In the ideal gas equation, the gas constant R has the dimension of −
Mole−atm/K
Litre/ mole
Litre−atm/K/mole
erg/K
The correct Answer is:3
To find the dimensions of the gas constant R in the ideal gas equation PV=nRT, we can follow these steps:
Step 1: Write down the ideal gas equation
The ideal gas equation is given by:
PV=nRT
Step 2: Rearrange the equation to isolate R
To find the gas constant R, we can rearrange the equation:
R=PVnT
Step 3: Identify the dimensions of each variable
- Pressure (P): The unit of pressure is typically expressed in atmospheres (atm) or pascals (Pa). In terms of base units, pressure can be expressed as:
(P)=Force/Area=Mass⋅AccelerationLength2=M⋅L⋅T−2L2=M⋅L−1⋅T−2
- Volume (V): The unit of volume is typically liters (L) or cubic meters (m³). In terms of base units:
(V)=L3
- Number of moles (n): The unit of the amount of substance is moles (mol):
(n)=mol
- Temperature (T): The unit of temperature is Kelvin (K):
(T)=K
Step 4: Substitute the dimensions into the equation for R
Now substituting the dimensions into the equation for R:
(R)=(P)(V)(n)(T)=(M⋅L−1⋅T−2)(L3)(mol)(K)
Step 5: Simplify the dimensions
Now simplifying the expression:
(R)=M⋅L−1⋅T−2⋅L3mol⋅K=M⋅L2⋅T−2mol⋅K
Conclusion
Thus, the dimensions of the gas constant R are:
(R)=M⋅L2mol⋅T2
Final Answer
The correct option for the dimensions of the gas constant R is:
Option C: M⋅L2mol⋅K
---
The ideal gas equation is given by:
PV=nRT
To find the gas constant R, we can rearrange the equation:
R=PVnT
- Pressure (P): The unit of pressure is typically expressed in atmospheres (atm) or pascals (Pa). In terms of base units, pressure can be expressed as:
(P)=Force/Area=Mass⋅AccelerationLength2=M⋅L⋅T−2L2=M⋅L−1⋅T−2
- Volume (V): The unit of volume is typically liters (L) or cubic meters (m³). In terms of base units:
(V)=L3
(n)=mol
(T)=K
Now substituting the dimensions into the equation for R:
(R)=(P)(V)(n)(T)=(M⋅L−1⋅T−2)(L3)(mol)(K)
Now simplifying the expression:
(R)=M⋅L−1⋅T−2⋅L3mol⋅K=M⋅L2⋅T−2mol⋅K
Thus, the dimensions of the gas constant R are:
(R)=M⋅L2mol⋅T2
The correct option for the dimensions of the gas constant R is:
Option C: M⋅L2mol⋅K
Topper's Solved these Questions
- GASEOUS STATEBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:GASEOUS STATEExercise:INORGANIC CHEMISTRY (COORDINATION COMPOUNDS)
Explore 36 Videos
- GASEOUS STATEBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:GASEOUS STATEExercise:ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Hydrocarbon)
Explore 17 Videos
- D & F-BLOCK ELEMENTS & THEIR IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS Book:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:D & F-BLOCK ELEMENTS & THEIR IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS Exercise:Match the column
Explore 1 Video
- GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY IIBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY IIExercise:Part-III: Section-5: Matching List Type
Explore 1 Video
Similar Questions
There are 6.02×1022 molecules each of N2,O2 and H2 which are mixed together at 760mm and 273K. The mass of the mixture in grams is :
View SolutionA certain quantity of a gas occupied 100ml when collected over water at 15∘C and 750mm pressure . It occupies 91.9ml in dry state at NTP. Find the V.P. of water at 15∘C
View SolutionCuSO4 reacts with NH3 to give blue complex of
View SolutionMatch List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists
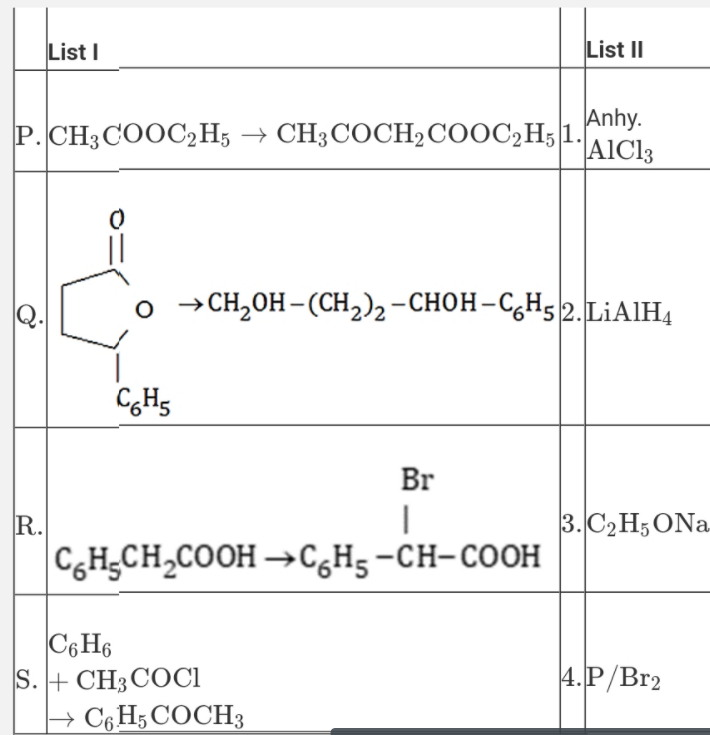
View SolutionIn the ideal gas equation, the gas constant R has the dimension of -
View Solutionआदर्श गैस के लिए अवस्था - समीकरण में गैस स्थिरांक का मान निर्भर करता है
View SolutionValue of gas constant R in the ideal gas equation PV = nRT depends upon
View SolutionIn the ideal gas equation, could Celsius temperature be used instead of Kelvin if an appropriate numerical value of the gas constant R is used,?
View SolutionGas constant 'R' has dimensions :
View SolutionIn the ideal gas equation, the gas constant R has the units :
View Solutionआदर्श गैस समीकरण लिखिए। गैस स्थिरांक की प्रकृति किस प्रकार की होती है इसकी विमाओ को लिख कर कर समझिये।
View SolutionIn the ideal gas equation, the correct value of the gas constant R in the SI unit is
View Solutionसार्वत्रिक गैस स्थिरांक (R) की विमा होती है
View SolutionThe value of gas constant R in the ideal gas equation PV = nRT depends on which of the following?
View SolutionGive calculation of gas constant R for unit of bar Lit mol−1K−1 in ideal gas equation.
View Solution
