Which one of the following species is stable in aqueous solution?
MnO2−4
MnO3−4
Cu+
Cr2+
The correct Answer is:A
To determine which species is stable in aqueous solution among the given options, we will analyze the oxidation states and electronic configurations of each species using crystal field theory.
1. Identify the Species and Their Oxidation States:
- The species given are:
- MnO4²⁻
- MnO3
- Cu⁺
- Cr²⁺
- We need to find the oxidation states of the central metal in each species.
2. Calculate Oxidation States:
- For MnO4²⁻:
- Let the oxidation state of Mn be x.
- The equation becomes x+4(−2)=−2 ⇒ x−8=−2 ⇒ x=+6.
- For MnO3:
- Let the oxidation state of Mn be x.
- The equation becomes x+3(−2)=−3 ⇒ x−6=−3 ⇒ x=+3.
- For Cu⁺:
- The oxidation state is simply +1.
- For Cr²⁺:
- The oxidation state is +2.
3. Determine Electronic Configurations:
- For Mn⁶⁺ (MnO4²⁻):
- Atomic number of Mn = 25.
- Electronic configuration: (Ar) 3d⁵ 4s².
- For Mn⁶⁺: loses 6 electrons ⇒ (Ar) 3d¹.
- For Mn³⁺ (MnO3):
- Loses 3 electrons ⇒ (Ar) 3d⁴.
- For Cu⁺:
- Atomic number of Cu = 29.
- Electronic configuration: (Ar) 3d¹⁰ 4s¹.
- For Cu⁺: loses 1 electron ⇒ (Ar) 3d¹⁰.
- For Cr²⁺:
- Atomic number of Cr = 24.
- Electronic configuration: (Ar) 3d⁵ 4s¹.
- For Cr²⁺: loses 2 electrons ⇒ (Ar) 3d⁴.
4. Analyze Stability Using Crystal Field Theory:
- Stability in aqueous solution is often related to the filling of d-orbitals.
- For Cu⁺:
- Configuration is 3d¹⁰ (fully filled), which is stable.
- For Mn⁶⁺:
- Configuration is 3d¹ (not stable due to unpaired electron).
- For Mn³⁺:
- Configuration is 3d⁴ (not stable due to unpaired electrons).
- For Cr²⁺:
- Configuration is 3d⁴ (not stable due to unpaired electrons).
5. Conclusion:
- The species that is stable in aqueous solution is Cu⁺ because it has a fully filled d-orbital configuration (3d¹⁰), which provides extra stability.
Final Answer:
Cu⁺ is the most stable species in aqueous solution.
- The species given are:
- MnO4²⁻
- MnO3
- Cu⁺
- Cr²⁺
- We need to find the oxidation states of the central metal in each species.
- For MnO4²⁻:
- Let the oxidation state of Mn be x.
- The equation becomes x+4(−2)=−2 ⇒ x−8=−2 ⇒ x=+6.
- For MnO3:
- Let the oxidation state of Mn be x.
- The equation becomes x+3(−2)=−3 ⇒ x−6=−3 ⇒ x=+3.
- For Cu⁺:
- The oxidation state is simply +1.
- For Cr²⁺:
- The oxidation state is +2.
- For Mn⁶⁺ (MnO4²⁻):
- Atomic number of Mn = 25.
- Electronic configuration: (Ar) 3d⁵ 4s².
- For Mn⁶⁺: loses 6 electrons ⇒ (Ar) 3d¹.
- For Mn³⁺ (MnO3):
- Loses 3 electrons ⇒ (Ar) 3d⁴.
- For Cu⁺:
- Atomic number of Cu = 29.
- Electronic configuration: (Ar) 3d¹⁰ 4s¹.
- For Cu⁺: loses 1 electron ⇒ (Ar) 3d¹⁰.
- For Cr²⁺:
- Atomic number of Cr = 24.
- Electronic configuration: (Ar) 3d⁵ 4s¹.
- For Cr²⁺: loses 2 electrons ⇒ (Ar) 3d⁴.
- Stability in aqueous solution is often related to the filling of d-orbitals.
- For Cu⁺:
- Configuration is 3d¹⁰ (fully filled), which is stable.
- For Mn⁶⁺:
- Configuration is 3d¹ (not stable due to unpaired electron).
- For Mn³⁺:
- Configuration is 3d⁴ (not stable due to unpaired electrons).
- For Cr²⁺:
- Configuration is 3d⁴ (not stable due to unpaired electrons).
- The species that is stable in aqueous solution is Cu⁺ because it has a fully filled d-orbital configuration (3d¹⁰), which provides extra stability.
Cu⁺ is the most stable species in aqueous solution.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- D & F-BLOCK ELEMENTS & THEIR IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS Book:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:D & F-BLOCK ELEMENTS & THEIR IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS Exercise:Additional Problems for Self practice (APSP)
Explore 30 Videos
- D & F-BLOCK ELEMENTS & THEIR IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS Book:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:D & F-BLOCK ELEMENTS & THEIR IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS Exercise:National Standard Examination In chemistry
Explore 35 Videos
- D & F-BLOCK ELEMENTS & THEIR IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS Book:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:D & F-BLOCK ELEMENTS & THEIR IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS Exercise:Exercise 2
Explore 40 Videos
- CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMExercise:Advanced Level Problems (Part-3)(Stage-5)
Explore 2 Videos
- GASEOUS STATEBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:GASEOUS STATEExercise:ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Hydrocarbon)
Explore 17 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Which of the following species is not stable?
A[Sn(OH)6]2−B[SiCl6]2−C[SiF6]2−D[GeCl6]2−Which one of the following is most stable?
A B
B C
C D
D
Which one of the following is most stable?
A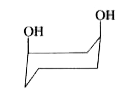 B
B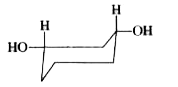 C
C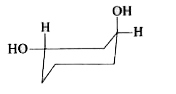 D
D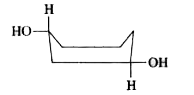
Which one of the following is most stable
View SolutionWhich of the following ions is the most stable in aqueous solution ?
(At.No.Ti=22,V=23,Cr=24,Mn=25)
View SolutionThe following species cannot exist in an aqueous solution?
View SolutionWhich one of the following is most stable ?
View SolutionWhich of the following species is least stable ?
View Solution
