NaX (Sodium salt of particular anion 'X') gives brisk effervescence of Y with dilute HCl. On heating, NaX evolves gas Y which can be completely absorbed in conc. KOH solution and is colorless odourless gas. Hence X and Y respectively are :
HSO−3,SO2
HS−&H2S
HCO−3,CO2
HC2O−4&CO2+COs
The correct Answer is:C
To solve the problem, we need to identify the anion 'X' and the gas 'Y' based on the information provided. Let's break it down step by step.
Step 1: Analyze the given information
We have a sodium salt NaX, which produces a gas Y when it reacts with dilute HCl. Additionally, when NaX is heated, it also evolves gas Y, which is colorless, odorless, and can be absorbed by concentrated KOH solution.
Hint: Focus on the properties of the gases produced and their reactions with KOH.
Step 2: Identify the possible gases
The gas Y must be colorless and odorless, and it should be completely absorbed by concentrated KOH. Common gases that fit these criteria include carbon dioxide (CO2) and ammonia (NH3). However, ammonia has a distinct smell, so it cannot be the gas we are looking for.
Hint: Consider the properties of common gases and their reactions with KOH.
Step 3: Consider the reaction with dilute HCl
When NaX reacts with dilute HCl, it produces gas Y. If we consider NaHCO3 (sodium bicarbonate), the reaction with HCl is as follows:
NaHCO3+HCl→NaCl+H2O+CO2↑
This reaction produces CO2, which is a colorless and odorless gas.
Hint: Look for a sodium salt that produces CO2 when reacting with acids.
Step 4: Analyze the heating of NaX
When NaHCO3 is heated, it decomposes to form:
2 NaHCO3→Na2CO3+H2O+CO2↑
Again, CO2 is evolved, which matches the criteria for gas Y.
Hint: Consider thermal decomposition reactions of sodium salts.
Step 5: Conclusion
From the analysis, we can conclude that:
- The anion X is bicarbonate, HCO−3.
- The gas Y is carbon dioxide, CO2.
Thus, X and Y respectively are:
X = HCO3^- and Y = CO2.
Final Answer:
X = HCO3^- (bicarbonate ion) and Y = CO2 (carbon dioxide).
---
We have a sodium salt NaX, which produces a gas Y when it reacts with dilute HCl. Additionally, when NaX is heated, it also evolves gas Y, which is colorless, odorless, and can be absorbed by concentrated KOH solution.
The gas Y must be colorless and odorless, and it should be completely absorbed by concentrated KOH. Common gases that fit these criteria include carbon dioxide (CO2) and ammonia (NH3). However, ammonia has a distinct smell, so it cannot be the gas we are looking for.
When NaX reacts with dilute HCl, it produces gas Y. If we consider NaHCO3 (sodium bicarbonate), the reaction with HCl is as follows:
NaHCO3+HCl→NaCl+H2O+CO2↑
When NaHCO3 is heated, it decomposes to form:
2 NaHCO3→Na2CO3+H2O+CO2↑
From the analysis, we can conclude that:
- The anion X is bicarbonate, HCO−3.
- The gas Y is carbon dioxide, CO2.
X = HCO3^- and Y = CO2.
X = HCO3^- (bicarbonate ion) and Y = CO2 (carbon dioxide).
Topper's Solved these Questions
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)BOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)EXERCISE - Match The Column
1 Video
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)BOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)EXERCISE - Single And Double Value Integer Type
3 Videos
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)BOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)EXERCISE - Part-II : National Standard Examination IN
8 Videos
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSISBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - QUALITATIVE ANALYSISEXERCISE - INORGANIC CHMISTRY(Qualitative analysis)
35 Videos
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS PART 1BOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS PART 1EXERCISE - A.L.P
37 Videos
Similar Questions
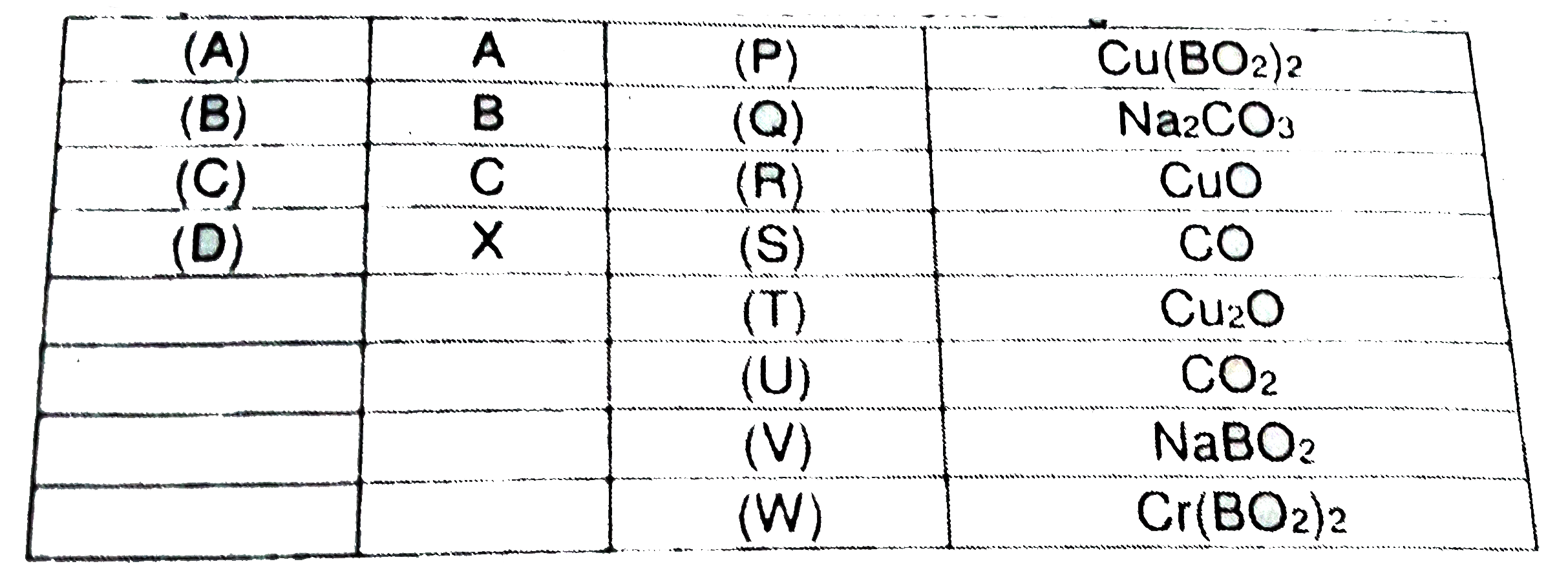
CuCO3 was strongly heated to obtain a residue A and gas B. The residue obtained was treated with a salt of sodium 'X' and oxide Y, which produced a blue colored glassy compound C on heating in oxidising flame. The same combination of x and Y gave a green colored glassy compound D when Cr2(SO4)3 was heated with them in oxidizing flame. Match the following accordingly :
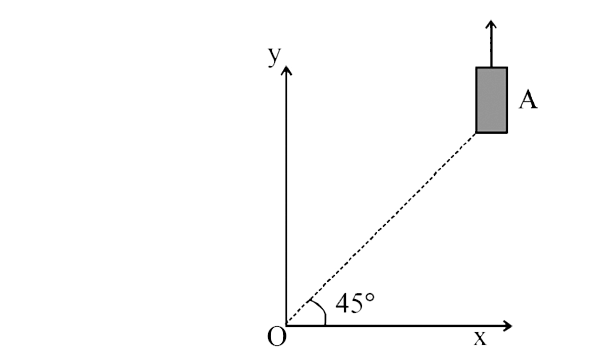
View SolutionOn a frictionless horizontal surface , assumed to be the x−y plane , a small trolley A is moving along a straight line parallel to the y−axis ( see figure) with a constant velocity of (√3−1)m/s . At a particular instant , when the line OA makes an angle of 45(∘) with the x− axis , a ball is thrown along the surface from the origin O. Its velocity makes an angle ϕ with the x− axis and it hits the trolley .
(a) The motion of the ball is observed from the frame of the trolley . Calculate the angle θ made by the velocity vector of the ball with the x−axis in this frame .
(b) Find the speed of the ball with respect to the surface , if ϕ=(4θ)/(3).
View SolutionWhich of the metal chloride is insoluble in cold water but dissolves in hot water ?
View SolutionS1: Silver iodide is fairly soluble in hypo solution.
S2: Heavy metal chloride like AgCl,HgCl2 etc. also respond to Chromyl chloride test.
S3: Bromine reacts with KI liberating violet vapours of iodine.
S4: Diphenylamine reagent test is also given by nitrites chlorates, bromates, iodates, etc. in addition to NO−3
View SolutionA red solide is insoluble in water. However it becomes soluble if some KI is added to water. On heating the red solid in a test tube, there is liberation of some violet coloured fumes and droplets of a metal appear on the cooler parts of the test tube. The red solid is :
View SolutionBarium sulphate on fusion charcoal and sodium carbonate yields a compound (X).(X) on reaction with dilute HCl liberates a gas (Y) . The gas (Y) can be identified by :
View SolutionpH of solutions of four sodium salts NaW, NaX, NaX, NaY and NaZ were found to be 7.0, 9.0, 10.0 and 11.0 respectively. If each solution has concentration 0.1 M, the weakest acid is :
View SolutionAn unknown organic liquid does not turn blue litmus red and gives no effervescence with sodium hydrogen carbonate. However, when a dry piece of sodium pellet is added to the liquid, a gas is evolved with brisk effervescence. Identify the liquid.
View SolutionNaX (Sodium salt of particular anion 'X') gives brisk effervescence of Y with dilute HCl. On heating, NaX evolves gas Y which can be completely absorbed in conc. KOH solution and is colorless odourless gas. Hence X and Y respectively are :
View SolutionX అనే పదార్థ ద్రావణానికి ఇథనోయిక్ ఆమ్లం కలిపిన రంగులేని, వాసనలేని వాయువు Y వెలువడింది. Y వాయువు సున్నపు తేట పాల వలె మార్చినచో X పదార్థాన్ని గుర్తించండి
View SolutionCO2 gas along with solid (Y) is obtained when sodium salt (X) is heated. (X) is again obtained when CO2 gas is passed into aqueous solution of (Y). (X) and (Y) are respectively
View SolutionBCl3 का जलान्शन X देता है, जो सोडियम कार्बोनेट से अभिक्रिया करके Y बनाता है। X तथा Y, क्रमशः है
View Solutionएक सफेद ठोस X तनु HCl से क्रिया करके रंगहीन गैस देता है जो आग बुझाने में प्रयुक्त की जाती है। यह ठोस X है-
View SolutionOn heating sodium salts (X) CO_(2) Gas (Y) is formed in excess of aqueous solution of (Y). CO_(2) Compounding X is obtained when the gas flows, so X and Y are:
View SolutionThe metal 'X' on heating with nitrogen gives compound 'Y' which dissolves in water to evolve a colourless gas. The gas on passing through CuSO4 solution gives a blue colour. The compound 'Y' is
View Solution

