, these reactions are termed as disproportionation reactions.
For calculating equivalent mass in redox reaction change in oxidtaion number is realted to n-factor which is reciprocal of molar ratio.
When P reacts with NaOH, the products are PH3 and NaH2PO2 which of the following statement is correct ?
View SolutionRedox is a reaction in which both oxidation and reduction will take place simultaneously . It is obvious that if one substance gives electron there must be another substance to accept these electrons . In some reactions, same substance is reduced as well as oxidised, these reactions are termed as disproportionation reactions. For calculating equivalent mass in redox reaction change in oxidtaion number is realted to n-factor which is reciprocal of molar ratio. How many moles of KMnO_(4) are reacted with one mole of ferrous oxalate in acidic medium ?
View SolutionRedox is a reaction in which both oxidation and reduction will take place simultaneously . It is obvious that if one substance gives electron there must be another substance to accept these electrons . In some reactions, same substance is reduced as well as oxidised, these reactions are termed as disproportionation reactions.
For calculating equivalent mass in redox reaction change in oxidtaion number is realted to n-factor which is reciprocal of molar ratio.
The equivalent weight of Cu2S in the following reaction is
Cu2S+O2→Cu+2+SO3
View Solution

